Part 15 - I used to do it this way… Now how do I do it? Administering Exchange 2003 vs. Exchange 2007
To return to part 1 click here
Administrative Tasks: Mailbox Permissions and Query-Based \ Dynamic Distribution Groups
Mailbox Permissions
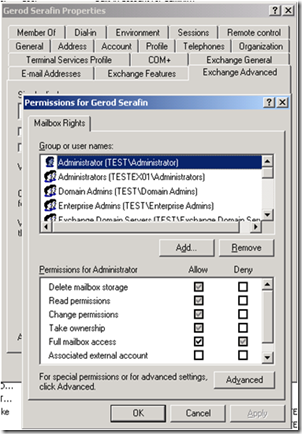
In Exchange 2003, you used Active Directory Users and Computers to manage mailbox permissions for users.
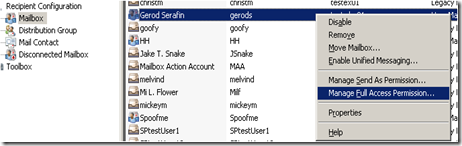
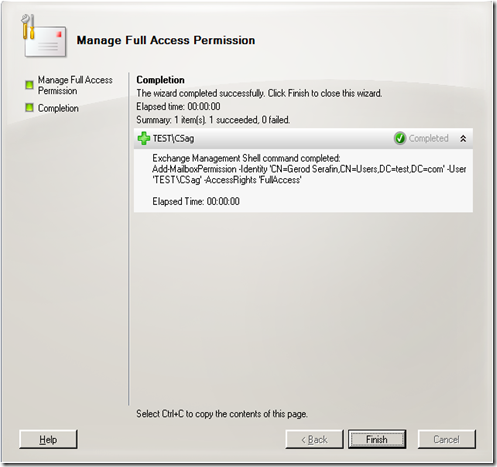
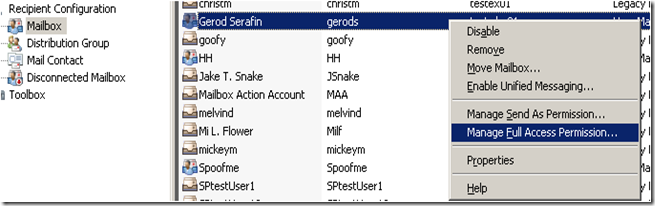
In Exchange 2007, you use the Exchange Management Console or the Exchange Management Shell to configure mailbox permissions. Using the MEC we just right click on the mailbox and choose “Manage Full Access Permission”.
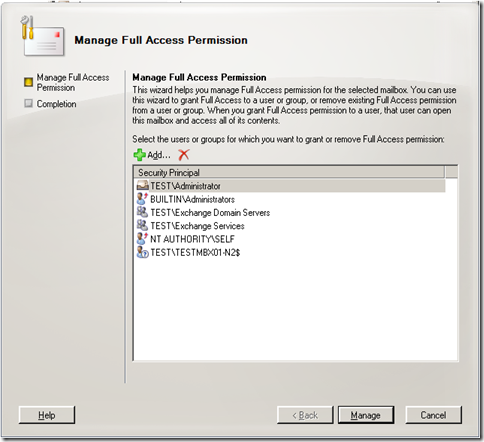
Add…
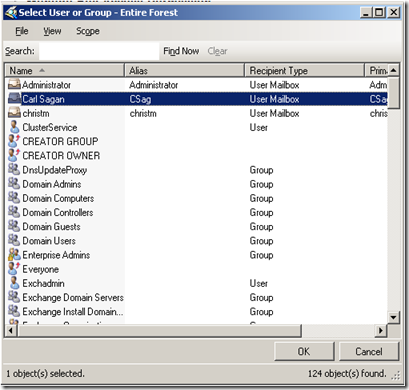
I’ll give Carl Sagan access to my mailbox.
And there is the cmdlet you would run from the shell
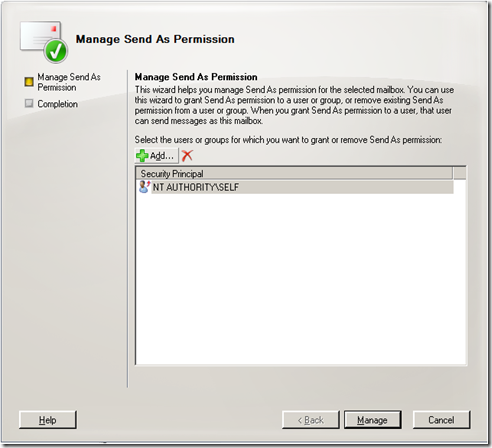
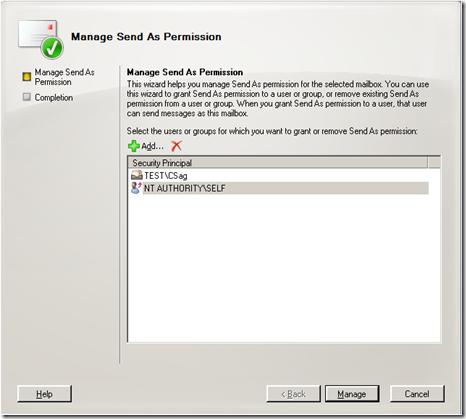
But, what if I didn’t want to give full mailbox permissions. What if I just wanted to give Send As permissions? In that case you would just click on “Manage Send As Permission”.
