Introduction
The SQL language
SQL is an acronym for Structured Query Language. SQL is used to communicate with relational databases. SQL statements are used to perform tasks such as update data in a database, or retrieve data from a database. For example, the SQL SELECT statement is used to query the database and return a set of data rows. Some common relational database management systems that use SQL include Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB, and Oracle.
There is a SQL language standard defined by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Each vendor adds their own variations and extensions.
In this module, you will learn how to:
- Understand what SQL is and how it is used
- Identify database objects in schemas
- Identify SQL statement types
- Use the SELECT statement to query tables in a database
- Work with data types
- Handle NULLs
Transact-SQL
Basic SQL statements, such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE are available no matter what relational database system you're working with. Although these SQL statements are part of the ANSI SQL standard, many database management systems also have their own extensions. These extensions provide functionality not covered by the SQL standard, and include areas such as security management and programmability. Microsoft database systems such as SQL Server, Azure SQL Database, Microsoft Fabric, and others use a dialect of SQL called Transact-SQL, or T-SQL. T-SQL includes language extensions for writing stored procedures and functions, which are application code that is stored in the database, and managing user accounts.
SQL is a Declarative language
Programming languages can be categorized as procedural or declarative. Procedural languages enable you to define a sequence of instructions that the computer follows to perform a task. Declarative languages enable you to describe the output you want, and leave the details of the steps required to produce the output to the execution engine.
SQL supports some procedural syntax, but querying data with SQL usually follows declarative semantics. You use SQL to describe the results you want, and the database engine's query processor develops a query plan to retrieve it. The query processor uses statistics about the data in the database and indexes that are defined on the tables to come up with a good query plan.
Relational data
SQL is most often (though not always) used to query data in relational databases. A relational database is one in which the data has been organized in multiple tables (technically referred to as relations), each representing a particular type of entity (such as a customer, product, or sales order). The attributes of these entities (for example, a customer's name, a product's price, or a sales order's order date) are defined as the columns, or attributes, of the table, and each row in the table represents an instance of the entity type (for example, a specific customer, product, or sales order).
The tables in the database are related to one another using key columns that uniquely identify the particular entity represented. A primary key is defined for each table, and a reference to this key is defined as a foreign key in any related table. This is easier to understand by looking at an example:
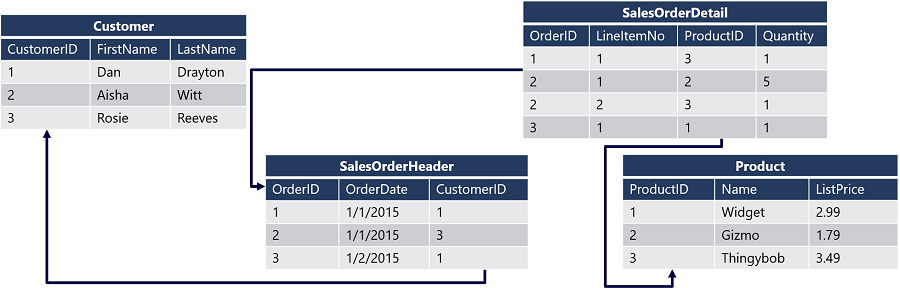
The diagram shows a relational database that contains four tables:
- Customer
- SalesOrderHeader
- SalesOrderDetail
- Product
Each customer is identified by a unique CustomerID field - this field is the primary key for the Customer table. The SalesOrderHeader table has a primary key named OrderID to identify each order, and it also includes a CustomerID foreign key that references the primary key in the Customer table so it identifies which customer is associated with each order. Data about the individual items in an order are stored in the SalesOrderDetail table, which has a composite primary key that combines the OrderID in the SalesOrderHeader table with a LineItemNo value. The combination of these values uniquely identifies a line item. The OrderID field is also used as a foreign key to indicate which order the line item belongs to, a ProductID field is used as a foreign key to the ProductID primary key of the Product table to indicate which product was ordered.
Set-based processing
Set theory is one of the mathematical foundations of the relational model of data management and is fundamental to working with relational databases. While you might be able to write queries in T-SQL without a thorough understanding of sets, you may eventually have difficulty writing some of the more complex types of statements that may be needed for optimum performance.
Without diving into the mathematics of set theory, you can think of a set as "a collection of definite, distinct objects considered as a whole." In terms applied to SQL Server databases, you can think of a set as a collection of distinct objects containing zero or more members of the same type. For example, the Customer table represents a set: specifically, the set of all customers. You will see that the results of a SELECT statement also form a set.
As you learn more about T-SQL query statements, it is important to always think of the entire set, instead of individual members. This mindset will better equip you to write set-based code, instead of thinking one row at a time. Working with sets requires thinking in terms of operations that occur "all at once" instead of one at a time.
One important feature to note about set theory is that there is no specification regarding any ordering of the members of a set. This lack of order applies to relational database tables. There is no concept of a first row, a second row, or a last row. Elements may be accessed (and retrieved) in any order. If you need to return results in a certain order, you must specify it explicitly by using an ORDER BY clause in your SELECT query.