Procédure : créer et exécuter un workflow de longue durée
L’une des fonctionnalités centrales de Windows Workflow Foundation (CWF) réside dans la capacité du runtime à rendre persistants et à décharger les workflows inactifs dans une base de données. Les étapes de la rubrique Procédure : exécuter un workflow illustraient les principes de base de l’hébergement de workflows à l’aide d’une application console. Des exemples de démarrage de workflow, gestionnaires de cycle de vie de workflow et de reprise des signets ont été donnés. Pour illustrer la persistance de workflow efficacement, un hôte de workflow plus complexe est nécessaire, prenant en charge le démarrage et la reprise de plusieurs instances de workflow. Cette étape du didacticiel explique comment créer une application hôte de formulaire Windows qui prend en charge le démarrage et la reprise de plusieurs instances de workflow, la persistance de workflow, et constitue une base pour les fonctionnalités avancées telles que le suivi et le versioning qui sont expliquées dans les étapes suivantes du didacticiel.
Notes
Cette étape du didacticiel et les étapes suivantes utilisent les trois types de workflow décrits dans Procédure : créer un workflow.
Pour créer la base de données de persistance
Ouvrez SQL Server Management Studio et connectez-vous au serveur local, par exemple .\SQLEXPRESS. Cliquez avec le bouton droit sur le nœud Bases de données sur le serveur local et sélectionnez Nouvelle base de données. Nommez la nouvelle base de données WF45GettingStartedTutorial, acceptez toutes les autres valeurs et sélectionnez OK.
Notes
Vérifiez que vous avez l’autorisation de Créer une base de données sur le serveur local avant de créer la base de données.
Dans le menu Fichier, sélectionnez Ouvrir, puis cliquez sur Fichier. Accédez au dossier suivant : C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\sql\en
Sélectionnez les deux fichiers suivants, puis cliquez sur Ouvrir.
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql
Choisissez SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreSchema.sql dans le menu Fenêtre. Assurez-vous que WF45GettingStartedTutorial est sélectionné dans la liste déroulante Bases de données disponibles et choisissez Exécuter dans le menu Requête.
Choisissez SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreLogic.sql dans le menu Fenêtre. Assurez-vous que WF45GettingStartedTutorial est sélectionné dans la liste déroulante Bases de données disponibles et choisissez Exécuter dans le menu Requête.
Avertissement
Il est important d'effectuer les deux étapes précédentes dans l'ordre approprié. Si les requêtes ne sont pas exécutées dans l'ordre, des erreurs se produisent et la base de données de persistance n'est pas configurée correctement.
Pour ajouter la référence aux assemblys DurableInstancing
Cliquez avec le bouton droit sur NumberGuessWorkflowHost dans l’Explorateur de solutions et sélectionnez Ajouter une référence.
Sélectionnez Assemblys dans la liste Ajouter une référence, puis tapez
DurableInstancingdans la zone Rechercher des assemblys. Cette opération filtre les assemblys et facilite la sélection des références souhaitées.Cochez les cases System.Activities.DurableInstancing et System.Runtime.DurableInstancing dans la liste Résultats de la recherche, puis cliquez sur OK.
Pour créer le formulaire hôte de workflow
Dans l’Explorateur de solutions, cliquez avec le bouton droit sur NumberGuessWorkflowHost, puis sélectionnez Ajouter, Nouvel élément.
Dans la liste de modèles Installés, sélectionnez Formulaire Windows, tapez
WorkflowHostFormdans la zone Nom, puis cliquez sur Ajouter.Configurez les propriétés suivantes sur le formulaire.
Propriété Valeur FormBorderStyle FixedSingle MaximizeBox False Taille 400, 420 Ajoutez les contrôles suivants au formulaire dans l'ordre spécifié et configurez les propriétés selon les instructions.
Control Propriété : valeur Button Name : NouveauJeu
Location : 13, 13
Size : 75, 23
Text : Nouveau jeuÉtiquette Location : 94, 18
Text : Deviner un nombre compris entre 1 etComboBox Name : PlageNombres
DropDownStyle : Liste déroulante
Items : 10, 100, 1000
Location : 228, 12
Size : 143, 21Étiquette Location : 13, 43
Text : Type de workflowComboBox Name : TypeWorkflow
DropDownStyle : Liste déroulante
Items : StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow, FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow, SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow
Location : 94, 40
Size : 277, 21Étiquette Name : VersionWorkflow
Location : 13, 362
Text : Version du workflowGroupBox Location : 13, 67
Size : 358, 287
Text : JeuNotes
Lorsque vous ajoutez les contrôles suivants, placez-les dans le GroupBox.