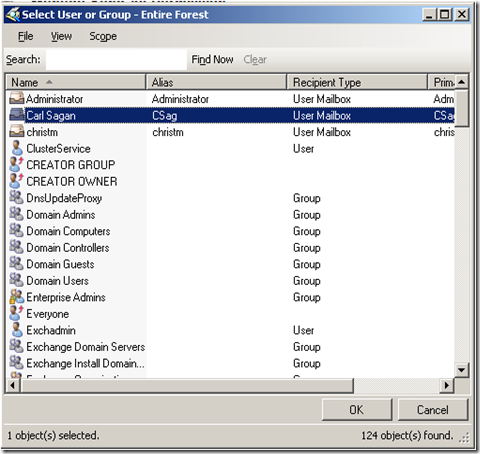
As you can see by default, only I (Self) have the right to send as myself. I click on “Add”.
I choose Carl again.
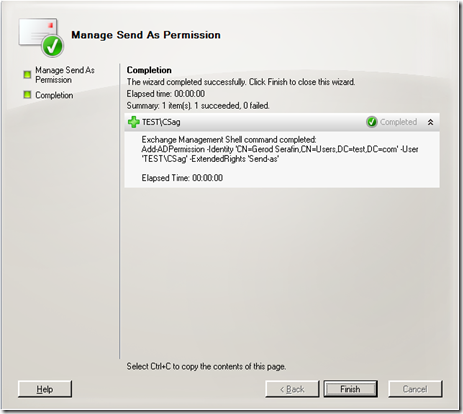
Now Carl can send as me.
And there is the cmdlet you would run from the shell.
Query-Based \ Dynamic Distribution Groups
In Exchange 2003, you created Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) queries to filter recipients using the Active Directory Users and Computers (ADU&C).
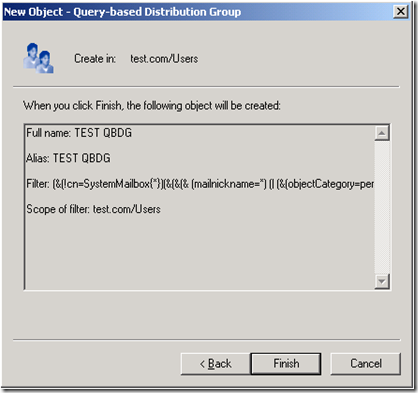
When finished creating a QBDG you can see the LDAP query.
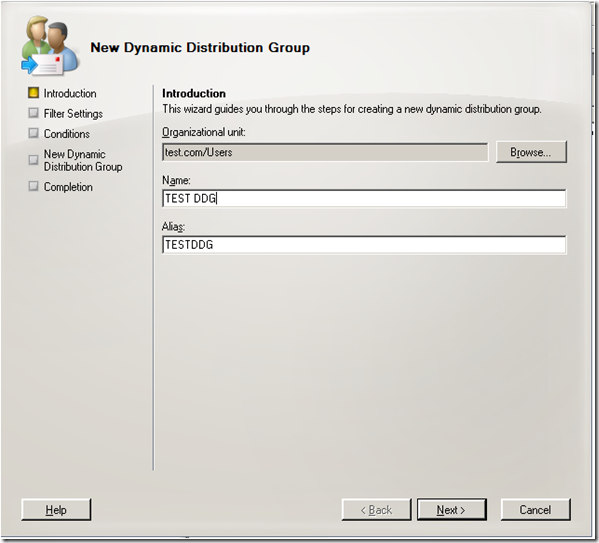
The name has changed in Exchange 2007 as well as the tool that you use to create it. It is now called a Dynamic Distribution Group and you create it using the Exchange Management Console at the Recipient Configuration level.
Lets walk through the wizard… Here we put in the standard details.
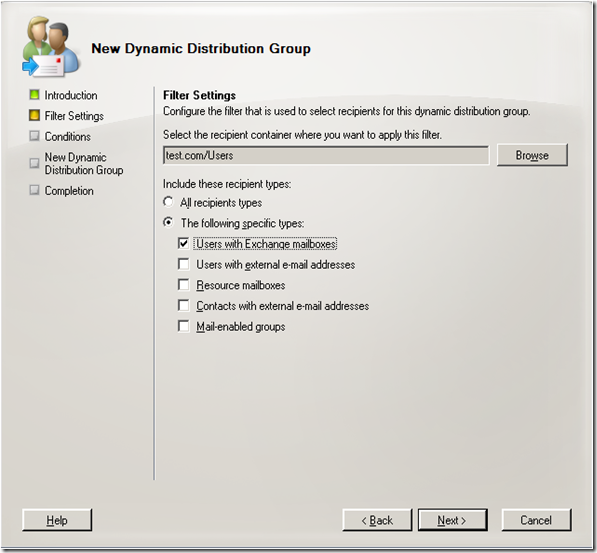
You have the option to set the scope to an OU here if you would like.
