Creating New Platform-Specific Library Projects for NuGet
Multiplatform Library projects that target specific platforms, like iOS and Android, work best with Shared Projects.
The NuGet can contain both iOS- and Android-specific code, as well as .NET code common to both.
Multiple assemblies are created and built into a single NuGet package. NuGet standards ensure that the package can be added to all supported project types, such as Xamarin.iOS and Android projects.
Steps to Create a Cross-Platform Library NuGet
Select File > New Solution (or right click an existing solution and choose Add > New Project).
Choose Multiplatform Library from the Multiplatform > Library section:
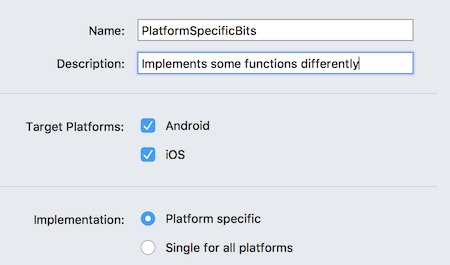
Enter a Name and Description, and choose Platform specific:
Complete the wizard. The following projects are added to the solution:
- Android Project – Android-specific code can optionally be added to this project.
- iOS Project – iOS-specific code can optionally be added to this project.
- NuGet Project – No code is added to this project. It references the other projects, and contains the metadata configuration for the NuGet package output.
- Shared Project – Common code should be added to this project, including platform-specific code inside
#ifcompiler directives.
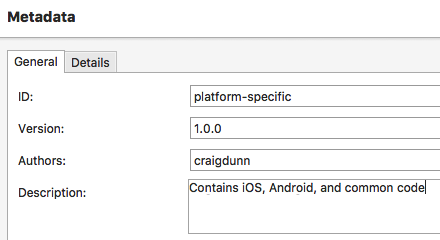
Right-click on the NuGet project and choose Options, then open the NuGet Package > Metadata section and enter the required metadata (as well as any optional metadata):
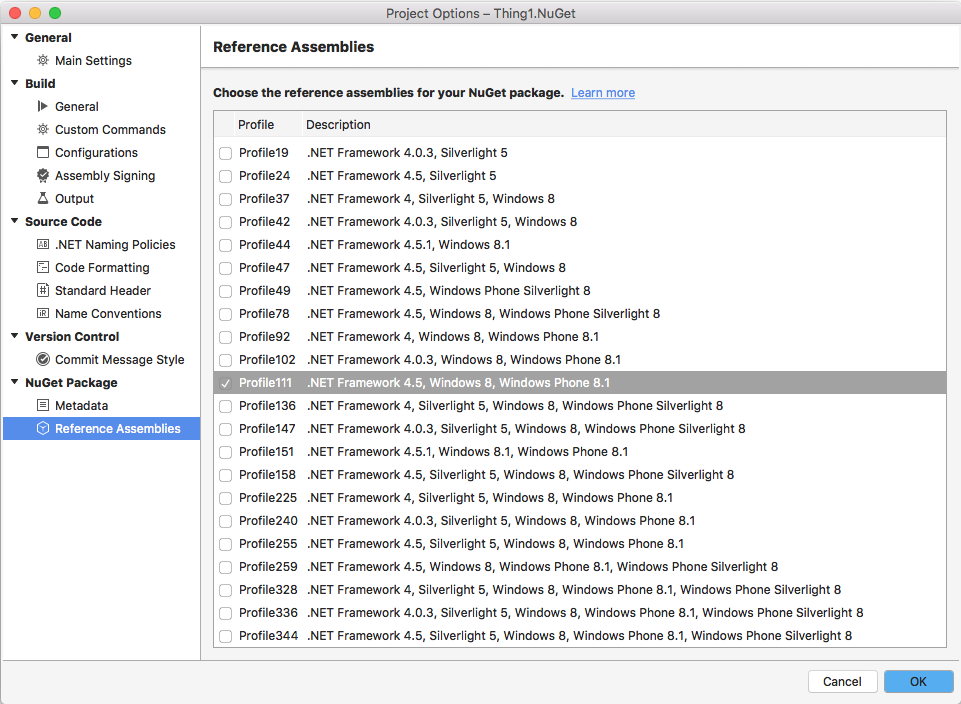
Also in the Project Options window, open the Reference Assemblies section and choose which PCL profiles the shared library will support via "bait and switch":
Note
"Bait and switch" means that the PCL assemblies will only contain the API exposed by the library (it cannot contain the platform-specific code). When the NuGet is added to a Xamarin project, shared libraries will be compiled against the PCL, but the platform-specific assemblies contain the code that is actually used by the iOS or Android project.
Right-click on the project and choose Create NuGet Package (or build or deploy the solution) and the .nupkg NuGet package file will be saved in the /bin/ folder (either Debug or Release, depending on configuration).
Verifying the Output
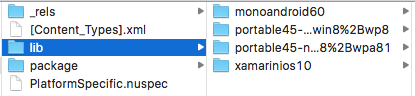
NuGet packages are also ZIP files, so it's possible to inspect the internal structure of the generated package.
This screenshot shows the contents of a platform-specific NuGet that supports iOS and Android, and had two reference assemblies selected: