Usare PowerShell per verificare PowerPivot per SharePoint
Si applica a: SQL Server 2019 e versioni precedenti di Analysis Services
SQL Server 2019 e versioni precedenti di Analysis Services  Azure Analysis Services
Azure Analysis Services  Fabric/Power BI Premium
Fabric/Power BI Premium
Importante
Il data mining è stato deprecato in SQL Server 2017 Analysis Services e ora è stato interrotto in SQL Server 2022 Analysis Services. La documentazione non viene aggiornata per le funzionalità deprecate e non più disponibili. Per altre informazioni, vedere Compatibilità con le versioni precedenti di Analysis Services.
Nessuna operazione di installazione o ripristino di PowerPivot per SharePoint viene completata senza un test di verifica solido che conferma che i servizi e i dati sono operativi. In questo articolo viene illustrata la modalità di esecuzione di queste procedure tramite Windows PowerShell. Ogni passaggio è inserito nella relativa sezione in modo da poter accedere direttamente ad attività specifiche. Ad esempio, eseguire lo script nella sezione Database di questo argomento per verificare il nome dell'applicazione di servizio e i database del contenuto, se si desidera programmarli per la manutenzione o il backup.
Alla fine dell'argomento è disponibile uno script completo di PowerShell. Usare lo script completo come punto di partenza per compilare uno script personalizzato per il controllo della distribuzione completa di Power Pivot per SharePoint.
Preparazione dell'ambiente di PowerShell
Con i passaggi descritti in questa sezione viene preparato l'ambiente di PowerShell. I passaggi possono non essere necessari, a seconda dell'ambiente di scripting attualmente configurato.
Autorizzazioni di PowerShell
Aprire una finestra di Powershell o PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) con privilegi amministrativi. Se non si dispone di questi privilegi quando si eseguono i comandi, verrà visualizzato un messaggio di errore simile al seguente:
Get-SPLogEvent: è necessario avere privilegi amministrativi per il computer per eseguire questo cmdlet.
SharePoint e Power Pivot per SharePoint Modulo
Se viene visualizzato un messaggio di errore analogo a quello riportato di seguito quando si eseguono i cmdlet correlati a SharePoint, eseguire il comando Add-PSSnapin:
Termine 'Get-PowerPivotSystemService' non riconosciuto come nome di cmdlet, funzione, programma eseguibile o file script. Verificare l'ortografia del nome, che il percorso sia incluso e corretto, quindi riprovare.
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Sharepoint.Powershell -EA 0
Windows PowerShell
 Facoltativamente, è possibile verificare la maggior parte dei componenti in Amministrazione centrale usando il dashboard di gestione di Power Pivot. Per aprire il dashboard in Amministrazione centrale, fare clic su Impostazioni generali dell'applicazione e quindi su Dashboard di gestione in Power Pivot. Per ulteriori informazioni sul dashboard, vedere Power Pivot Management Dashboard and Usage Data.
Facoltativamente, è possibile verificare la maggior parte dei componenti in Amministrazione centrale usando il dashboard di gestione di Power Pivot. Per aprire il dashboard in Amministrazione centrale, fare clic su Impostazioni generali dell'applicazione e quindi su Dashboard di gestione in Power Pivot. Per ulteriori informazioni sul dashboard, vedere Power Pivot Management Dashboard and Usage Data.
Sintomi e azioni consigliate
Nella tabella seguente è riportato un elenco di sintomi o problemi e la sezione suggerita di questo argomento da consultare per consentire la risoluzione del problema.
| Sintomo | Sezione di riferimento |
|---|---|
| Aggiornamento dati non in fase di esecuzione | Vedere la sezione Processi timer e verificare che il processo timer di aggiornamento dati PowerPivot online sia online. |
| Dati del dashboard di gestione obsoleti | Vedere la sezione Processi timer e verificare che Processo timer di elaborazione dashboard di gestione dati PowerPivot sia online. |
| Alcune parti del dashboard di gestione | Se si installa Power Pivot per SharePoint in una farm con la topologia di Amministrazione centrale, senza Excel Services o Power Pivot per SharePoint, è necessario scaricare e installare la libreria client di Microsoft ADOMD.NET se si desidera l'accesso completo ai report predefiniti nel dashboard di gestione di PowerPivot. Alcuni report nel dashboard usano ADOMD.NET per accedere ai dati interni che forniscono dati di report sull'elaborazione delle query Power Pivot e sull'integrità del server nella farm. |
Servizio Windows Analysis Services
Lo script in questa sezione verifica l'istanza di SQL Server Analysis Services in modalità SharePoint. Verificare che il servizio sia in esecuzione.
