Troubleshoot SNAT port exhaustion on Azure Kubernetes Service nodes
This article helps you find and troubleshoot Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) nodes that experience Source Network Address Translation (SNAT) port exhaustion.
Note
- To troubleshoot SNAT port exhaustion on AKS nodes in an AKS cluster running Kubernetes jobs, perform the following steps only when the jobs are actively running on the AKS nodes.
- To learn more about SNAT ports and their allocation per virtual machine, see What SNAT ports are.
Step 1: Locate the node that experiences SNAT port exhaustion
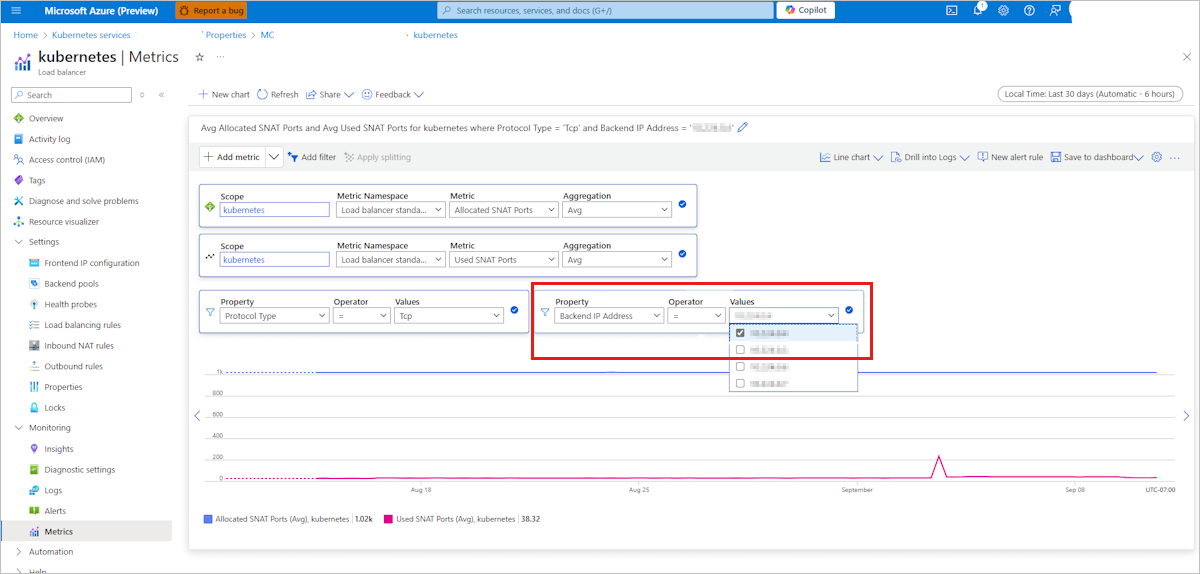
Get the IP address of the AKS node that experiences active SNAT port exhaustion from the Azure portal.
Locate the default Kubernetes load balancer by navigating to your AKS cluster's resource group.
Locate the AKS node that's experiencing SNAT port exhaustion by checking SNAT port usage and allocation on the load balancer metrics page. The Values drop-down list shows node IP addresses.
Connect to your AKS cluster and use the node IP address to get the node name by running the following
kubectlcommand:kubectl get nodes -o wide | grep <node IP>
Step 2: Locate the Linux pod that has high outbound connections
Note
- Tcptracer is one of the BPF Compiler Collection (BCC) tools that are pre-installed on Linux nodes. It allows you to trace TCP established connections (
connect(),accept(), andclose()). You can use it to find high outbound connections from the source IP address and network namespace (netns) of a pod. - To access the BCC tools, use kubectl node-shell only.
- All the following commands in this section are run as the root user on a Linux node that has the BCC tools installed.
