SPN and UPN uniqueness
Author: Justin Turner, Senior Support Escalation Engineer with the Windows group
Note
This content is written by a Microsoft customer support engineer, and is intended for experienced administrators and systems architects who are looking for deeper technical explanations of features and solutions in Windows Server 2012 R2 than topics on TechNet usually provide. However, it has not undergone the same editing passes, so some of the language may seem less polished than what is typically found on TechNet.
Overview
Domain Controllers running Windows Server 2012 R2 block the creation of duplicate service principal names (SPN) and user principal names (UPN). This includes if the restoration or reanimation of a deleted object or the renaming of an object would result in a duplicate.
Background
Duplicate Service Principal Names (SPN) commonly occur and result in authentication failures and may lead to excessive LSASS CPU utilization. There's no in-box method to block the addition of a duplicate SPN or UPN. *
Duplicate UPN values break synchronization between on-premises AD and Office 365.
*Setspn.exe is commonly used to create new SPNs, and functionally was built into the version released with Windows Server 2008 that adds a check for duplicates.
Table SEQ Table \* ARABIC 1: UPN and SPN uniqueness
| Feature | Comment |
|---|---|
| UPN uniqueness | Duplicate UPNs break synchronization of on-premises AD accounts with Microsoft Entra ID-based services such as Office 365. |
| SPN uniqueness | Kerberos requires SPNs for mutual authentication. Duplicate SPNs result in authentication failures. |
For more information about uniqueness requirements for UPNs and SPNs, see Uniqueness Constraints.
Symptoms
Error codes 8467 or 8468 or their hex, symbolic or string equivalents are logged in various on-screen dialogues and in event ID 2974 in the Directory Services event log. The attempt to create a duplicate UPN or SPN is blocked only under the following circumstances:
- The write is processed by a Windows Server 2012 R2 DC
Table SEQ Table \* ARABIC 2: UPN and SPN uniqueness error codes
| Decimal | Hex | Symbolic | String |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8647 | 21C7 | ERROR_DS_SPN_VALUE_NOT_UNIQUE_IN_FOREST | The operation failed because SPN value provided for addition/modification isn't unique forest-wide. |
| 8648 | 21C8 | ERROR_DS_UPN_VALUE_NOT_UNIQUE_IN_FOREST | The operation failed because UPN value provided for addition/modification isn't unique forest-wide. |
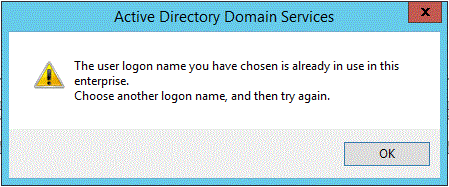
New user creation fails if UPN isn't unique
DSA.msc
The user logon name you have chosen is already in use in this enterprise. Choose another logon name, and then try again.
Modify an existing account:
The specified user logon name already exists in the enterprise. Specify a new one, either by changing the prefix or selecting a different suffix from the list.
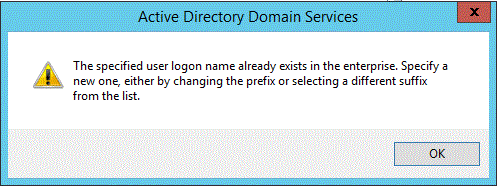
Active Directory Administrative Center (DSAC.exe)
An attempt to create a new user in Active Directory Administrative Center with a UPN that already exists returns the following error.

Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 1 error displayed in AD Administrative Center when new user creation fails due to duplicate UPN
Event 2974 Source: ActiveDirectory_DomainService
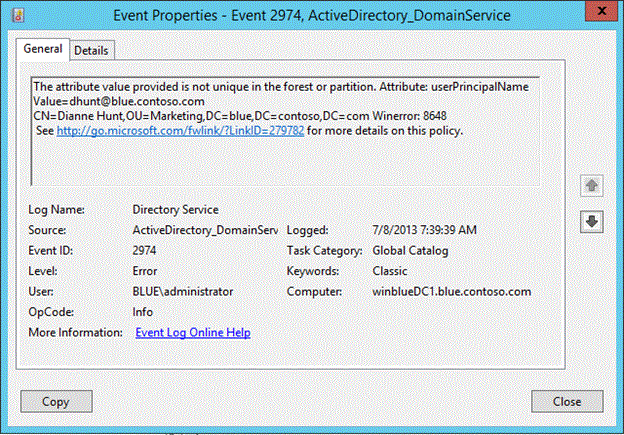
Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 2 Event ID 2974 with error 8648
The event 2974 lists the value that was blocked and a list of one or more objects (up to 10) that already contain that value. In the following figure, you can see that UPN attribute value dhunt@blue.contoso.com already exists on four other objects. Since this is a new feature in Windows Server 2012 R2, accidental creation of duplicate UPN and SPNs in a mixed environment will still occur when down-level DCs process the write attempt.