get-service | select name, displayname, status | where {$_.Name -eq "msolap`$powerpivot"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
Name DisplayName Status
---- ----------- ------
MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT SQL Server Analysis Services (POWERPIVOT) Running
PowerPivotSystemService e PowerPivotEngineService
Gli script in questa sezione verificano i servizi di sistema di Power Pivot per SharePoint. Sono disponibili un servizio di sistema per una distribuzione di SharePoint 2013 e due servizi per una distribuzione di SharePoint 2010.
PowerPivotSystemService
Verificare che lo stato sia Online.
Get-PowerPivotSystemService | select typename, status, applications, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
TypeName Status Applications Farm
-------- ------ ------------ ----
SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application Online {Default PowerPivot Service Application} SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config_77d8ab0744a34e8aa27c806a2b8c760c
PowerPivotEngineService
Nota
Ignorare questo script se si utilizza SharePoint 2013. PowerPivotEngineService non fa parte di una distribuzione di SharePoint 2013. Se si esegue il cmdlet Get-PowerPivotEngineService in SharePoint 2013, viene visualizzato un messaggio di errore simile a quello riportato di seguito. Questo messaggio viene restituito anche se è stato eseguito il comando Add-PSSnapin descritto nella sezione relativa ai prerequisiti di questo argomento.
Termine 'Get-PowerPivotEngineService' non è riconosciuto come nome di un cmdlet
In una distribuzione di SharePoint 2010 verificare che lo stato sia Online.
Get-PowerPivotEngineService | select typename, status, name, instances, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
TypeName : SQL Server Analysis Services
Status : Online
Name : MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Instances : {POWERPIVOT}
Farm : SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
Proxy e applicazioni del servizio Power Pivot
Verificare che lo stato sia Online. Tramite l'applicazione Excel Services non viene utilizzato un database dell'applicazione di servizio e pertanto il cmdlet non restituisce un nome di database. Si noti che il database usato dall'applicazione di servizio Power Pivot consente di verificare che il database sia online nella sezione database più avanti in questo argomento.
Applicazioni di Power Pivot ed Excel Service
Per una distribuzione di SharePoint 2010, verificare che lo stato sia Online.
Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select typename,name, status, unattendedaccount, applicationpool, farm, database
Get-SPExcelServiceApplication | select typename, DisplayName, status
Output di esempio
TypeName : PowerPivot Service Application
Name : PowerPivotServiceApplication1
Status : Online
UnattendedAccount : PowerPivotUnattendedAccount
ApplicationPool : SPIisWebServiceApplicationPool Name=sqlbi_serviceapp
Farm : SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
Database : GeminiServiceDatabase Name=PowerPivotServiceApplication1_19648f3f2c944e27acdc6c20aab8487a
TypeName : Excel Services Application Web Service Application
DisplayName : Excel Services Application
Status : Online
Pool di applicazioni di servizio
Nota
Nell'esempio di codice seguente viene prima restituita la proprietà applicationpool dell'applicazione di servizio Power Pivot per SharePoint predefinita. Il nome viene analizzato dalla stringa e viene utilizzato per ottenere lo stato dell'oggetto pool di applicazioni.
Verificare che lo stato sia Online. Se lo stato non è Online o viene visualizzato l'errore http quando si esplora il sito Power Pivot, verificare che le credenziali di identità nei pool di applicazioni IIS siano ancora corrette. Il nome del pool IIS è il valore della proprietà ID restituita dal comando Get-SPServiceApplicationPool.
$poolname=[string](Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select -property applicationpool)
$position=$poolname.lastindexof("=")
$poolname=$poolname.substring($position+1)
$poolname=$poolname.substring(0,$poolname.length-1)
Get-SPServiceApplicationPool | select name, status, processaccountname, id | where {$_.Name -eq $poolname} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
Name Status ProcessAccountName Id
---- ------ ------------------ -------
SharePoint Web Services System Online DOMAIN\account 89b50ec3-49e3-4de7-881a-2cec4b8b73ea
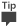 Il pool di applicazioni può essere verificato anche nella pagina Amministrazione centrale Gestire le applicazioni di servizio. Fare clic sul nome dell'applicazione di servizio, quindi su Proprietà sulla barra multifunzione.
