Manage search schema (preview)
The search schema determines how your content ingested via a Microsoft Graph connector is used in various Microsoft Graph experiences. The schema defines the structure of how content is collected from data sources, indexed, queried, and retrieved from the search index. By changing the search schema, you can control what users can search for, how users can search for it, and how you can present the results on Microsoft Search endpoints.
The search schema contains crawled properties, search attributes, semantic labels, and aliases. The next sections will define the various constituents of schema and management capabilities provided.
Note
Read the Setup your Microsoft Graph connector article to understand the general Microsoft Graph connectors setup instructions. Steps 6 and 7 define the schema while setting up a new connection.
Note
If you are looking to modify the SharePoint Online search schema, read Manage the search schema in SharePoint.
Crawled properties
To build up the search index, you must first crawl content. You can crawl various content sources as listed in the connectors gallery. The contents and metadata of the items that you crawl are represented as crawled properties (or source properties).
For example, the following table presents sample crawled properties for a work tickets system connector.
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| ticketId | String |
| title | String |
| createdBy | String |
| assignedTo | String |
| lastEditedDate | DateTime |
| lastEditedBy | String |
| workItemType | String |
| priority | Int64 |
| tags | StringCollection |
| status | String |
| url | String |
| resolved | Boolean |
Note
- For Microsoft built connectors, the crawled properties are selected in step 4 of Setup your Microsoft Graph connector article.
Search attributes
Content property
This property is used for full-text indexing of content, search results page snippet generation, result cluster participation, language detection, HTML/text support, ranking and relevance, and query formulation.
If you select a content property, you have the option of using the system-generated property ResultSnippet when you create your result type. This property serves as a placeholder for the dynamic snippets that are generated from the content property at query time. If you use this property in your result type, snippets are generated in your search results.
Searchable
If a property is searchable, its value is added to the full-text index. When a user performs a search, we return results if there is a search hit in one of the searchable fields or its content.
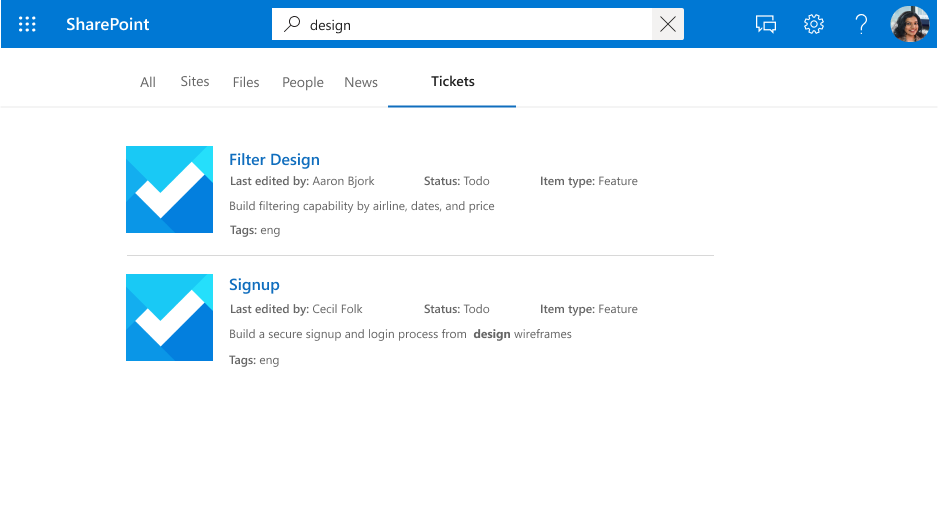
A search for "design" displaying results for hits against the property (title) and content.
Queryable
If a property is queryable, you can query against it using knowledge query language (KQL). KQL consists of one or more free text keywords (words or phrases) or property restrictions. The property name must be included in the query, either specified in the query itself or included in the query programmatically. You can use prefix matching with the wildcard operator(*).
Note
Suffix matching is not supported.
A search for "search ba*" displaying results that match this prefix.
A search for "tags:design" scoping down results in items with "design" in the tags property.
Retrievable
If a property is retrievable, its value can be returned in search results. Any property that you want to add to the display template or be returned from the query and be relevant in search results must be retrievable. Marking large or too many properties as retrievable increases search latency. Be careful when choosing the right properties.
As a result, a set of retrievable properties (title and lastEditedBy) is rendered.
Refinable
Note
The "int" datatype properties cannot be refined, even if marked as refinable.
If a property is refinable, an admin can configure it as a custom filter on the Microsoft Search results page. A refinable property cannot be searchable.
Refine results by tags, a refinable property.
Note
- For Microsoft built connectors, the search attributes are selected in step 7 of Setup your Microsoft Graph connector article.
Semantic labels
A semantic label is a well-known tag published by Microsoft that you can add against a property in your schema. Adding a semantic label helps various Microsoft products understand the property and provide a better experience.
Semantic labels provide a domain-independent approach to assigning properties from different content domains to a set of well-known classes. They find applications in many different content experiences and provide automated support for tasks such as:
- Data integration in heterogenous experiences
- Building common knowledge graphs (for example, Topics)
- Default templates for user experiences
Labels provide semantic meaning, and let you integrate your connector data into Microsoft 365 experiences.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
| title | The title of the item that you want to be shown in search and other experiences. |
| url | The target URL of the item in the data source. |
| createdBy | The name of the person who created the item in the data source. |
| lastModifiedBy | The name of the person who most recently edited the item in the data source. |
| authors | The names of all the people who participated/collaborated on the item in the data source. |
| createdDateTime | The date and time that the item was created in the data source. |
| lastModifiedDateTime | The date and time that the item was last modified in the data source. |
| fileName | In the case of a file, the name of the file in the data source. |
| fileExtension | In the case of a file, the extension of the file is in the data source. |
| iconUrl | The URL of an icon. |
For example, the crawled property lastEditedBy has the same meaning as the Microsoft label lastModifiedBy.
