Thread Synchronization and TDR
The following figure shows how thread synchronization works for the kernel-mode display miniport driver (KMD) in the WDDM.
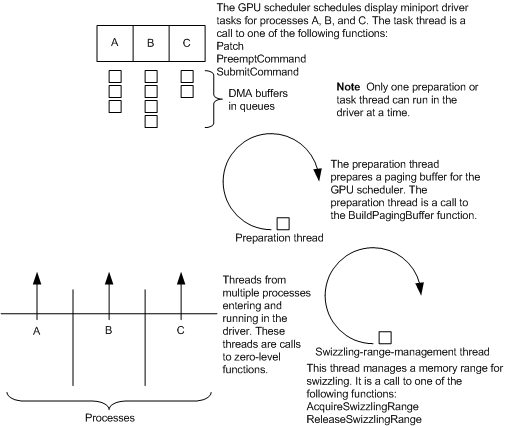
If a hardware timeout occurs, the system initiates the Timeout Detection and Recovery (TDR) process. The GPU scheduler calls the driver's DxgkDdiResetFromTimeout function, which resets the GPU:
- DxgkDdiResetFromTimeout is called synchronously with any other KMD function, except for the runtime power management functions DxgkDdiSetPowerComponentFState and DxgkDdiPowerRuntimeControlRequest. That is, the OS guarantees that no other thread runs in the driver while the DxgkDdiResetFromTimeout thread runs.
- The OS also guarantees that applications can't access the frame buffer during the call to DxgkDdiResetFromTimeout. Therefore, the driver can reset a memory controller phase locked loop (PLL) and so on.
While the recovery thread executes DxgkDdiResetFromTimeout, interrupts and deferred procedure calls (DPCs) can continue to be called. The KeSynchronizeExecution function can be used to synchronize portions of the reset procedure with device interrupts.
After the driver returns from DxgkDdiResetFromTimeout, most driver functions can again be called, and the OS starts to clean up resources that are no longer required. During the cleanup period, the following driver functions are called for the indicated reasons:
The driver is called to notify about an allocation being evicted.
For example, if the allocation was paged in a memory segment, the driver's DxgkDdiBuildPagingBuffer function is called with the Operation member of the DXGKARG_BUILDPAGINGBUFFER structure set to DXGK_OPERATION_TRANSFER and with the Transfer.Size member set to zero to inform the driver about the eviction. No content transfer is involved because the content was lost during the reset.
If the allocation was paged in an aperture segment, the driver's DxgkDdiBuildPagingBuffer function is called with the Operation member of DXGKARG_BUILDPAGINGBUFFER set to DXGK_OPERATION_UNMAP_APERTURE_SEGMENT to inform the driver to unmap the allocation from the aperture.
The driver's DxgkDdiReleaseSwizzlingRange function is called to release an unswizzling aperture and segment aperture ranges.
The driver shouldn't access the GPU during the preceding calls unless absolutely necessary.
After the cleanup period is over, the OS calls the driver's DxgkDdiRestartFromTimeout function to inform the driver that cleanup is complete and that the OS will resume using the adapter for rendering.