Serial Support on the Windows Subsystem for Linux
This is part of a series of blog posts on the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). For background information you may want to read the architectural overview, introduction to pico processes, WSL system calls, and WSL file system blog posts.
Posted on behalf of Stephen Hufnagel
Summary
In Windows Insider build #16176 WSL now allows access to serial devices (COM ports).
This blog post will describe how to use this feature and the work that was involved in exposing this functionality within WSL.
On Windows, COM ports are named COM1 through COM256. On Linux, serial devices can have arbitrary names but are typically character devices with a major number of 4 and a minor number from 64 to 256 represented by /dev/ttyS0 through /dev/ttyS191. By default init will populate this mapping using the mknod system call. Alternate mknod mappings can be created at runtime if needed.
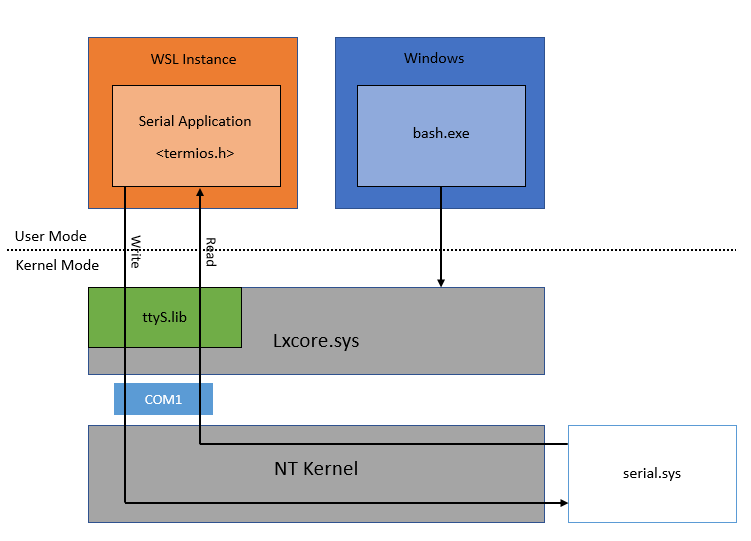
In WSL, the lxcore driver maps COM ports to Linux devices by the COM port number so /dev/ttyS<N> is tied to COM<N>. More specifically, the mapping is on the minor number, so minor number 65 (/dev/ttyS1) is COM1, 66 (/dev/ttyS2) is COM2, and so forth. Since pty, tty, and ttyS share a terminal library code base, ttyS will behave similarly but also support the following termios settings which are simply mapped to Windows serial driver ioctls:
- Standard baud rates - B*
- Stop bits - CSTOPB
- Word length - CSIZE
- Parity checking - PARENB, PARODD, CMSPAR, INPCK
- Software flow control - IXON, IXOFF
- Hardware flow control - CRTSCTS, CLOCAL
- Control characters - VSTART, VSTOP, VEOF
To use your favorite serial tool\library in WSL, just map from the COM port of the device using device manager or the SERIALCOMM registry key (HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\HARDWARE\DEVICEMAP\SERIALCOMM).
Figure 1. This diagram shows the basic architecture of WSL exposes Windows COM ports as serial devices in WSL.
Scenarios
The following scenarios were tested and confirmed to be working:
- Programming pixhawk light controller - Thanks @lovettchris!
- Connecting to Raspberry Pi 2 serial terminal using the
cutool - Transferring data on various serial configurations:
- Hyper-V virtual COM port
- FTDI USB to serial converter
- Prolific USB to serial converter
- Physical COM port
Please note that some serial drivers have known bugs. These issues exist on both native Windows and within WSL.
The following areas are known to not work. We are tracking updates to future Windows Insider builds to address them.
- Using legacy raw ioctls instead TCGETS or TCSETS* to configure and query the serial device
- Screen and minicom depend on the above so they do not currently work as a serial terminal, but cu is an alternative.
Example
On a Windows 10 machine where a Raspberry Pi is connected on COM5 connect using the following steps:
sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS5- This is required since cu changes it's uid which drops capabilities even when running as root. Not all serial programs have the same behavior.stty -F /dev/ttyS5 -a. Optionally check your current serial settings before updating.- Set your serial settings, depending on your application this usually will be raw or sane. Either one seems to work fine with cu:
stty -F /dev/ttyS5 sane 9600stty -F /dev/ttyS5 raw 9600 -echo -echoe -echok -echoctl -echoke -iexten -onlcr cs8 crtscts
cu -l /dev/ttyS5 -s 9600- Hit enter to refresh the cu console
Feedback
Please let us know on our Github about the specific serial scenarios that you are trying. Your feedback helps us prioritize what we should focus on next.
Comments
- Anonymous
April 18, 2017
Information was useful. thank you - Anonymous
April 26, 2017
What doespicocomuse? - Anonymous
May 18, 2017
Has this made the mainstream builds yet? I had insider once and it totally messed up my tablet.- Anonymous
September 21, 2017
This serial support is in current Insiders builds, and will be released broadly in Fall Creators Update starting mid October 2017.Sorry to hear you had issues with prior Insiders builds, but understand that when you install Insiders, you're literally installing a weekly snapshot of Windows as it's being built. Though we do our best to try and avoid releasing major bugs, there may well be the occasional breaking or undiscovered issue. This is why we recommend that you do not install Insiders (fast ring builds in particular) on your primary or only machine.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
May 25, 2017
Will these updates be applied to Windows 10 Creators or must we wait for the next release?- Anonymous
September 21, 2017
Insiders builds are ~weekly snapshots of the next version of Windows as it's being built. Therefore, current Insiders builds are snapshots of what will become Fall Creators Update.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
June 04, 2017
This is great! But same comment and question here: I don't find it in the main build? When is it going to be available in the standard build? Is there a way to upgrade just Windows bash? - Anonymous
June 10, 2017
COM1 through COM256...I remember when you only had COM1-4 and even then, 3 and 4 were problematic due to IRQ sharing. I'm old! - Anonymous
October 24, 2017
Amazing! YOU solved my problem, I have tested minicom on WSL for a whole afternoon, but nothing comes out from the terminal. It doesn't work right now. - Anonymous
November 11, 2017
Hello,Would you mind to tell me how to backup the WSL before I reset my Windows 10. - Anonymous
May 14, 2018
Hi @Rich Turner! I've tried to follow this blog to solve my problem. I'm trying to use a Movidius Neural Compute Stick (https://movidius.github.io/ncsdk/ncs.html) on WLS, but the system is not able to recognize the USB stick. With 'sudo chmod 666 /dev/ttyS5' I had this error: "Input/Output error".Thanks for your help! - Anonymous
December 08, 2018
Unable to set a non-standard baud rate:Failed to set custom baud rate (74880): [Errno 25] Inappropriate ioctl for device74880 is the baud rate of the ESP8266 chip (which is very popular). Please make it work! - Anonymous
December 11, 2018
I have the problem that serial ports in the linux shell stop working at some point (most likely after putting Windows to sleep a few times). Is there a way to reset/remap the serial ports without having to reboot the system (restarting shell does not work)? - Anonymous
March 25, 2019
Problem with Silicon Labs CP210x Universal Drivers for Windows 10 version 10.1.6: stty -F /dev/ttyS5 -a >> input/output error. COM5 is accessible with PuTTY in Windows, but inaccessible from WSL/Debian.Solution: Use version 6.7.6 for Windows 7/8/8.1. At least I can read the current settings now. - Anonymous
March 25, 2019
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
April 06, 2019
Very useful indeed. Thanks