Control Propriété : valeur Étiquette Location : 7, 20
Text : ID de l’instance de workflowComboBox Name : IDInstance
DropDownStyle : Liste déroulante
Location : 121, 17
Size : 227, 21Étiquette Location : 7, 47
Text : DevinetteTextBox Name : Devinette
Location : 50, 44
Size : 65, 20Button Name : FaireUneDevinette
Location : 121, 42
Size : 75, 23
Text : Faire une devinetteButton Name : QuitterJeu
Location : 274, 42
Size : 75, 23
Text : QuitterTextBox Name : StatutWorkflow
Location : 10, 73
Multiline : True
ReadOnly : True
ScrollBars : Verticales
Size : 338, 208Affectez la valeur EnterGuess à la propriété AcceptButton du formulaire.
L'exemple suivant illustre le formulaire terminé.
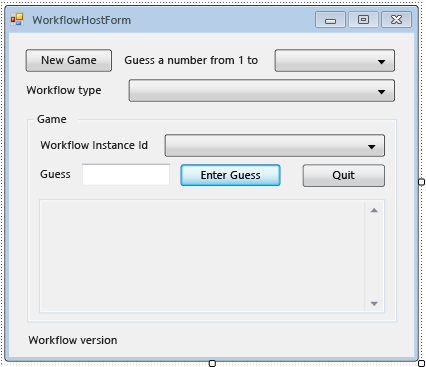
Pour ajouter les propriétés et les méthodes d'assistance au formulaire
La procédure de cette section permet d'ajouter des propriétés et des méthodes d'assistance à la classe de formulaire qui configure l'interface utilisateur du formulaire pour prendre en charge l'exécution et la reprise des workflows d'estimation.
Cliquez avec le bouton droit sur WorkflowHostForm dans l’Explorateur de solutions et sélectionnez Afficher le code.
Ajoutez les instructions
using(ouImports) suivantes au début du fichier avec les autres instructionsusing(ouImports).Imports System.Activities Imports System.Activities.DurableInstancing Imports System.Data.SqlClient Imports System.IO Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Activities; using System.Activities.DurableInstancing; using System.Data.SqlClient; using System.IO; using System.Windows.Forms;Ajoutez les déclarations de membre suivantes à la classe WorkflowHostForm.
Important
Microsoft vous recommande d’utiliser le flux d’authentification le plus sécurisé disponible. Si vous vous connectez à Azure SQL, les identités managées pour les ressources Azure sont la méthode d'authentification recommandée.
Const connectionString = "Server=.\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI" Dim store As SqlWorkflowInstanceStore Dim workflowStarting As Booleanconst string connectionString = "Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Initial Catalog=WF45GettingStartedTutorial;Integrated Security=SSPI"; SqlWorkflowInstanceStore store; bool workflowStarting;Remarque
Si votre chaîne de connexion est différente, mettez à jour
connectionStringpour faire référence à votre base de données.Ajoutez une propriété
WorkflowInstanceIdà la classeWorkflowFormHost.Public ReadOnly Property WorkflowInstanceId() As Guid Get If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return Guid.Empty Else Return New Guid(InstanceId.SelectedItem.ToString()) End If End Get End Propertypublic Guid WorkflowInstanceId { get { return InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1 ? Guid.Empty : (Guid)InstanceId.SelectedItem; } }La zone de liste modifiable
InstanceIdaffiche la liste des ID d’instances de workflow persistantes, et la propriétéWorkflowInstanceIdretourne le workflow sélectionné.Ajoutez un gestionnaire pour l'événement
Loaddu formulaire. Pour ajouter le gestionnaire, basculez en Mode Design pour le formulaire, cliquez sur l’icône Événements en haut de la fenêtre Propriétés, puis double-cliquez sur Charger.Private Sub WorkflowHostForm_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Me.Load End Subprivate void WorkflowHostForm_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Ajoutez le code suivant à
WorkflowHostForm_Load.' Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for ' multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = New SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString) WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, Nothing, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any) ' Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0 WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0 ListPersistedWorkflows()// Initialize the store and configure it so that it can be used for // multiple WorkflowApplication instances. store = new SqlWorkflowInstanceStore(connectionString); WorkflowApplication.CreateDefaultInstanceOwner(store, null, WorkflowIdentityFilter.Any); // Set default ComboBox selections. NumberRange.SelectedIndex = 0; WorkflowType.SelectedIndex = 0; ListPersistedWorkflows();Lors du chargement du formulaire,
SqlWorkflowInstanceStoreest configuré, les zones de liste déroulante de plage et de type de workflow ont les valeurs par défaut, et les instances persistantes de workflow sont ajoutées à la zone de liste modifiableInstanceId.Ajoutez un gestionnaire
SelectedIndexChangedpourInstanceId. Pour ajouter le gestionnaire, basculez en Mode Design pour le formulaire, sélectionnez la zone de liste modifiableInstanceId, cliquez sur l’icône Événements en haut de la fenêtre Propriétés, puis double-cliquez sur SelectedIndexChanged.Private Sub InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles InstanceId.SelectedIndexChanged End Subprivate void InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Ajoutez le code suivant à
