Administration Architecture
The following illustration shows the components that make up the AD RMS administration architecture.
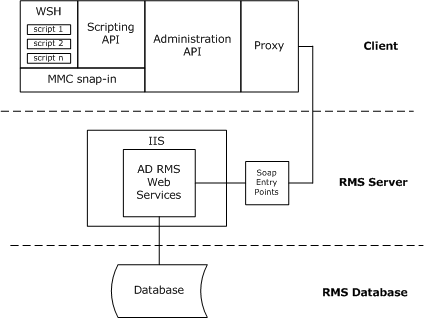
As shown by the illustration, architectural components are installed on clients, one or more RMS servers, and at least one database server.
An RMS server contains the following:
- Web Services: Core functionality is implemented as a set of Microsoft ASP.NET web services that run on Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS). The services include administration, account certification, and licensing.
- SOAP Interfaces: Each service is exposed to clients through a SOAP entry point.
Clients contain the following:
- Web Services Proxy: Clients use the proxy to communicate with web services on the RMS server.
- Administration API: This API is an abstraction layer on top of the web services proxy that exposes administration functionality to the client. The API contains public and private objects and is implemented in a strong named assembly installed in the global assembly cache (GAC).
- MMC Snap-in: The snap-in, hosted in the Microsoft Management Console (MMS), has access to all of the functionality implemented by the administration API.
- Scripting API: The AD RMS Scripting API is exposed through a COM object that you must create from the administration API. For more information, see Installing the AD RMS Scripting API.
- Custom Scripts: You can use the AD RMS Scripting API to create custom scripts that can automate your administrative tasks. The scripts are hosted in Windows Script Host (WSH) on the client computer.
The database server runs the following databases:
- Configuration
- Logging
- Directory Services
Related topics