Il pool di applicazioni può essere verificato anche nella pagina Amministrazione centrale Gestire le applicazioni di servizio. Fare clic sul nome dell'applicazione di servizio, quindi su Proprietà sulla barra multifunzione.
Proxy dell'applicazione Power Pivot ed Excel Service
Verificare che lo stato sia Online.
Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | select typename, status, unattendedaccount, displayname | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
TypeName Status UnattendedAccount DisplayName
-------- ------ ----------------- -----------
PowerPivot Service Application Proxy Online PowerPivotUnattendedAccount PowerPivotServiceApplication1
Excel Services Application Web Service Application Proxy Online Excel Services Application
Database
Con lo script seguente viene restituito lo stato dei database dell'applicazione di servizio e di tutti i database del contenuto. Verificare che lo stato sia Online.
Get-SPDatabase | select name, status, server, typename | where {$_.TypeName -eq "content database" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Gemini*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
Name Status Server TypeName
---- ------ ------ --------
DefaultPowerPivotServiceApplicationDB-38422181-2b68-4ab2-b2bb-9c00c39e5a5e Online SPServer Name=TESTSERVER Microsoft.AnalysisServices.SPAddin.GeminiServiceDatabase
DefaultWebApplicationDB-f0db1a8e-4c22-408c-b9b9-153bd74b0312 Online TESTSERVER\POWERPIVOT Content Database
SharePoint_Admin_3cadf0b098bf49e0bb15abd487f5c684 Online TESTSERVER\POWERPIVOT Content Database
Funzionalità di SharePoint
Verificare che le funzionalità del sito, del Web e della farm siano online.
Get-SPFeature | select displayname, status, scope, farm | where {$_.displayName -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
DisplayName Status Scope Farm
----------- ------ ----- ----
PowerPivotSite Online Site SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
PowerPivotAdmin Online Web SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
PowerPivot Online Farm SPFarm Name=SharePoint_Config
Processi timer
Verificare che i processi timer siano Online. Power Pivot EngineService non è installato in SharePoint 2013, pertanto lo script non elenca i processi timer EngineService in una distribuzione di SharePoint 2013.
Get-SPTimerJob | where {$_.service -like "*power*" -or $_.service -like "*mid*"} | select status, displayname, LastRunTime, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
Status DisplayName LastRunTime Service
------ ----------- ----------- -------
Online Health Analysis Job (Daily, SQL Server Analysis Services, All Servers) 4/9/2014 12:00:01 AM EngineService Name=MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Online Health Analysis Job (Hourly, SQL Server Analysis Services, All Servers) 4/9/2014 1:00:01 PM EngineService Name=MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Online Health Analysis Job (Weekly, SQL Server Analysis Services, All Servers) 4/6/2014 12:00:10 AM EngineService Name=MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Online PowerPivot Management Dashboard Processing Timer Job 4/8/2014 3:45:38 AM MidTierService
Online PowerPivot Health Statistics Collector Timer Job 4/9/2014 1:00:12 PM MidTierService
Online PowerPivot Data Refresh Timer Job 4/9/2014 1:09:36 PM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Daily, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, All Servers) 4/9/2014 12:00:00 AM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Daily, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, Any Server) 4/9/2014 12:00:00 AM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Weekly, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, All Servers) 4/6/2014 12:00:03 AM MidTierService
Online Health Analysis Job (Weekly, SQL Server PowerPivot Service Application, Any Server) 4/6/2014 12:00:03 AM MidTierService
Online PowerPivot Setup Extension Timer Job 4/1/2014 1:40:31 AM MidTierService
Regole di integrità
Sono presenti meno regole in una distribuzione di SharePoint 2013. Per un elenco completo delle regole per ogni ambiente di SharePoint e una spiegazione della relativa modalità d'uso, vedere Configurare le regole di integrità di Power Pivot.
Get-SPHealthAnalysisRule | select name, enabled, summary | where {$_.summary -like "*power*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
Name Enabled Summary
---- ------- -------
SecondaryLogonHealthRule True PowerPivot: Secondary Logon service (seclogon) is disabled
DataRefreshTimerJobHealthRule True PowerPivot: The PowerPivot Data Refresh timer job is disabled.
