Describe Azure Firewall
A firewall is a security device, either hardware, software, or a combination of both, that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. Its primary purpose is to establish a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the internet, to protect the internal network from malicious attacks.
Azure Firewall is a managed, cloud-based network security service that provides threat protection for your cloud workloads and resources running in Azure.
You can deploy Azure Firewall on any virtual network but the best approach is to use it on a centralized virtual network. All your other virtual and on-premises networks will then route through it. The advantage of this model is the ability to centrally exert control of network traffic for all your VNets across different subscriptions.
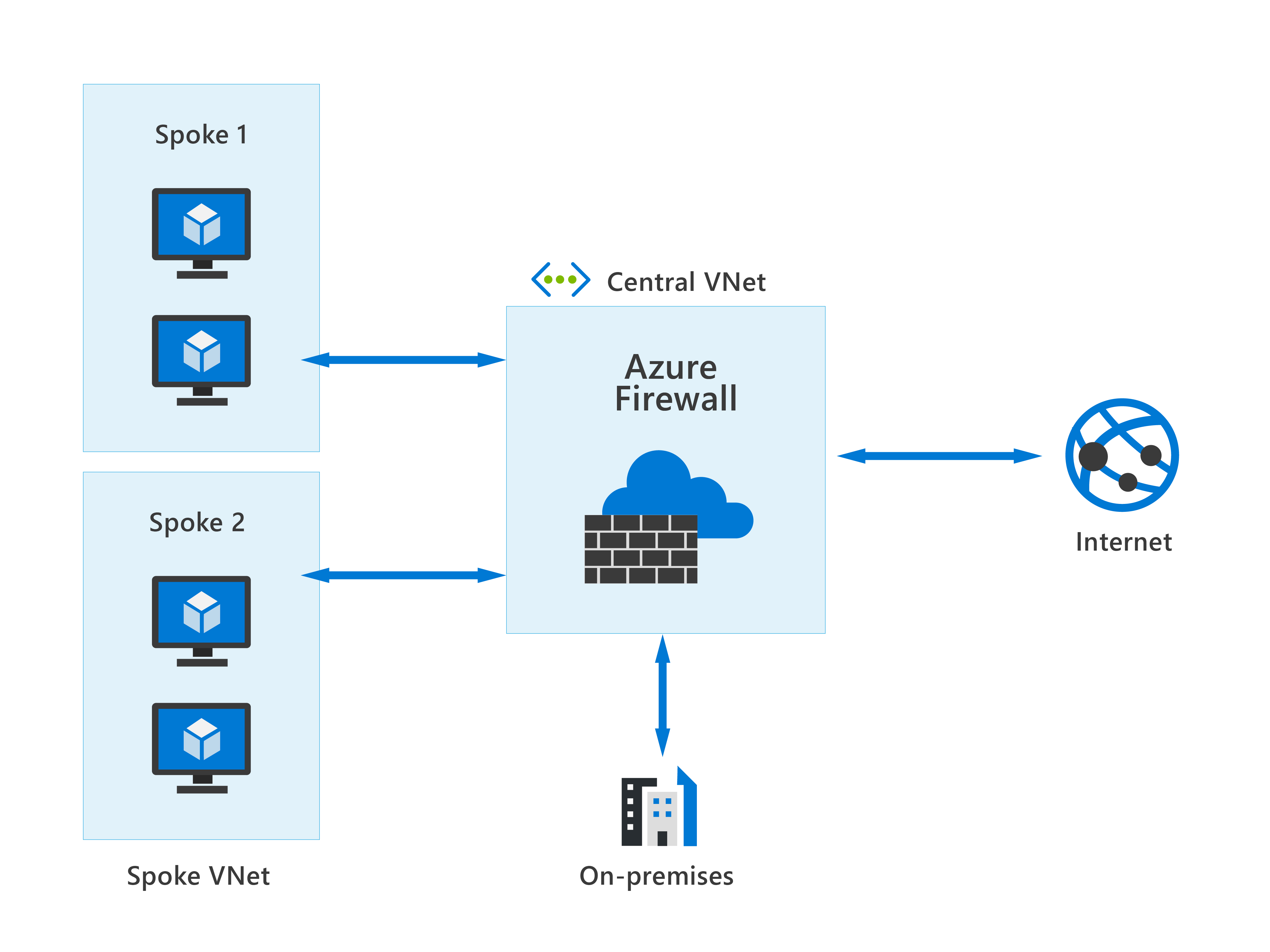
With Azure Firewall, you can scale up the usage to accommodate changing network traffic flows, so you don't need to budget for peak traffic. Network traffic is subjected to the configured firewall rules when you route it to the firewall as the subnet default gateway.
