Deploying the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server Components
Applies to: Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2017. See Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2018 version.
This section contains information about the deployment of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components. It is important to understand the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components environment and consider the factors that will affect the installation and configuration, such as network architecture and infrastructure, users, security, and the deployment phase.
When you deploy the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components, you get both the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client and the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Tablet client.
Network Architecture and Topology
The following illustration shows the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components environment.
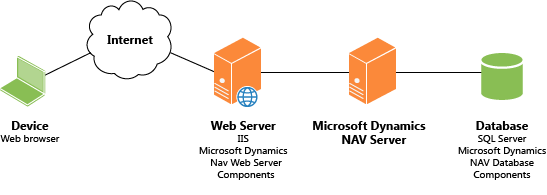
You can deploy the components on one computer or on separate computers. For example, you can install the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components on one computer and the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and SQL Server database on another computer. The topology that you choose depends on the network resources and the infrastructure of the Dynamics NAV components. The installation and configuration process is different for each scenario.
For information about the common deployment scenarios, see Deployment Scenarios for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server Components.
Important
The Dynamics NAV mobile app is not supported in a deployment scenario that uses Azure Active Directory Application Proxy.
Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server Components Installation on IIS
To deploy the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client, you install Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components on a computer that is running Internet Information Services (IIS). For more information about how to install the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components and IIS, see How to: Install the Web Server Components and How to: Install and Configure Internet Information Services for Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Client.
When you install Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components, a web server instance is added on IIS for the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client. The web server instance consists of a virtual directory and application. The following illustration shows the structure in Internet Information Services Manager. For more information about these elements in IIS, see IIS Manager UI.
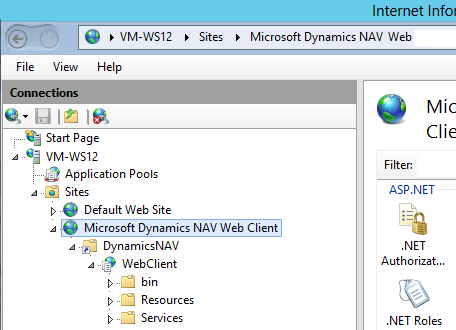
The following table includes the default settings for each element of the website structure.
Website
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2018 Web Client |
| Binding | Type: http or https (if you configure SSL on the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components) Port: Port number you assigned the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client (default 8080) |
| Application pool | DefaultAppPool |
| Application pool identity | ApplicationPoolIdentity |
| Physical path | %systemroot%\inetpub\wwwroot\NavWebApplicationContainer |
| Authentication | Windows Authentication |
Virtual directory
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Physical path | %systemroot%\inetpub\wwwroot\DynamicsNAV110 |
| Virtual path/Alias | /DynamicsNAV110 By default, this name matches the name of the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server instance that the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components connects to. |
Web application
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Application pool | Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2018 Web Client Application Pool |
| Application pool identity | ApplicationPoolIdentity |
| Physical path | %systemroot%\inetpub\wwwroot\DynamicsNAV110\WebClient Note: This folder is a symbolic link that targets the %systemroot%\Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics NAV\100\Web Client folder. |
| Virtual path/Alias | /DynamicsNAV110/WebClient |
| Protocol | http |
| Authentication | Windows Authentication, Forms authentication, Anonymous Authentication, and ASP.NET Impersonation. |
Deployment Phases
Typically, you will deploy the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client in phases, which can influence the network topology and security settings that you deploy. For example, in the development phase, you develop, test, and fine-tune the application. In this phase, you might consider deploying the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client in a single-computer scenario. When you move to the production phase, you deploy the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client in the full network infrastructure.
Security
User Authentication
Dynamics NAV supports four methods for authenticating users who try to access the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client: Windows, UserName, NavUserPassword, and AccessControlService. Windows authentication is configured by default. For more information, see Users and Credential Types and How to: Configure Authentication of Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Client Users.
Service Account for Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and Dynamics NAV Database Access
When you install Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and Dynamics NAV database components, you must identify an Active Directory account to provide credentials for the servers. By default, Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2018 Setup runs Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and the Dynamics NAV database under the Network Service account, a predefined local account that is used by the service control manager.
Tip
We recommend that you create and use a domain user account for running Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server and accessing the Dynamics NAV database. The Network Service account is considered less secure because it is a shared account that can be used by other unrelated network services.
For more information, see Provisioning the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Server Account.
Securing the Connection to Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Client With SSL
You can help secure Dynamics NAV data that is transmitted over the Internet by enabling Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) on the connection to the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web client. You can configure SSL when you install the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Server components or after the installation.
For more information, see How to: Install the Web Server Components and How to: Configure SSL to Secure the Connection to Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Client.
See Also
Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Client
How to: Install the Web Server Components