InstanceId_SelectedIndexChanged. Chaque fois que l'utilisateur sélectionne un workflow à l'aide de la zone de liste modifiable, ce gestionnaire met à jour la fenêtre d'état.If InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 Then Return End If ' Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear() ' Get the workflow version and display it. ' If the workflow is just starting then this info will not ' be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. If Not workflowStarting Then Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) WorkflowVersion.Text = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Unload the instance. instance.Abandon() End Ifif (InstanceId.SelectedIndex == -1) { return; } // Clear the status window. WorkflowStatus.Clear(); // Get the workflow version and display it. // If the workflow is just starting then this info will not // be available in the persistence store so do not try and retrieve it. if (!workflowStarting) { WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(this.WorkflowInstanceId, store); WorkflowVersion.Text = WorkflowVersionMap.GetIdentityDescription(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Unload the instance. instance.Abandon(); }Ajoutez la méthode
ListPersistedWorkflowssuivante à la classe de formulaire.Private Sub ListPersistedWorkflows() Using localCon As New SqlConnection(connectionString) Dim localCmd As String = _ "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]" Dim cmd As SqlCommand = localCon.CreateCommand() cmd.CommandText = localCmd localCon.Open() Using reader As SqlDataReader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection) While (reader.Read()) ' Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Dim id As Guid = Guid.Parse(reader(0).ToString()) InstanceId.Items.Add(id) End While End Using End Using End Subusing (var localCon = new SqlConnection(connectionString)) { string localCmd = "SELECT [InstanceId] FROM [System.Activities.DurableInstancing].[Instances] ORDER BY [CreationTime]"; SqlCommand cmd = localCon.CreateCommand(); cmd.CommandText = localCmd; localCon.Open(); using (SqlDataReader reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection)) { while (reader.Read()) { // Get the InstanceId of the persisted Workflow. Guid id = Guid.Parse(reader[0].ToString()); InstanceId.Items.Add(id); } } }ListPersistedWorkflowsinterroge le magasin d'instances pour les instances persistantes de workflow, et ajoute les ID d'instance à la zone de liste modifiablecboInstanceId.Ajoutez la méthode
UpdateStatussuivante et le délégué correspondant à la classe de formulaire. Cette méthode met à jour la fenêtre d'état du formulaire avec l'état du workflow en cours d'exécution.Private Delegate Sub UpdateStatusDelegate(msg As String) Public Sub UpdateStatus(msg As String) ' We may be on a different thread so we need to ' make this call using BeginInvoke. If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New UpdateStatusDelegate(AddressOf UpdateStatus), msg) Else If Not msg.EndsWith(vbCrLf) Then msg = msg & vbCrLf End If WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg) ' Ensure that the newly added status is visible. WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret() End If End Subprivate delegate void UpdateStatusDelegate(string msg); public void UpdateStatus(string msg) { // We may be on a different thread so we need to // make this call using BeginInvoke. if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new UpdateStatusDelegate(UpdateStatus), msg); } else { if (!msg.EndsWith("\r\n")) { msg += "\r\n"; } WorkflowStatus.AppendText(msg); WorkflowStatus.SelectionStart = WorkflowStatus.Text.Length; WorkflowStatus.ScrollToCaret(); } }Ajoutez la méthode
GameOversuivante et le délégué correspondant à la classe de formulaire. Lorsqu’un workflow se termine, cette méthode met à jour l’interface utilisateur du formulaire en supprimant l’ID d’instance du workflow terminé de la zone de liste modifiable InstanceId.Private Delegate Sub GameOverDelegate() Private Sub GameOver() If InvokeRequired Then BeginInvoke(New GameOverDelegate(AddressOf GameOver)) Else ' Remove this instance from the InstanceId combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem) InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1 End If End Subprivate delegate void GameOverDelegate(); private void GameOver() { if (InvokeRequired) { BeginInvoke(new GameOverDelegate(GameOver)); } else { // Remove this instance from the combo box. InstanceId.Items.Remove(InstanceId.SelectedItem); InstanceId.SelectedIndex = -1; } }
Pour configurer le magasin d'instances, les gestionnaires de cycle de vie de workflow et les extensions
Ajoutez une méthode
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationà la classe de formulaire.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { }Cette méthode configure
WorkflowApplication, ajoute les extensions souhaitées, et ajoute des gestionnaires pour les événements de cycle de vie de workflow.Dans