ASUsageLoadHealthRule True PowerPivot: The ratio of load events to connections is too high.
ASMiniDumpHealthRule True PowerPivot: One or more minidump files were found in the Logs directory, indicating a program crash
ASUsageCubeRule True PowerPivot: Usage data is not getting updated at the expected frequency.
ASADOMDNETHealthRule True PowerPivot: ADOMD.NET is not installed on a standalone WFE that is configured for central admin
MidTierAcctReadPermissionRule True PowerPivot: MidTier process account should have 'Full Read' permission on all associated SPWebApplications.
Log di Servizio di registrazione unificato e di Windows
Registro eventi di Windows
Il comando seguente cercherà nel registro eventi di Windows gli eventi correlati all'istanza di SQL Server Analysis Services in modalità SharePoint. Per informazioni sulla disabilitazione degli eventi o sulla modifica del livello di evento, vedere Configurare e visualizzare i file di log e la registrazione diagnostica di SharePoint (PowerPivot per SharePoint)
Nome servizio: MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT
Nome visualizzato nei servizi Windows : SQL Server Analysis Services (POWERPIVOT)
Get-EventLog "application" | Where-Object {$_.source -like "msolap`$powerpivot*"} |select timegenerated, entrytype , source, message | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
TimeGenerated EntryType Source Message
------------- --------- ------ -------
4/16/2014 1:45:19 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT Software usage metrics are disabled.
4/16/2014 1:45:19 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT Service started. Microsoft SQL Server Analysis Services 64 Bit Evaluation (x64) RTM 12.0.1997.5.
4/16/2014 1:45:18 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT The flight recorder was started.
4/14/2014 6:45:37 PM Information MSOLAP$POWERPIVOT Software usage metrics are disabled.
Log di Servizio di registrazione unificato di SharePoint, ultime 48 ore
Il comando seguente restituirà i messaggi di Power Pivot dal log ULS creato nelle ultime 48 ore. Modificare il parametro addhours in base alle esigenze.
Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.Area -eq "powerpivot service" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid,level, message| format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Con la variazione seguente del comando vengono restituiti solo gli eventi del log per la categoria di aggiornamento dati .
Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.category -eq "data refresh" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid, level, correlation, message
Output di esempio
Timestamp : 4/14/2014 7:15:01 PM
Area : PowerPivot Service
Category : Data Refresh
EventID : 43
Level : High
Correlation : 5755879c-7cab-e097-8f80-f27895d44a77
Message : The following error occured when working with the service application, Default PowerPivot Service Application. Skipping the service application..
Timestamp : 4/14/2014 7:15:02 PM
Area : PowerPivot Service
Category : Data Refresh
EventID : 99
Level : High
Correlation : 5755879c-7cab-e097-8f80-f27895d44a77
Message : EXCEPTION: System.TimeoutException: The request channel timed out while waiting for a reply after 00:00:47.0625313. Increase the timeout value passed to
the call to Request or increase the SendTimeout value on the Binding. The time allotted to this operation may have been a portion of a longer timeout.
---> System.TimeoutException: The HTTP request to 'http://localhost:32843/SecurityTokenServiceApplication/securitytoken.svc/actas' has exceeded the
allotted timeout of 00:00:54.5930000. The time allotted to this operation may have been a portion of a longer timeout. ---> System.Net.WebException: The
operation has timed out at System.Net.HttpWebRequest.GetResponse() at
System.ServiceModel.Channels.HttpChannelFactory`1.HttpRequestChannel.HttpChannelRequest.WaitForReply(TimeSpan timeout...
Provider MSOLAP
Verificare che si tratti del provider MSOLAP. SQL Server 2012 (11.x) e SQL Server 2014 (12.x) Power Pivot richiedono MSOLAP.5.