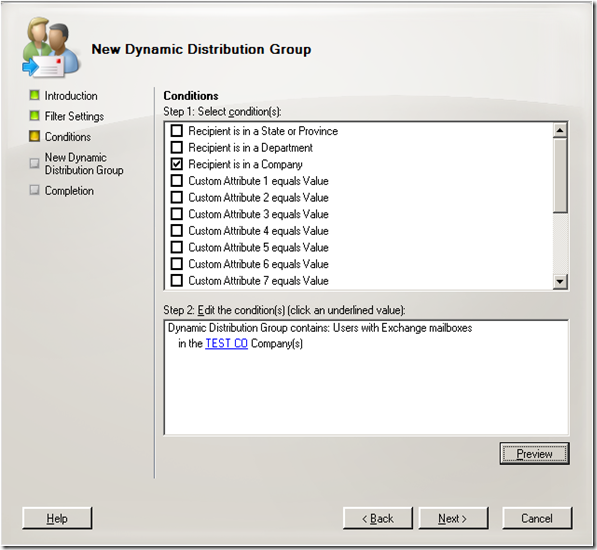
Here you can set more conditions like Company name.
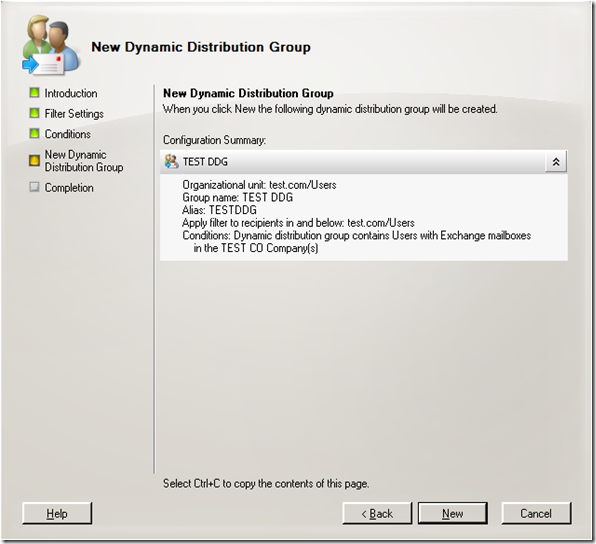
Here is the summary.
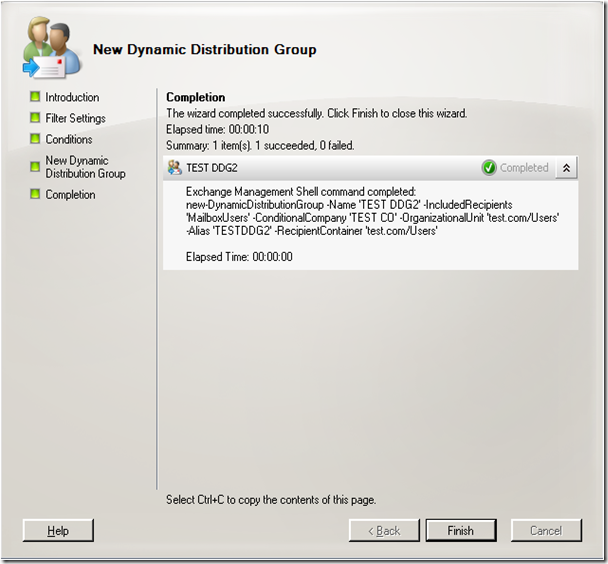
And the final part of the wizard shows the cmdlet to run again.
But, what if the wizard doesn’t have all of the options that you want to filter on? In that case you would need to us OPATH syntax for a custom filter. What is OPATH? It is the basis for the filtering syntax used by PowerShell. It has been around for some time and was actually used before Exchange 2007, but it looks like we are the heaviest users of it now. You can find more about it at https://msexchangeteam.com/archive/2007/01/10/432143.aspx.
OPATH allows you to use –and, –or, –not, –eq (Equals), –ne (Not Equals), –lt (Less Than), –gt (Greater Than), like, and –notlike in your filters. In some cases you can also use wildcards.
If you have an LDAP filter that you would like to try to convert to an OPATH filter for Exchange 2007, you may find that the script found at this blog may be helpful.
Next: Part 16 – Administrative Tasks: Resource Scheduling
Comments
Anonymous
January 01, 2003
What's the difference between the Microsoft Exchange Server Unified Messaging (UM) role and MicrosoftAnonymous
January 01, 2003
To return to part 1 click here   Administrative Tasks: Creating Mailboxes and Exmerge   Creating