ConfigureWorkflowApplication, spécifiez leSqlWorkflowInstanceStorepourWorkflowApplication.' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store// Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store;Ensuite, créez une instance de
StringWriteret ajoutez-la à la collectionExtensionsdeWorkflowApplication. Lorsqu’une instance deStringWriterest ajoutée aux extensions, elles capture toute la sortie d’activitéWriteLine. Lorsque le workflow devient inactif, la sortie deWriteLinepeut être récupérée à partir deStringWriteret s'afficher sur le formulaire.' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw)// Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw);Ajoutez le gestionnaire suivant pour l'événement
Completed. Lorsqu'un workflow se termine correctement, le nombre de tours utilisés pour deviner le nombre est affiché dans la fenêtre d'état. Si le workflow se termine, les informations sur les exceptions qui ont provoqué l'arrêt sont affichées. À la fin du gestionnaire, la méthodeGameOverest appelée, ce qui supprime le workflow terminé de la liste de workflow.wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End SubwfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); };Ajoutez les gestionnaires
AbortedetOnUnhandledExceptionsuivants. La méthodeGameOvern'est pas appelée à partir du gestionnaireAborted, car lorsqu'une instance du workflow est interrompue, elle ne se termine pas, et il est possible de reprendre l'instance ultérieurement.wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End FunctionwfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; };Ajoutez le gestionnaire
PersistableIdlesuivant. Ce gestionnaire extrait l’extensionStringWriterajoutée, récupère la sortie des activitésWriteLine, et l’affiche dans la fenêtre d’état.wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End FunctionwfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; };L'énumération PersistableIdleAction a trois valeurs : None, Persist et Unload. Persist entraîne la persistance du workflow, mais pas son déchargement. Unload entraîne la persistance du workflow et son déchargement.
L'exemple suivant illustre la méthode
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationcomplète.Private Sub ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp As WorkflowApplication) ' Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store ' Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output ' from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. Dim sw As New StringWriter() wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw) wfApp.Completed = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs) If e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Faulted Then UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.TerminationException.Message}") ElseIf e.CompletionState = ActivityInstanceState.Canceled Then UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled.") Else Dim turns As Integer = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs("Turns")) UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns.") End If GameOver() End Sub wfApp.Aborted = _ Sub(e As WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.Reason.Message}") End Sub wfApp.OnUnhandledException = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs) UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}{vbCrLf}{e.UnhandledException.Message}") GameOver() Return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate End Function wfApp.PersistableIdle = _ Function(e As WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs) ' Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. Dim writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions(Of StringWriter)() For Each writer In writers UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()) Next Return PersistableIdleAction.Unload End Function End Subprivate void ConfigureWorkflowApplication(WorkflowApplication wfApp) { // Configure the persistence store. wfApp.InstanceStore = store; // Add a StringWriter to the extensions. This captures the output // from the WriteLine activities so we can display it in the form. var sw = new StringWriter(); wfApp.Extensions.Add(sw); wfApp.Completed = delegate(WorkflowApplicationCompletedEventArgs e) { if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Faulted) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Terminated. Exception: {e.TerminationException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.TerminationException.Message}"); } else if (e.CompletionState == ActivityInstanceState.Canceled) { UpdateStatus("Workflow Canceled."); } else { int turns = Convert.ToInt32(e.Outputs["Turns"]); UpdateStatus($"Congratulations, you guessed the number in {turns} turns."); } GameOver(); }; wfApp.Aborted = delegate(WorkflowApplicationAbortedEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Workflow Aborted. Exception: {e.Reason.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.Reason.Message}"); }; wfApp.OnUnhandledException = delegate(WorkflowApplicationUnhandledExceptionEventArgs e) { UpdateStatus($"Unhandled Exception: {e.UnhandledException.GetType().FullName}\r\n{e.UnhandledException.Message}"); GameOver(); return UnhandledExceptionAction.Terminate; }; wfApp.PersistableIdle = delegate(WorkflowApplicationIdleEventArgs e) { // Send the current WriteLine outputs to the status window. var writers = e.GetInstanceExtensions<StringWriter>(); foreach (var writer in writers) { UpdateStatus(writer.ToString()); } return PersistableIdleAction.Unload; }; }
