Sécurité de transport avec l'authentification de base
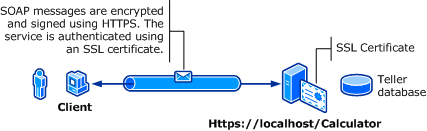
L’illustration suivante montre un service et un client Windows Communication Foundation (WCF). Le serveur nécessite un certificat X.509 valide qui peut être utilisé pour SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) et les clients doivent approuver le certificat du serveur. De plus, le service Web contient déjà une implémentation SSL disponible. Pour plus d’informations sur l’activation de l’authentification de base sur Internet Information Services (IIS), consultez Authentification de base.
| Caractéristique | Description |
|---|---|
| Mode de sécurité | Transport |
| Interopérabilité | Avec les clients de service Web et les services existants |
| Authentification (serveur) Authentification (client) |
Oui (à l'aide de HTTPS) Oui (à l'aide du Nom d'utilisateur/Mot de passe) |
| Intégrité | Oui |
| Confidentialité | Oui |
| Transport | HTTPS |
| Liaison | WSHttpBinding |
Service
La configuration et le code ci-dessous sont conçus pour s'exécuter indépendamment. Effectuez l’une des opérations suivantes :
Créez un service autonome à l'aide du code sans configuration.
Créez un service à l'aide de la configuration fournie, mais ne définissez pas de point de terminaison.
Code
Le code suivant montre comment créer un point de terminaison de service qui utilise un nom d'utilisateur de domaine et un mot de passe Windows pour la sécurité de transfert. Notez que le service requiert un certificat X.509 pour s'authentifier auprès du client. Pour plus d’informations, consultez Utilisation des certificats et Guide pratique pour configurer un port avec un certificat SSL.
// Create the binding.
WSHttpBinding binding = new WSHttpBinding();
binding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
binding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
// Create the URI for the endpoint.
Uri httpUri = new Uri("https://localhost/Calculator");
// Create the service host and add an endpoint.
ServiceHost myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(
typeof(ServiceModel.Calculator), httpUri);
myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(
typeof(ServiceModel.ICalculator), binding, "");
// Open the service.
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Listening...");
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit.");
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the service.
myServiceHost.Close();
' Create the binding.
Dim binding As New WSHttpBinding()
binding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport
binding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType = HttpClientCredentialType.Basic
' Create the URI for the endpoint.
Dim httpUri As New Uri("https://localhost/Calculator")
' Create the service host and add an endpoint.
Dim myServiceHost As New ServiceHost(GetType(ServiceModel.Calculator), httpUri)
myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(GetType(ServiceModel.ICalculator), binding, "")
' Open the service.
myServiceHost.Open()
Console.WriteLine("Listening...")
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit.")
Console.ReadLine()
' Close the service.
myServiceHost.Close()
Configuration
Les éléments suivants configurent un service pour utiliser l'authentification de base avec la sécurité au niveau du transport :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="UsernameWithTransport">
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Basic" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<services>
<service name="BasicAuthentication.Calculator">
<endpoint address="https://localhost/Calculator"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="UsernameWithTransport"
name="BasicEndpoint"
contract="BasicAuthentication.ICalculator" />
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Client
Code
Le code suivant affiche le code client qui inclut le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe. Notez que l'utilisateur doit fournir un nom d'utilisateur et un mot de passe Windows valides. Le code pour retourner le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe n'est pas indiqué. Utilisez une boîte de dialogue ou une autre interface pour demander les informations à l'utilisateur.
Notes
Le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe peuvent être définis uniquement à l'aide de code.
// Create the binding.
WSHttpBinding myBinding = new WSHttpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
// Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
// must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
// used to authenticate the service.
EndpointAddress ea = new
EndpointAddress("https://machineName/Calculator");
// Create the client. The code for the calculator
// client is not shown here. See the sample applications
// for examples of the calculator code.
CalculatorClient cc =
new CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea);
// The client must provide a user name and password. The code
// to return the user name and password is not shown here. Use
// a database to store the user name and passwords, or use the
// ASP.NET Membership provider database.
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = ReturnUsername();
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = ReturnPassword();
try
{
// Begin using the client.
cc.Open();
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 11));
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the client.
cc.Close();
}
' Create the binding.
Dim myBinding As New WSHttpBinding()
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType = HttpClientCredentialType.Basic
' Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
' must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
' used to authenticate the service.
Dim ea As New EndpointAddress("https://machineName/Calculator")
' Create the client. The code for the calculator
' client is not shown here. See the sample applications
' for examples of the calculator code.
Dim cc As New CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea)
' The client must provide a user name and password. The code
' to return the user name and password is not shown here. Use
' a database to store the user name and passwords, or use the
' ASP.NET Membership provider database.
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = ReturnUsername()
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = ReturnPassword()
' Begin using the client.
Try
cc.Open()
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 11))
Console.ReadLine()
' Close the client.
cc.Close()
Catch tex As TimeoutException
Console.WriteLine(tex.Message)
cc.Abort()
Catch cex As CommunicationException
Console.WriteLine(cex.Message)
cc.Abort()
Finally
Console.WriteLine("Closed the client")
Console.ReadLine()
End Try
Configuration
Le code suivant affiche la configuration du client.
Notes
Vous ne pouvez pas utiliser la configuration pour définir le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe. La configuration indiquée ici doit être augmentée à l'aide du code pour définir le nom d'utilisateur et le mot de passe.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator" >
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Basic" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<client>
<endpoint address="https://machineName/Calculator"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator"
contract="ICalculator"
name="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator" />
</client>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>