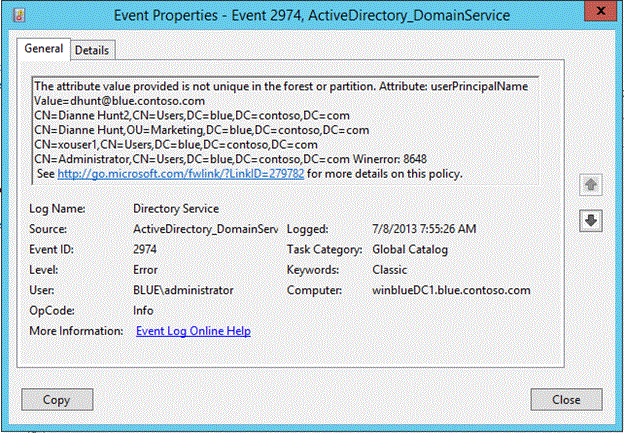
Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 3 Event 2974 showing all objects containing the duplicate UPN
Tip
Review event ID 2974s regularly to:
- identify attempts to create duplicate UPN or SPNs
- identify objects that already contain duplicates
8648 = "The operation failed because UPN value provided for addition/modification isn't unique forest-wide."
SetSPN:
Setspn.exe has had duplicate SPN detection built-in to it since the Windows Server 2008 release when using the "-S" option. You can bypass the duplicate SPN detection by using the "-A" option however. Creation of a duplicate SPN is blocked when targeting a Windows Server 2012 R2 DC using SetSPN with the -A option. The error message displayed is the same as the one displayed when using the -S option: "Duplicate SPN found, aborting operation!"
ADSIEDIT:
Operation failed. Error code: 0x21c8
The operation failed because UPN value provided for addition/modification is not unique forest-wide.
000021C8: AtrErr: DSID-03200BBA, #1: 0: 000021C8: DSID-03200BBA, problem 1005 (CONSTRAINT_ATT_TYPE), data 0, Att 90290 (userPrincipalName)
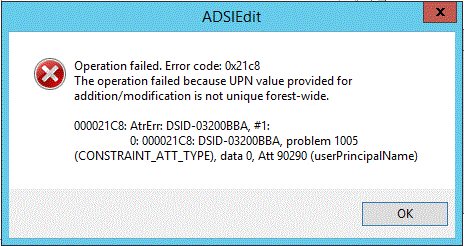
Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 4 Error message displayed in ADSIEdit when addition of duplicate UPN is blocked
Windows PowerShell
Windows Server 2012 R2:
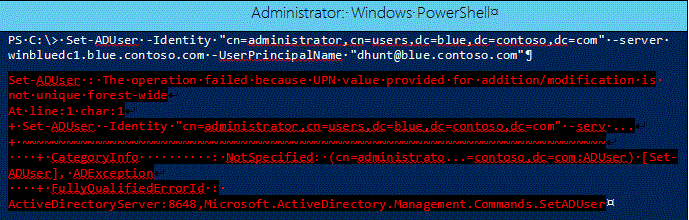
PowerShell running from Server 2012 targeting a Windows Server 2012 R2 DC:
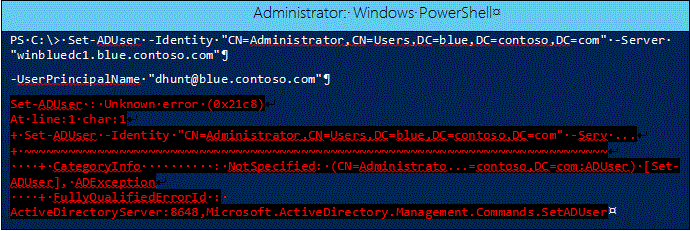
DSAC.exe running on Windows Server 2012 targeting a Windows Server 2012 R2 DC:

Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 5 DSAC user creation error on non-Windows Server 2012 R2 while targeting Windows Server 2012 R2 DC

Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 6 DSAC user modification error on non-Windows Server 2012 R2 while targeting Windows Server 2012 R2 DC
Restore of an object that would result in a duplicate UPN fails:
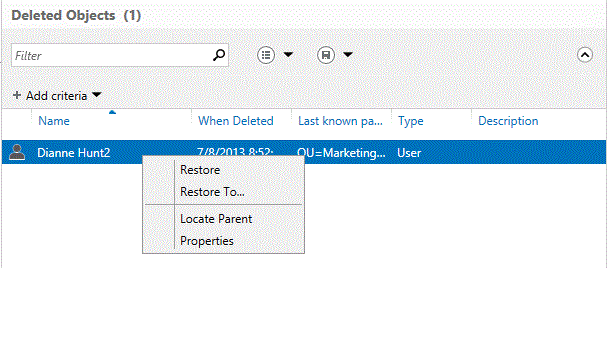
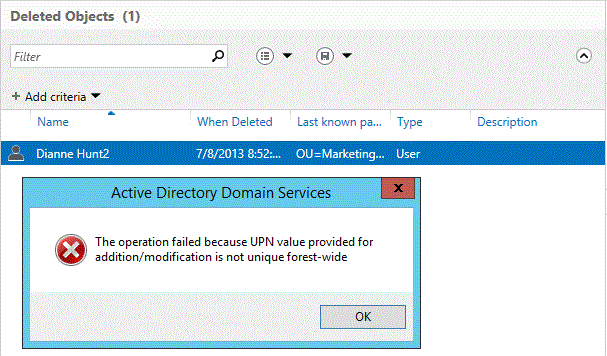
No event is logged when an object fails to restore because of a duplicate UPN / SPN.
The UPN of the object must be unique in order for it to be restored.
Identify the UPN that exists on the object in the Recycle Bin
Identify all objects that have the same value
Remove the duplicate UPN(s)
Identify the conflicting UPN on the deleted objectUsing repadmin.exe
Repadmin /showattr DCName "DN of deleted objects container" /subtree /filter:"(msDS-LastKnownRDN=<NAME>)" /deleted /atts:userprincipalname
repadmin /showattr DCName "CN=Deleted Objects,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com" /subtree /filter:"(msDS-LastKnownRDN=Dianne Hunt2)" /deleted /atts:userprincipalname
C:\>repadmin /showattr winbluedc1 "cn=deleted objects,dc=blue,dc=contoso,dc=com" /subtree /filter:"(msds-lastknownrdn=Dianne Hunt2)" /deleted /atts:userprincipalname
DN: CN=Dianne Hunt2\0ADEL:dd3ab8a4-3005-4f2f-814f-d6fc54a1a1c0,CN=Deleted Object
s,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
1> userPrincipalName: dhunt@blue.contoso.com
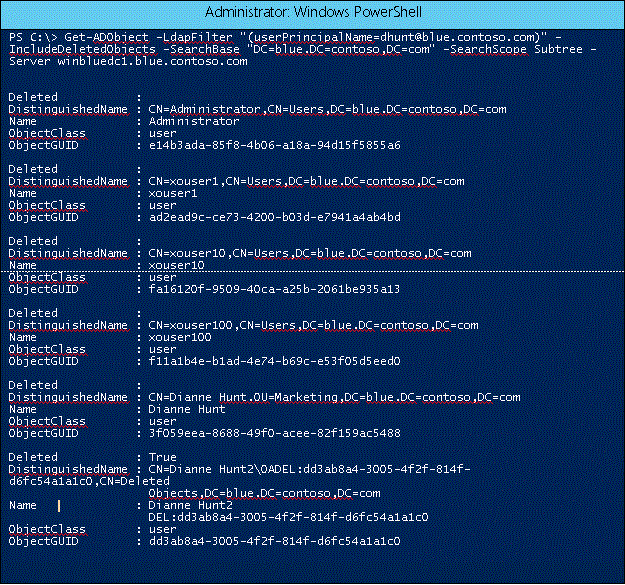
To identify all objects with the same UPN:Using Repadmin.exe
repadmin /showattr WinBlueDC1 "DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com" /subtree /filter:"(userPrincipalName=dhunt@blue.contoso.com)" /deleted /atts:DN
C:\>repadmin /showattr winbluedc1 "dc=blue,dc=contoso,dc=com" /subtree /filter:"(userPrincipalName=dhunt@blue.contoso.com)" /deleted /atts:DN
DN: CN=Administrator,CN=Users,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