Pour activer le démarrage et la reprise de plusieurs types de workflow
Afin de reprendre une instance de workflow, l'hôte doit fournir la définition du workflow. Dans ce didacticiel il existe trois types de workflow, et les étapes suivantes présentent plusieurs versions de ces types. WorkflowIdentity offre un moyen pour une application hôte d'associer les informations d'identification à une instance persistante de workflow. Les étapes de cette section expliquent comment créer une classe utilitaire pour assister le mappage de l'identité de workflow d'une instance persistante de workflow à la définition correspondante de workflow. Pour plus d’informations sur WorkflowIdentity et le contrôle de version, consultez Utilisation de WorkflowIdentity et du contrôle de version.
Dans l’Explorateur de solutions, cliquez avec le bouton droit sur NumberGuessWorkflowHost, puis sélectionnez Ajouter, Classe. Tapez
WorkflowVersionMapdans la zone Nom, puis cliquez sur Ajouter.Ajoutez les instructions
using(ouImports) suivantes au début du fichier avec les autres instructionsusing(ouImports).Imports System.Activities Imports NumberGuessWorkflowActivitiesusing System.Activities; using NumberGuessWorkflowActivities;Remplacez la déclaration de classe
WorkflowVersionMappar la déclaration suivante.Public Module WorkflowVersionMap Dim map As Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Current version identities. Public StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Public SequentialNumberGuessIdentity As WorkflowIdentity Sub New() map = New Dictionary(Of WorkflowIdentity, Activity) ' Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = New WorkflowIdentity With { .Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", .Version = New Version(1, 0, 0, 0) } map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, New StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, New FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()) map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, New SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()) End Sub Public Function GetWorkflowDefinition(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As Activity Return map(identity) End Function Public Function GetIdentityDescription(identity As WorkflowIdentity) As String Return identity.ToString() End Function End Modulepublic static class WorkflowVersionMap { static Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity> map; // Current version identities. static public WorkflowIdentity StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; static public WorkflowIdentity SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; static WorkflowVersionMap() { map = new Dictionary<WorkflowIdentity, Activity>(); // Add the current workflow version identities. StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; SequentialNumberGuessIdentity = new WorkflowIdentity { Name = "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow", Version = new Version(1, 0, 0, 0) }; map.Add(StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity, new StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity, new FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow()); map.Add(SequentialNumberGuessIdentity, new SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow()); } public static Activity GetWorkflowDefinition(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return map[identity]; } public static string GetIdentityDescription(WorkflowIdentity identity) { return identity.ToString(); } }WorkflowVersionMapcontient trois identités de workflow mappées aux trois définitions de workflow de ce didacticiel et est utilisé dans les sections suivantes lorsque des workflow sont démarrés et repris.
Pour démarrer un nouveau workflow
Ajoutez un gestionnaire
ClickpourNewGame. Pour ajouter le gestionnaire, basculez en Mode Design pour le formulaire, puis double-cliquez surNewGame. Un gestionnaireNewGame_Clickest ajouté et l'affichage bascule en mode Code pour le formulaire. Chaque fois que l'utilisateur clique sur ce bouton un nouveau workflow est démarré.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Ajoutez le code suivant au gestionnaire de clics. Ce code crée un dictionnaire d'arguments d'entrée du workflow, indexés par nom d'argument. Ce dictionnaire a une entrée qui contient la plage du nombre généré de manière aléatoire extrait de la zone de liste modifiable de plage.
Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem))var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem));Ensuite, ajoutez le code suivant qui démarre le workflow.
