IEC-61883 Protocol Driver in a Client Driver Stack
IEC-61883 client drivers rely on 61883.sys to communicate with their devices using the IEC-61883 protocol.
The following diagram shows an example of the 61883.sys in an AV/C driver stack. The vendor-supplied AV/C subunit driver is the IEC-61883 client in this example.
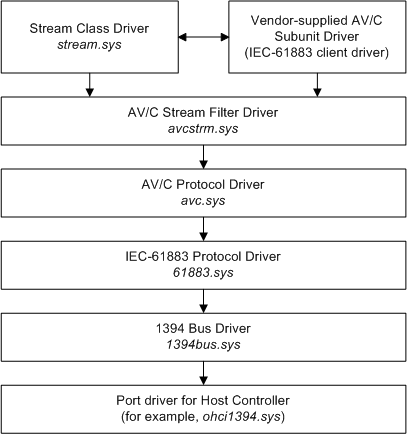
Starting from the top of the diagram:
The stream class driver, stream.sys, supports kernel streaming drivers for devices such as DVD, video capture, and external sound devices. The stream class driver is documented in the Streaming Minidrivers.
In this example, the IEC-61883 client is a vendor-supplied AV/C subunit driver. This is a Writing a Stream Minidriver that uses facilities provided by lower drivers in the AV/C stack to control its device. (For more information about AV/C subunit drivers, see AV/C Client Drivers.)
AV/C subunit drivers set up plug connections and streams, and expose subunit control, status, and notification. They use the kernel streaming framework to expose a generic pin property set and device-specific property and event sets.
The AV/C stream filter driver, avcstrm.sys, is an optional WDM filter driver that isolates stream-specific format handling for subunit drivers. The AV/C stream filter driver is specified as a lower driver by third-party INF files. It supports DV and MPEG stream format for subunit drivers and supplies CMP helper functions in conjunction with avc.sys. It also provides kernel-streaming data structures and data intersection handlers.
The AV/C protocol driver, avc.sys, maps AV/C commands to WDM IRPs, retries requests (for example, if a subunit is busy), handles interim responses as pending IRPs, and routes responses to the correct subunit driver based on type, ID, and operation code. For Microsoft Windows XP and later, avc.sys also provides plug connection management. (For more information about support that Microsoft provides for the AV/C protocol, see AV/C Client Drivers.)
The IEC-61883 protocol driver, 61883.sys, handles function control protocol (FCP), common isochronous packet (CIP) format, and connection management procedures (CMP) requests sent down the AV/C driver stack.
The 1394 bus driver, 1394bus.sys, enumerates devices on the IEEE 1394 bus and responds to Plug and Play and power management IRPs on their behalf.
The port driver for the host controller provides a hardware-independent interface to the IEEE 1394 bus. The port driver handles some IRPs and forwards others to the port driver for the motherboard's host controller. Microsoft supplies a standard port driver, ohci1394.sys, for host controllers that satisfy the 1394 Open Host Controller Interface Specification.
AV/C subunit drivers are just one of the possible types of IEC-61883 client drivers. Another example would be a driver that utilizes the HAVi protocol layered above IEC-61883. Although 61883.sys and the IEC-61883 protocol do not have any AV/C or HAVi dependencies, clients of 61883.sys can operate under different constraints. For example, AV/C subunit drivers are usually clients of avc.sys, which provides FCP-related functions and blocks upper-level drivers from sending FCP-related requests down the stack to be handled by 61883.sys.