DN: CN=xouser1,CN=Users,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
DN: CN=xouser10,CN=Users,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
DN: CN=xouser100,CN=Users,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
DN: CN=Dianne Hunt,OU=Marketing,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
DN: CN=Dianne Hunt2\0ADEL:dd3ab8a4-3005-4f2f-814f-d6fc54a1a1c0,CN=Deleted Objects,DC=blue,DC=contoso,DC=com
Tip
The previously undocumented /deleted parameter in repadmin.exe is used to include deleted objects in the result set
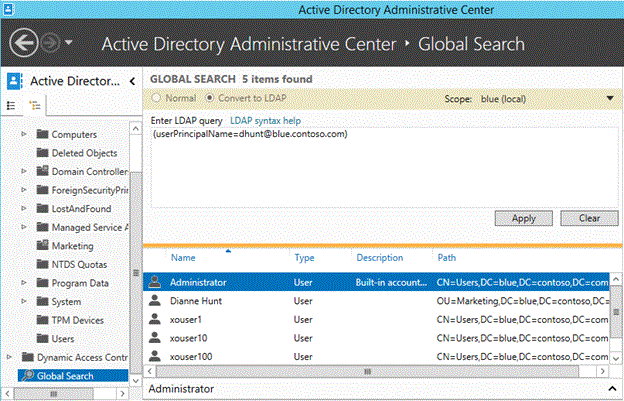
Using Global Search
Open Active Directory Administrative Center and navigate to Global Search
Select the Convert to LDAP radio button
Type (userPrincipalName=ConflictingUPN)
- Replace ConflictingUPN with the actual UPN that is in conflict
Select Apply
Using Windows PowerShell
Get-ADObject -LdapFilter "(userPrincipalName=dhunt@blue.contoso.com)" -IncludeDeletedObjects -SearchBase "DC=blue,DC=Contoso,DC=com" -SearchScope Subtree -Server winbluedc1.blue.contoso.com
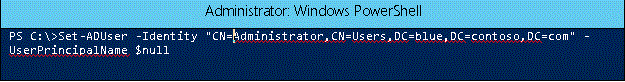
If the object needs to be restored, you'll need remove the duplicate UPNs from the other objects. For only one object, it's simple enough to use ADSIEdit to remove the duplicate. If there are multiple objects with duplicates, then Windows PowerShell might be the better tool to use.
To null out the UserPrincipalName attribute using Windows PowerShell:
Note
The userPrincipalName attribute is single-valued attribute, so this procedure will only remove the duplicate UPN.
Duplicate SPN
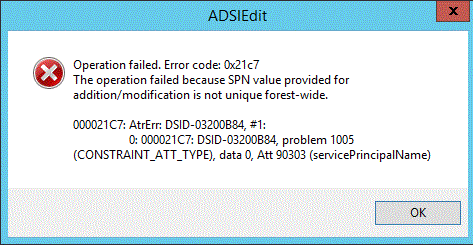
Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 8 Error message displayed in ADSIEdit when addition of duplicate SPN is blocked
Logged in the Directory Services event log is an ActiveDirectory_DomainService event ID 2974.