WorkflowIdentityet la définition de workflow correspondant au type de workflow sélectionné sont récupérés à l'aide de la classe d'assistanceWorkflowVersionMap. Ensuite, une nouvelle instanceWorkflowApplicationest créée à l’aide de la définition de workflow,WorkflowIdentity, et du dictionnaire d’arguments d’entrée.Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity)WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); WorkflowApplication wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity);Ensuite, ajoutez le code suivant qui ajoute le workflow à la liste de workflow et affiche les informations de version du workflow sur le formulaire.
' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False// Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false;Appelez
ConfigureWorkflowApplicationpour configurer le magasin d'instances, les extensions et les gestionnaires du cycle de vie de workflow pour cette instanceWorkflowApplication.' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp)// Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp);Pour finir, appelez
Run.' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run()// Start the workflow. wfApp.Run();Cet exemple est le gestionnaire
NewGame_Clickterminé.Private Sub NewGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles NewGame.Click ' Start a new workflow. Dim inputs As New Dictionary(Of String, Object)() inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)) Dim identity As WorkflowIdentity = Nothing Select Case WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString() Case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity Case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity Case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow" identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity End Select Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity) Dim wfApp = New WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity) ' Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = True InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id) WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString() workflowStarting = False ' Configure the instance store, extensions, and ' workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Start the workflow. wfApp.Run() End Subprivate void NewGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { var inputs = new Dictionary<string, object>(); inputs.Add("MaxNumber", Convert.ToInt32(NumberRange.SelectedItem)); WorkflowIdentity identity = null; switch (WorkflowType.SelectedItem.ToString()) { case "SequentialNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.SequentialNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "StateMachineNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.StateMachineNumberGuessIdentity; break; case "FlowchartNumberGuessWorkflow": identity = WorkflowVersionMap.FlowchartNumberGuessIdentity; break; }; Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(identity); var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, inputs, identity); // Add the workflow to the list and display the version information. workflowStarting = true; InstanceId.SelectedIndex = InstanceId.Items.Add(wfApp.Id); WorkflowVersion.Text = identity.ToString(); workflowStarting = false; // Configure the instance store, extensions, and // workflow lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Start the workflow. wfApp.Run(); }
Pour reprendre un workflow
Ajoutez un gestionnaire
ClickpourEnterGuess. Pour ajouter le gestionnaire, basculez en Mode Design pour le formulaire, puis double-cliquez surEnterGuess. Chaque fois que l'utilisateur clique sur ce bouton un nouveau workflow reprend.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Ajoutez le code suivant pour vous assurer qu'un workflow est sélectionné dans la liste de workflow, et que l'estimation de l'utilisateur est valide.
If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End Ifif (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; }Ensuite, récupérez
WorkflowApplicationInstancede l'instance persistante de workflow.WorkflowApplicationInstancereprésente une instance persistante de workflow qui n'a pas encore été associée à une définition de workflow.DefinitionIdentitydeWorkflowApplicationInstancecontientWorkflowIdentityde l'instance persistante de workflow. Dans ce didacticiel, la classe utilitaireWorkflowVersionMapest utilisée pour mapperWorkflowIdentityà la définition appropriée de workflow. Une fois que la définition de workflow est récupérée,WorkflowApplicationest créé, à l'aide de la définition appropriée de workflow.Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity)WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity);Une fois que
WorkflowApplicationest créé, configurez le magasin d’instances, les gestionnaires du cycle de vie de workflow et les extensions en appelantConfigureWorkflowApplication. Ces étapes doivent être effectuées chaque fois qu'un nouveauWorkflowApplicationest créé, et elles doivent être effectuées avant que l'instance de workflow ne soit chargée dansWorkflowApplication. Une fois que le workflow est chargé, il reprend à l'estimation de l'utilisateur.' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess)// Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess);Enfin, effacez la zone de texte d'estimation et préparez le formulaire pour recevoir une autre estimation.
' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus()// Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus();Cet exemple est le gestionnaire
EnterGuess_Clickterminé.Private Sub EnterGuess_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles EnterGuess.Click If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim userGuess As Integer If Not Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, userGuess) Then MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer.") Guess.SelectAll() Guess.Focus() Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = _ WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ' Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is ' loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", userGuess) ' Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear() Guess.Focus() End Subprivate void EnterGuess_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } int guess; if (!Int32.TryParse(Guess.Text, out guess)) { MessageBox.Show("Please enter an integer."); Guess.SelectAll(); Guess.Focus(); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. // Do this before the instance is loaded. Once the instance is // loaded it is too late to add extensions. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Resume the workflow. wfApp.ResumeBookmark("EnterGuess", guess); // Clear the Guess textbox. Guess.Clear(); Guess.Focus(); }
Pour terminer un workflow
Ajoutez un gestionnaire
ClickpourQuitGame. Pour ajouter le gestionnaire, basculez en Mode Design pour le formulaire, puis double-cliquez surQuitGame. Chaque fois que l'utilisateur clique sur ce bouton le workflow actuellement sélectionné est terminé.Private Sub QuitGame_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles QuitGame.Click End Subprivate void QuitGame_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { }Ajoutez le code suivant au gestionnaire
QuitGame_Click. Ce code vérifie d'abord qu'un workflow est sélectionné dans la liste de workflow. Ensuite, il charge l'instance persistante dansWorkflowApplicationInstance, utiliseDefinitionIdentitypour déterminer la définition appropriée de workflow, puis initialiseWorkflowApplication. Ensuite, les extensions et les gestionnaires de cycle de vie de workflow sont configurés avec un appel àConfigureWorkflowApplication. Une fois queWorkflowApplicationest configuré, il est chargé, puisTerminateest appelé.If WorkflowInstanceId = Guid.Empty Then MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow.") Return End If Dim instance As WorkflowApplicationInstance = _ WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store) ' Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow ' definition from the dictionary. Dim wf As Activity = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition. Dim wfApp As New WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity) ' Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers. ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp) ' Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance) ' Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.")if (WorkflowInstanceId == Guid.Empty) { MessageBox.Show("Please select a workflow."); return; } WorkflowApplicationInstance instance = WorkflowApplication.GetInstance(WorkflowInstanceId, store); // Use the persisted WorkflowIdentity to retrieve the correct workflow // definition from the dictionary. Activity wf = WorkflowVersionMap.GetWorkflowDefinition(instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Associate the WorkflowApplication with the correct definition var wfApp = new WorkflowApplication(wf, instance.DefinitionIdentity); // Configure the extensions and lifecycle handlers ConfigureWorkflowApplication(wfApp); // Load the workflow. wfApp.Load(instance); // Terminate the workflow. wfApp.Terminate("User resigns.");
Pour générer et exécuter l'application
Double-cliquez sur Program.cs (ou sur Module1.vb) dans l’Explorateur de solutions pour afficher le code.
Ajoutez l'instruction
using(ouImports) suivante au début du fichier avec les autres instructionsusing(ouImports).Imports System.Windows.Formsusing System.Windows.Forms;Supprimez ou commentez le code d’hébergement de workflow existant décrit dans Procédure : exécuter un workflow et remplacez-le par le code suivant.
Sub Main() Application.EnableVisualStyles() Application.Run(New WorkflowHostForm()) End Substatic void Main(string[] args) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.Run(new WorkflowHostForm()); }Dans l’Explorateur de solutions, cliquez avec le bouton droit sur NumberGuessWorkflowHost et sélectionnez Propriétés. Dans l’onglet Application, spécifiez Application Windows pour Type de sortie. Cette étape est facultative, mais si elle n'est pas suivie, la fenêtre de console s'affiche en plus du formulaire.
Appuyez sur Ctrl+Maj+B pour générer l'application.
Assurez-vous que NumberGuessWorkflowHost est défini comme application de démarrage, puis appuyez sur Ctrl+F5 pour démarrer l’application.
Sélectionnez une plage pour le jeu de devinettes et le type de workflow à démarrer, puis cliquez sur Nouvelle partie. Entrez une proposition dans la zone Deviner et cliquez sur Aller à pour soumettre votre proposition. Notez que la sortie des activités
WriteLines'affiche sur le formulaire.Démarrez plusieurs workflow au moyen de différents types de workflow et plages de nombres, entrez des propositions, et basculez entre les workflows en effectuant une sélection dans la liste ID d’instance de workflow.
Notez que lorsque vous basculez vers un nouveau workflow, les propositions précédentes et la progression du workflow ne s'affichent pas dans la fenêtre d'état. En effet, l'état n'est pas disponible, car il n'est pas capturé ni enregistré. Dans l’étape suivante du tutoriel, Procédure : créer un participant de suivi personnalisé, vous allez créer un participant de suivi personnalisé qui enregistre ces informations.
