Implement and manage user risk policy
There are two risk policies that can be enabled in the directory:
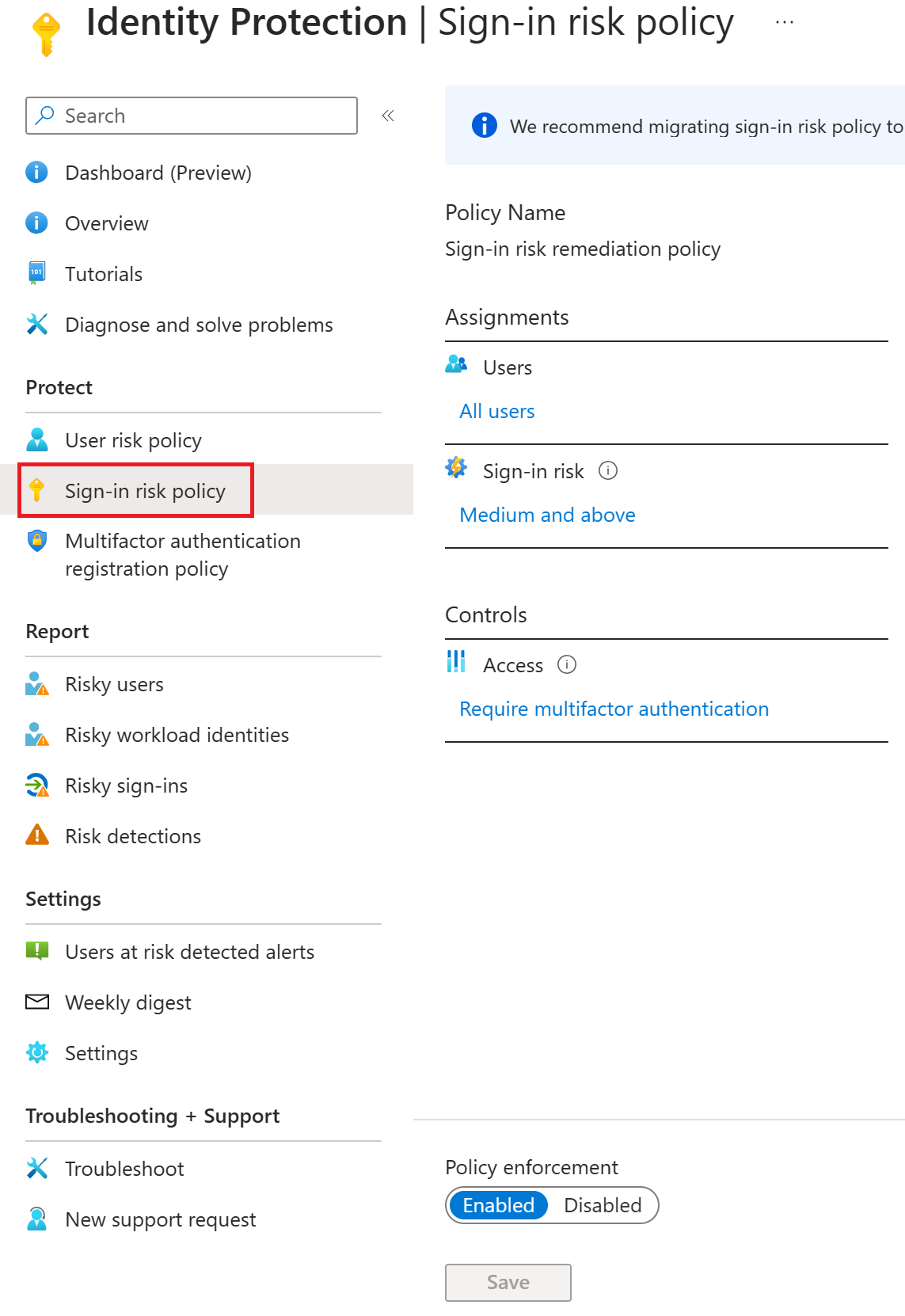
Sign-in risk policy: The sign-in risk policy detects suspicious actions that come along with the sign-in. It's focused on the sign-in activity itself and analyzes the probability that the sign-in was performed by some other than the user.
User risk policy: The user risk policy detects the probability that a user account has been compromised by detecting risk events that are atypical of a user's behavior.
Both policies work to automate the response to risk detections in your environment and allow users to self-remediate when risk is detected.
Watch the video
In this video, learn how to deploy Microsoft Entra Identity Protection by configuring risk-based policies (user risk and sign-in risk) in your organization. You also learn best practices on how to gradually roll out these policies and MFA registration in your organization.
Prerequisites
If your organization wants to allow users to self-remediate when risks are detected, users must be registered for both self-service password reset and multifactor authentication. We recommend enabling the combined security information registration experience. Allowing users to self-remediate gets them back to a productive state more quickly without requiring administrator intervention. Administrators can still see these events and investigate them after the fact.
Choosing acceptable risk levels
Organizations must decide the level of risk they're willing to accept, balancing user experience and security posture.
Microsoft's recommendation is to set the user risk policy threshold to High and the sign-in risk policy to Medium and higher.
Choosing a High threshold reduces the number of times a policy is triggered and minimizes the challenge to users. However, it excludes Low and Medium risk detections from the policy, which does not block an attacker from exploiting a compromised identity. Selecting a Low threshold introduces extra user interrupts but increased security posture.
Exclusions
All of the policies allow for excluding users such as your emergency access or break-glass administrator accounts. Organizations determine when they need to exclude other accounts from specific policies based on the way the accounts are used. All exclusions should be reviewed regularly to see if they're still applicable.
Configured trusted network locations are used by Identity Protection in some risk detections to reduce false positives.