Operation failed. Error code: 0x21c7
The operation failed
The attribute value provided is not unique in the forest or partition. Attribute:
servicePrincipalName Value=<SPN>
<Object DN> Winerror: 8467
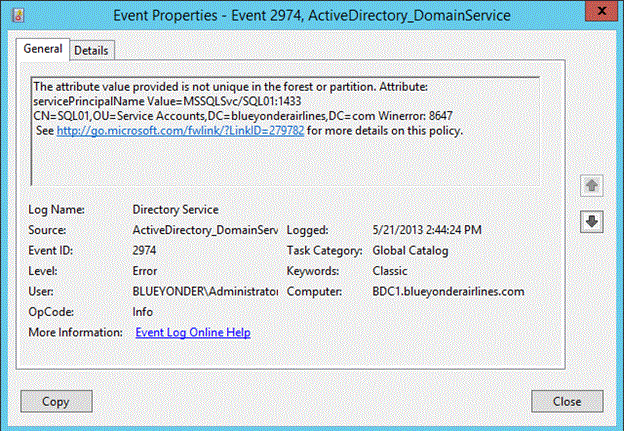
Figure SEQ Figure \* ARABIC 9 Error logged when creation of duplicate SPN is blocked
Workflow
If DC == GC
No offbox call required, query can be satisfied locally
UPN case
Query local forest-wide UPN index for supplied UPN (userPrincipalName; a global index)
If entries returned == 0 -> write proceeds
If entries returned !=0 -> write fails
Event logged
Also returns extended error:
8648:
ERROR_DS_UPN_VALUE_NOT_UNIQUE_IN_FOREST
SPN case
Query local forest-wide SPN index for supplied SPN (servicePrincipalName; a global index)
If entries returned == 0 -> write proceeds
If entries returned !=0 -> write fails
Event logged
Also returns extended error:
8647:
ERROR_DS_SPN_VALUE_NOT_UNIQUE_IN_FOREST
If DC != GC
Offbox call desirable but not critical, that is, this is a best-effort uniqueness check
Check proceeds against local DIT only if GC can't be located
Event logged to indicate such
UPN case
Submit LDAP query against closest GC ? query GC's forest-wide UPN index for supplied UPN (userPrincipalName; a global index)
If entries returned == 0 -> write proceeds
If entries returned !=0 -> write fails
Event logged
Also returns extended error:
8648:
ERROR_DS_UPN_VALUE_NOT_UNIQUE_IN_FOREST
SPN case
Submit LDAP query against closest GC ? query GC's forest-wide SPN index for supplied SPN (servicePrincipalName; a global index)
If entries returned == 0 -> write proceeds
If entries returned !=0 -> write fails
Event logged
Also returns extended error:
8647:
ERROR_DS_SPN_VALUE_NOT_UNIQUE_IN_FOREST
When deleted objects are reanimated, SPN or UPN values present are checked for uniqueness. If a duplicate is found, the request fails.
For certain attribute changes like DNS Host Name, SAM Account Name etc., when the modification is made, SPNs are updated accordingly. In the process, the obsolete SPNs are deleted and new SPNs are constructed and added to the database. The requisite attribute modifications against which this path is triggered are:
ATT_DNS_HOST_NAME
ATT_MS_DS_ADDITIONAL_DNS_HOST_NAME
ATT_SAM_ACCOUNT_NAME
ATT_MS_DS_ADDITIONAL_SAM_ACCOUNT_NAME
ATT_SERVER_REFERENCE_BL
ATT_USER_ACCOUNT_CONTROL
If any of the new SPN value is a duplicate, we fail the modification. Of the above list, the important attributes are ATT_DNS_HOST_NAME (Machine name) and ATT_SAM_ACCOUNT_NAME (SAM Account Name).
Try This: Exploring SPN and UPN uniqueness
This is the first of several "Try This" activities in the module. There isn't a separate lab guide for this module. The Try This activities are free-form activities that allow you explore the lesson material in the lab environment. You have the option of following the prompt or going off script and come up with your own activity.
Note
- This is the first of several "Try This" activities.
- There is not a separate lab guide for this module.
- The Try This activities are essentially free-form activities that allow you explore the lesson material in the lab environment.
- You have the option of following the prompt or going off script and come up with your own activity.
- While not all sections have a Try This prompt, you are still encouraged to explore the lesson content in the lab where appropriate.
Experiment with SPN and UPN uniqueness. Follow these prompts, or complete your own.
Create new users with UPN
Create accounts with SPNs
Either create a new user with a UPN already previously defined or change an existing account's UPN. Do the same for an SPN on another account
Populate an existing user account with a UPN already in use
- Using PowerShell, ADSIEDIT, or Active Directory Administrative Center (DSAC.exe)
Populate an existing account with an SPN already in use
- Using Windows PowerShell, ADSIEDIT, or SetSPN
Observe the errors
Optionally
Verify with the classroom instructor that it's ok to enable the AD Recycle Bin in Active Directory Administrative Center. If so, move on to the next step.
Populate the UPN on a user account
Delete the account
Populate a different account with the same UPN as the deleted account
Attempt to use the Recycle Bin GUI to restore the account
Imagine you have been presented with the error you see in the previous step. (and don't have a history of the steps you just performed) Your goal is to complete the restore of the account. See the workbook, for example, steps.