$excelApp=Get-SPExcelServiceApplication
get-spexceldataprovider -ExcelServiceApplication $excelApp |select providerid,providertype,description | where {$_.providerid -like "msolap*" } | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
ProviderId ProviderType Description
---------- ------------ -----------
MSOLAP Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services
MSOLAP.3 Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services 9.0
MSOLAP.4 Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services 10.0
MSOLAP.5 Oledb Microsoft OLE DB Provider for OLAP Services 11.0
Libreria client ADOMD.NET
get-wmiobject -class win32_product | Where-Object {$_.name -like "*ado*"} | select name, version, vendor | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
name version vendor
---- ------- ------
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Analysis Services ADOMD.NET 10.1.2531.0 Microsoft Corporation
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Analysis Services ADOMD.NET 9.00.1399.06 Microsoft Corporation
Regole di raccolta dati di integrità
Verificare che lo Stato sia online e Abilitato sia True.
get-spusagedefinition | select name, status, enabled, tablename, DaysToKeepDetailedData | where {$_.name -like "powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio
Name Status Enabled TableName DaysToKeepDetailedData
---- ------ ------- --------- ----------------------
PowerPivot Connections OnlineTrue AnalysisServicesConnections 14
PowerPivot Load Data Usage Online True AnalysisServicesLoads 14
PowerPivot Query Usage Online True AnalysisServicesRequests 14
PowerPivot Unload Data Usage Online True AnalysisServicesUnloads 14
Per altre informazioni, vedere Power Pivot Usage Data Collection.
Soluzioni
Se gli altri componenti sono online, è possibile ignorare la verifica delle soluzioni. Se tuttavia mancano le regole di integrità, verificare che le due soluzioni esistano e mostrare Verificare che le due soluzioni Power Pivot siano online e distribuite.
get-spsolution | select name, status, deployed, DeploymentState, DeployedServers | where {$_.Name -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Output di esempio di SharePoint 2013
Name Status Deployed DeploymentState DeployedServers
---- ------ -------- --------------- ---------------
powerpivotfarm14solution.wsp Online True GlobalDeployed {UETESTA00}
powerpivotfarmsolution.wsp Online True GlobalDeployed {UETESTA00}
powerpivotwebapplicationsolution.wsp Online True WebApplicationDeployed {UETESTA00}
Output di esempio di SharePoint 2010
Name Status Deployed DeploymentState DeployedServers
---- ------ -------- --------------- ---------------
powerpivotfarm.wsp Online True GlobalDeployed {uesql11spoint2}
powerpivotwebapp.wsp Online True WebApplicationDeployed {uesql11spoint2}
Per altre informazioni sulla distribuzione delle soluzioni SharePoint, vedere Distribuire pacchetti delle soluzioni (SharePoint Server 2010).
Passaggi di verifica manuali
In questa sezione vengono descritti i passaggi di verifica che non possono essere completati con i cmdlet di PowerShell.
Aggiornamento dati pianificato: configurare la pianificazione dell'aggiornamento di una cartella di lavoro su Aggiorna anche appena possibile. Per altre informazioni, vedere la sezione "Verifica aggiornamento dati" di Pianificare l'aggiornamento dati e le origini dati che non supportano l'autenticazione di Windows (Power Pivot per SharePoint).
Altre risorse
Web Server (IIS) Administration Cmdlets in Windows PowerShell(Cmdlet di amministrazione di server Web IIS in Windows PowerShell).
PowerShell per controllare i servizi, i siti di IIS e il pool di applicazioni in SharePoint.
Informazioni di riferimento su Windows PowerShell per SharePoint 2013
Informazioni di riferimento su Windows PowerShell per SharePoint Foundation 2010
Gestire Excel Services con Windows PowerShell (SharePoint Server 2010)
Visualizzare e leggere i file di log del programma di installazione di SQL Server
Utilizzare il cmdlet Get-EvenLog
Script completo di PowerShell
Nello script seguente sono contenuti tutti i comandi delle sezioni precedenti. Tramite lo script vengono eseguiti i comandi nello stesso ordine di presentazione in questo argomento. Nello script sono contenute alcune variazioni facoltative dei comandi riportati in questo argomento nel caso sia necessario il filtro aggiuntivo. Le variazioni sono disabilitate con un indicatore di commento (#). Lo script include anche alcune istruzioni per verificare Reporting Services modalità SharePoint. Le istruzioni Reporting Services sono disabilitate con un carattere di commento (#).