On the Linux node that experiences SNAT port exhaustion, install kubectl node-shell:
curl -LO https://github.com/kvaps/kubectl-node-shell/raw/master/kubectl-node_shell chmod +x ./kubectl-node_shell sudo mv ./kubectl-node_shell /usr/local/bin/kubectl-node_shellUse SSH to connect to the node that experiences SNAT port exhaustion and use
tcptracerto trace TCP established connections:kubectl node-shell <node name> cd /usr/share/bcc/tools /usr/share/bcc/tools# python3 tcptracer -t4vHere's a command output example:
Tracing TCP established connections. Ctrl-C to end. TIME(ns) TYPE PID COMM IP SADDR DADDR SPORT DPORT NETNS 0 connect 18627 curl 4 1.2.3.4 5.6.7.8 53746 80 4026532785 3xxx9 close 18627 curl 4 1.2.3.4 5.6.7.8 53746 80 4026532785 1xxxx4 connect 18629 curl 4 1.2.3.4 9.10.11.12 35686 80 4026532785 2xxxx9 close 18629 curl 4 1.2.3.4 9.10.11.12 35686 80 4026532785 4xxxx5 connect 18631 curl 4 1.2.3.4 9.10.11.12 35688 80 4026532785 4xxxx8 close 18631 curl 4 1.2.3.4 9.10.11.12 35688 80 4026532785 7xxxx3 connect 18633 curl 4 1.2.3.4 13.14.15.16 35690 80 4026532785 9xxxx7 close 18633 curl 4 1.2.3.4 13.14.15.16 35690 80 4026532785Write the previous command output to a log file, and then sort the output to review a list of high connections:
python3 tcptracer -t4v > log head -n +2 log | tail -n 1 | awk '{print "Count",$6,$10}'; awk '{print $6,$10}' log | sort | uniq -c | sort -nrk 1 | column -tHere's a command output example:
Count SADDR NETNS 387 1.2.3.4 4026532785 8 11.22.33.44 4026532184 8 55.66.77.88 4026531992Map the IP address with the most connections from the previous output to a pod. If it doesn't work, you can continue.
Note the
SADDRorNETNSvalue with the most connections from the previous output, and then run the following lsns command to map it to a PID. Lsns is a Linux tool that lists namespaces and maps namespaces to PIDs in the Linux process tree.lsns -t netHere's a command output example:
NS TYPE NPROCS PID USER COMMAND 4026532785 net 3 19832 root bashMap the previous PID to a containerd process by using pstree. Pstree is a Linux tool that lists processes in a tree format for readability.
pstree -aps 19832Here's a command output example:
systemd,1 `-containerd-shim,20946 -namespace k8s.io -id 2xxxf...Note the first five characters of the containerd
-idin the command output. It will be used in step 7.Map the previous containerd
-idvalue to a POD ID by using crictl. Crictl provides a CLI for CRI-compatible container runtimes.crictl ps -aHere's a command output example:
CONTAINER IMAGE CREATED STATE NAME ATTEMPT POD ID POD 6b5xxxxb fbxxxxx1 6 hours ago Running ubuntu 0 2xxxxxxxxf nginxUse the first five characters of the previous containerd
-idvalue to match a POD ID.Get all pods running on the node and use the previous POD ID to match the pod that has high outbound connections from the command output:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces -o wide --field-selector spec.nodeName=<nodename>
Step 3: Find all outbound network connections made by the application
Execute into the pod that's identified as having high outbound connections in Step 2 by using one of the following commands:
-
kubectl exec -it <pod name> -n <namespace> /bin/bash -
kubectl exec -it <pod name> -n <namespace> /bin/sh
-
Install the netstat command-line tool in the pod by running the following command. Netstat is a network troubleshooting tool for admins only.
On Debian, Ubuntu, or Linux Mint
apt update apt install net-toolsOn RHEL, CentOS, Fedora, AlmaLinux, or Rocky Linux
yum update yum install net-toolsOn Gentoo Linux
emerge -a sys-apps/net-toolsOn Alpine Linux
apk add net-toolsOn Arch Linux
pacman -S net-toolsOn OpenSUSE
zypper install net-tools
Once netstat is installed in the pod, run the following command:
netstat -ptn | grep -i establishedHere's a command output example:
tcp 0 0 10.x.x.x:xxxx 20.x.x.x:443 ESTABLISHED xxxxx3/telnet
In the command output, the local address is the pod's IP address, and the foreign address is the IP to which the application connects. The public IP connections in the ESTABLISHED state are the connections that utilize SNAT. Ensure that you count only the connections in the ESTABLISHED state to public IP addresses and ignore any connections in the ESTABLISHED state to private IP addresses.
Repeat the steps in this section for all other pods running on the node. The pod that has the most connections in the ESTABLISHED state to public IP addresses hosts the application that causes SNAT port exhaustion on the node. Work with your application developers to tune the application for improved network performance using the recommendations mentioned in Design connection-efficient applications. After implementing the recommendations, verify that you see less SNAT port exhaustion.
Contact us for help
If you have questions or need help, create a support request, or ask Azure community support. You can also submit product feedback to Azure feedback community.