Convalidare il mirroring delle porte
Si applica a: Advanced Threat Analytics versione 1.9
Nota
Questo articolo è pertinente solo se si distribuiscono gateway ATA anziché gateway ATA Lightweight. Per determinare se è necessario usare i gateway ATA, vedere Scelta dei gateway appropriati per la distribuzione.
I passaggi seguenti illustrano il processo per la convalida della corretta configurazione del mirroring delle porte. Per il corretto funzionamento di ATA, il gateway ATA deve essere in grado di visualizzare il traffico da e verso il controller di dominio. L'origine dati principale usata da ATA è l'ispezione approfondita dei pacchetti del traffico di rete da e verso i controller di dominio. Per consentire ad ATA di visualizzare il traffico di rete, è necessario configurare il mirroring delle porte. Il mirroring delle porte copia il traffico da una porta (la porta di origine) a un'altra porta (la porta di destinazione).
Convalidare il mirroring delle porte usando uno script di Windows PowerShell
- Salvare il testo di questo script in un file denominato ATAdiag.ps1.
- Eseguire questo script nel gateway ATA che si vuole convalidare. Lo script genera il traffico ICMP dal gateway ATA al controller di dominio e cerca tale traffico nella scheda di interfaccia di rete di acquisizione nel controller di dominio. Se il gateway ATA visualizza il traffico ICMP con un indirizzo IP di destinazione uguale all'indirizzo IP del controller di dominio immesso nella console ATA, il mirroring delle porte viene configurato.
Esempio di come eseguire lo script:
# ATAdiag.ps1 -CaptureIP n.n.n.n -DCIP n.n.n.n -TestCount n
param([parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$CaptureIP, [parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$DCIP, [int]$PingCount = 10)
# Set variables
$ErrorActionPreference = "stop"
$starttime = get-date
$byteIn = new-object byte[] 4
$byteOut = new-object byte[] 4
$byteData = new-object byte[] 4096 # size of data
$byteIn[0] = 1 # for promiscuous mode
$byteIn[1-3] = 0
$byteOut[0-3] = 0
# Convert network data to host format
function NetworkToHostUInt16 ($value)
{
[Array]::Reverse($value)
[BitConverter]::ToUInt16($value,0)
}
function NetworkToHostUInt32 ($value)
{
[Array]::Reverse($value)
[BitConverter]::ToUInt32($value,0)
}
function ByteToString ($value)
{
$AsciiEncoding = new-object system.text.asciiencoding
$AsciiEncoding.GetString($value)
}
Write-Host "Testing Port Mirroring..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Here is a summary of the connection we will test." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Initialize a first ping connection
Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $DCIP -ea SilentlyContinue
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Press any key to continue..." -ForegroundColor Red
[void][System.Console]::ReadKey($true)
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Sending ICMP and Capturing data..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Open a socket
$socket = new-object system.net.sockets.socket([Net.Sockets.AddressFamily]::InterNetwork,[Net.Sockets.SocketType]::Raw,[Net.Sockets.ProtocolType]::IP)
# Include the IP header
$socket.setsocketoption("IP","HeaderIncluded",$true)
$socket.ReceiveBufferSize = 10000
$ipendpoint = new-object system.net.ipendpoint([net.ipaddress]"$CaptureIP",0)
$socket.bind($ipendpoint)
# Enable promiscuous mode
[void]$socket.iocontrol([net.sockets.iocontrolcode]::ReceiveAll,$byteIn,$byteOut)
# Initialize test variables
$tests = 0
$TestResult = "Noise"
$OneSuccess = 0
while ($tests -le $PingCount)
{
if (!$socket.Available) # see if any packets are in the queue
{
start-sleep -milliseconds 500
continue
}
# Capture traffic
$rcv = $socket.receive($byteData,0,$byteData.length,[net.sockets.socketflags]::None)
# Decode the header so we can read ICMP
$MemoryStream = new-object System.IO.MemoryStream($byteData,0,$rcv)
$BinaryReader = new-object System.IO.BinaryReader($MemoryStream)
# Set IP version & header length
$VersionAndHeaderLength = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
# TOS
$TypeOfService= $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
# More values, and the Protocol Number for ICMP traffic
# Convert network format of big-endian to host format of little-endian
$TotalLength = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$Identification = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$FlagsAndOffset = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$TTL = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
$ProtocolNumber = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
$Checksum = [Net.IPAddress]::NetworkToHostOrder($BinaryReader.ReadInt16())
# The source and destination IP addresses
$SourceIPAddress = $BinaryReader.ReadUInt32()
$DestinationIPAddress = $BinaryReader.ReadUInt32()
# The source and destimation ports
$sourcePort = [uint16]0
$destPort = [uint16]0
# Close the stream reader
$BinaryReader.Close()
$memorystream.Close()
# Cast DCIP into an IPaddress type
$DCIPP = [ipaddress] $DCIP
$DestinationIPAddressP = [ipaddress] $DestinationIPAddress
#Ping the DC at the end after starting the capture
Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $DCIP -ea SilentlyContinue | Out-Null
# This is the match logic - check to see if Destination IP from the Ping sent matches the DCIP entered by in the ATA Console
# The only way the ATA Gateway should see a destination of the DC is if Port Spanning is configured
if ($DestinationIPAddressP -eq $DCIPP) # is the destination IP eq to the DC IP?
{
$TestResult = "Port Spanning success!"