# This script audits services related to PowerPivot for SharePoint
$starttime=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
Write-Host "Import the SharePoint PowerShell snappin"
Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Sharepoint.Powershell -EA 0
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Analysis Services Windows Service"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-service | select name, displayname, status | where {$_.Name -eq "msolap`$powerpivot"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivotEngineService and PowerPivotSystemService"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-PowerPivotSystemService | select typename, status, applications, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
# If needed, you can run the following to compare job definitions specific to the service against the results of the timer job definition section
#Get-PowerPivotSystemService | select -ExpandProperty jobdefinitions | select displayname, schedule, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Get-PowerPivotEngineService | select typename, status, name, instances, farm | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
# If needed, you can run the following to compare job definitions specific to the service against the results of the timer job definition section
#Get-PowerPivotEngineService | select -ExpandProperty jobdefinitions | select displayname, schedule, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
#Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Service Instances - optional if you want to associate services with the server"
#Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
#Get-SPServiceInstance | select typename, status, server, service, instance | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Analysis Services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-PowerPivotEngineServiceInstance | select typename, ASServername, status, server, service, instance
#Get-PowerPivotSystemServiceInstance | select typename, ASSServerName, status, server, service, instance
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivot And Excel Service Applications"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select typename,name, status, unattendedaccount, applicationpool, farm, database
Get-SPExcelServiceApplication | select typename, DisplayName, status
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivot Service Application pool"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
# the following assumes there is only 1 PowerPivot Service Application, and returns that applicaitons pool name. if you have more than one, use the 2nd version
$poolname=[string](Get-PowerPivotServiceApplication | select -property applicationpool)
$position=$poolname.lastindexof("=")
$poolname=$poolname.substring($position+1)
$poolname=$poolname.substring(0,$poolname.length-1)
Get-SPServiceApplicationPool | select name, status, processaccountname, id | where {$_.Name -eq $poolname} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "PowerPivot and Excel Service Application Proxy"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | select typename, status, unattendedaccount, displayname | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-SPServiceApplicationProxy | select typename, status, unattendedaccount, displayname | where {$_.TypeName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Reporting Services*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*excel services*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "DATABASES"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPDatabase | select name, status, server, typename | where {$_.TypeName -eq "content database" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Gemini*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-SPDatabase | select name, status, server, typename | where {$_.TypeName -eq "content database" -or $_.TypeName -like "*Gemini*" -or $_.TypeName -like "*ReportingServices*"}
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "features"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPFeature | select displayname, status, scope, farm| where {$_.displayName -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Get-SPFeature | select displayname, status, scope, farm | where {$_.displayName -like "*powerpivot*" -or $_.displayName -like "*ReportServer*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Timer Jobs (Job Definitions) -- list is the same as seen in the 'Review timer job definitions' section of the management dashboard"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPTimerJob | where {$_.service -like "*power*" -or $_.service -like "*mid*"} | select status, displayname, LastRunTime, service | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "health rules"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPHealthAnalysisRule | select name, enabled, summary | where {$_.summary -like "*power*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray EndTime $time
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Windows Event Log data MSSQL$POWERPIVOT and "
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-EventLog "application" | Where-Object {$_.source -like "msolap`$powerpivot*"} |select timegenerated, entrytype , source, message | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#The following is the same command but with the Inforamtion events filtered out.
#Get-EventLog "application" | Where-Object {$_.source -like "msolap`$powerpivot*" -and ($_.entrytype -match "error" -or $_.entrytype -match "critical" -or $_.entrytype -match "warning")} |select timegenerated, entrytype , source, message | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "ULS Log data"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.Area -eq "powerpivot service" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid,level, correlation, message| format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#the following example filters for the category 'data refresh'
#Get-SPLogEvent -starttime(get-date).addhours(-48) | Where-Object {$_.category -eq "data refresh" -and $_.level -eq "high"} | select timestamp, area, category, eventid, level, correlation, message
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray EndTime $time
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "MSOLAP data provider for Excel Servivces, service application"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
$excelApp=Get-SPExcelServiceApplication
get-spexceldataprovider -ExcelServiceApplication $excelApp |select providerid,providertype,description | where {$_.providerid -like "msolap*" } | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "ADOMD.net client library"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-wmiobject -class win32_product | Where-Object {$_.name -like "*ado*"} | select name, version, vendor | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
#Write-Host ""
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Usage Data Rules"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-spusagedefinition | select name, status, enabled, tablename, DaysToKeepDetailedData | where {$_.name -like "powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green "Solutions"
Write-Host -ForegroundColor Green ">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>"
get-spsolution | select name, status, deployed, DeploymentState, DeployedServers | where {$_.Name -like "*powerpivot*"} | format-table -property * -autosize | out-default
$time=Get-Date
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray StartTime $starttime
write-host -foregroundcolor DarkGray EndTime $time