Key features of Azure Firewall
The list that follows provides a brief description of some of the basic capabilities of Azure Firewall.
Stateful Firewall: Azure Firewall is a stateful firewall, meaning it can keep track of the state of active connections and make decisions based on the context of the traffic.
Built-in high availability and availability zones: Azure Firewall has built-in high availability, meaning it's designed to ensure continuous operation and minimal downtime, even in the event of failures or high traffic loads. Azure Firewall can be configured to span multiple availability zones where each availability zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. Azure Firewall's support for availability zones ensures higher availability and resilience by distributing resources across these separate zones.
Network and application level filtering: Azure Firewall allows you to create and enforce network traffic filtering rules for both inbound and outbound traffic. You can define rules based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols. Azure Firewall can filter traffic based on the application-layer protocols such as HTTP/S. This means you can control access to fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
Source and destination network address translation (NAT): Network Address Translation is a method of remapping an IP address into another IP address to manage and secure network traffic. Azure Firewall supports source network address translation (SNAT). SNAT translates the private IP address of a network resource (the source) to an Azure public IP address. This identifies and allows traffic originating from the virtual network to internet destinations. Similarly, Azure Firewall supports destination network address translation (DNAT). With DNAT, the public IP address used to access specific services inside your network is translated and filtered to the private IP addresses of the resource on the virtual network (the destination). This allows traffic, originating from the internet, to access your private resources.
Threat intelligence: Azure Firewall integrates with Microsoft's Threat Intelligence feed to alert you about known malicious IP addresses and domains, helping to protect your network from threats. Threat intelligence-based filtering can be enabled for your firewall to alert and deny traffic from/to known malicious IP addresses and domains.
Logging and Monitoring: Azure Firewall provides logging and monitoring capabilities to help you keep track of firewall activity and diagnose issues. Logs can be sent to Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, or Event Hubs for further analysis.
Integration with Azure Services: It integrates seamlessly with other Azure services, such as Azure Virtual Networks, Azure Policy, and Azure Security Center, providing a cohesive security solution for your cloud infrastructure.
Azure Firewall is offered in three SKUs: Standard, Premium, and Basic. Detailed information of the features included for each of the available SKUs (standard, premium, and basic) is provided in the Learn more section in the summary and resources unit.
Integration with Security Copilot
Azure Firewall is integrated with Microsoft Security Copilot.
For organizations onboarded to Microsoft Security Copilot, users can experience the Copilot integration through the standalone experience.
The Azure Firewall integration helps analysts perform detailed investigations of the malicious traffic intercepted by the network intrusion detection and prevention system (available in the standard and premium Azure Firewall SKUs) and/or the threat intelligence features, using natural language questions in the Security Copilot standalone experience.
To use the Azure Firewall integration with Copilot:
- The Azure Firewalls to be used with Security Copilot must be configured with resource specific structured logs for IDPS and these logs must be sent to a Log Analytics workspace.
- The users must have role permissions to use Microsoft Security Copilot and must have the appropriate Azure role-based access control (RBAC) roles to access the Firewall and associated Log Analytics workspace.
- The Azure Firewall plugin in Security Copilot must be turned on.
Azure Firewall capabilities in Copilot are built-in prompts that you can use but you can also enter your own prompts based on the capabilities supported.
The summary and resources unit of this module provides a link to more detailed information on Azure Firewall integration in Microsoft Security Copilot.