$OneSuccess = 1
} else {
$TestResult = "Noise"
}
# Put source, destination, test result in Powershell object
new-object psobject | add-member -pass noteproperty CaptureSource $([system.net.ipaddress]$SourceIPAddress) | add-member -pass noteproperty CaptureDestination $([system.net.ipaddress]$DestinationIPAddress) | Add-Member -pass NoteProperty Result $TestResult | Format-List | Out-Host
#Count tests
$tests ++
}
if ($OneSuccess -eq 1)
{
Write-Host "Port Spanning Success!" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "At least one packet which was addressed to the DC, was picked up by the Gateway." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host "A little noise is OK, but if you don't see a majority of successes, you might want to re-run." -ForegroundColor Yellow
} else {
Write-Host "No joy, all noise. You may want to re-run, increase the number of Ping Counts, or check your config." -ForegroundColor Red
}
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Press any key to continue..." -ForegroundColor Red
[void][System.Console]::ReadKey($true)
Convalidare il mirroring delle porte con Net Mon
Installare Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 nel gateway ATA che si vuole convalidare.
Importante
Non installare Microsoft Message Analyzer o altri software di acquisizione del traffico nel gateway ATA.
Aprire Monitoraggio di rete e creare una nuova scheda di acquisizione.
Selezionare solo la scheda di rete Capture o la scheda di rete connessa alla porta del commutatore configurata come destinazione del mirroring delle porte.
Assicurarsi che la modalità P sia abilitata.
Fare clic su Nuova acquisizione.

Nella finestra Filtro visualizzato immettere il filtro seguente: KerberosV5 OR LDAP e quindi fare clic su Applica.
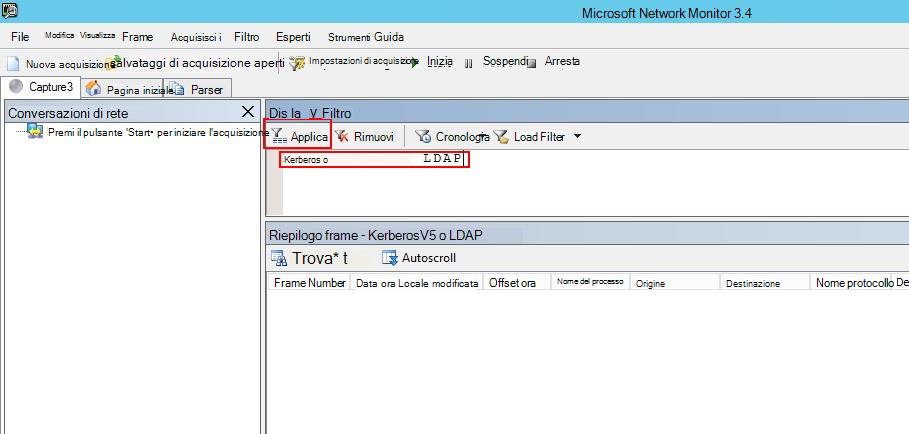
Fare clic su Avvia per avviare la sessione di acquisizione. Se il traffico da e verso il controller di dominio non viene visualizzato, esaminare la configurazione del mirroring delle porte.
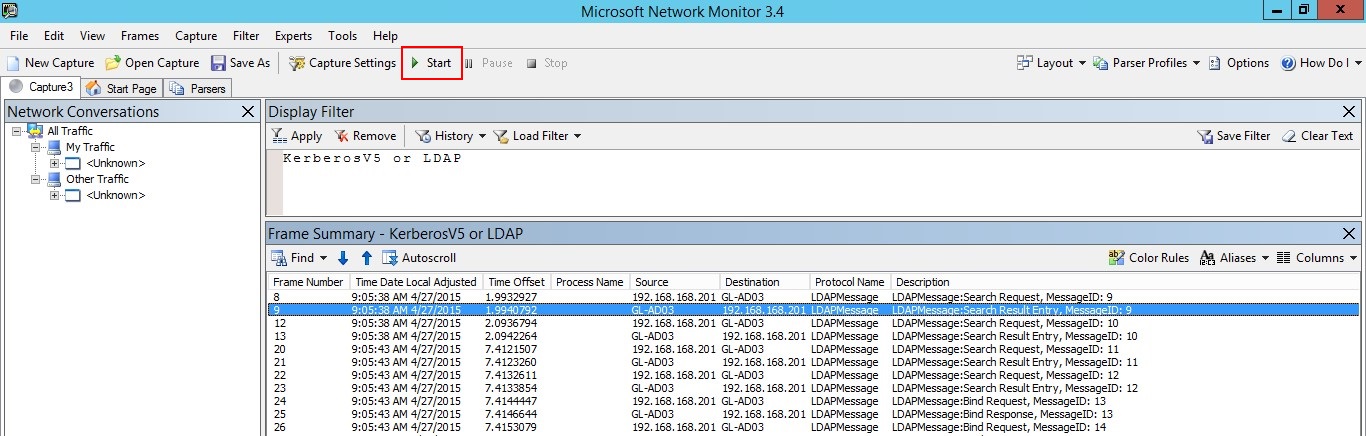
Nota
È importante assicurarsi di visualizzare il traffico da e verso i controller di dominio.
Se il traffico viene visualizzato solo in una direzione, è consigliabile collaborare con i team di rete o di virtualizzazione per risolvere i problemi relativi alla configurazione del mirroring delle porte.