Important
All properties that you map to labels must be retrievable.
The label title is the most important label. Make sure that you assign a property to this label to allow your connection to participate in the result cluster experience. Incorrectly mapping labels degrades the search experience. It's okay for some labels to not have a property assigned to them.
Note
- For Microsoft built connectors, the semantic labels are selected in step 6 of Setup your Microsoft Graph connector article.
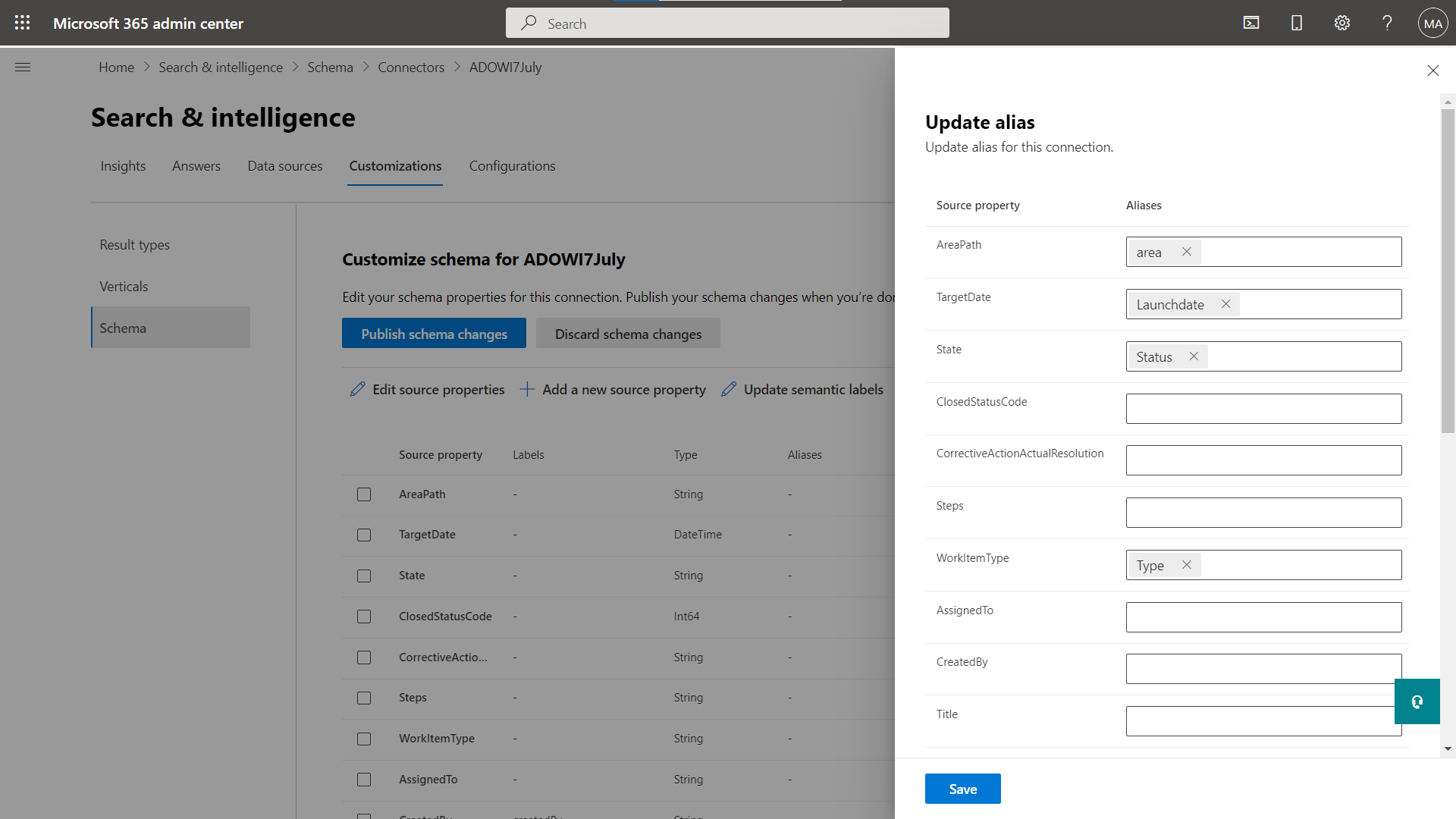
Aliases
Aliases are friendly names for properties that you assign. These are used in queries and selections in refinable property filters.
Note
- For Microsoft built connectors, aliases are defined in step 7 of Setup your Microsoft Graph connector article.
Schema update capabilities
This section includes information about the update capabilities for the search schema of Microsoft built connectors.
Note
We recommend that you run a full crawl after an update to bring them to the latest schema. Without a full crawl, the behavior of the items will be inconsistent.
Manage schema
- In the Microsoft 365 admin center, go to the Schema page in the Customization section.
- Click View details under Microsoft Graph connectors schema.
- Select the connection for which you want to update the schema and click Customize schema.
- After making the required schema changes, click Publish schema changes to publish the new schema.
Add a crawled property
You can add a property to your schema. When you add a property, you can include all the search attributes that you need.
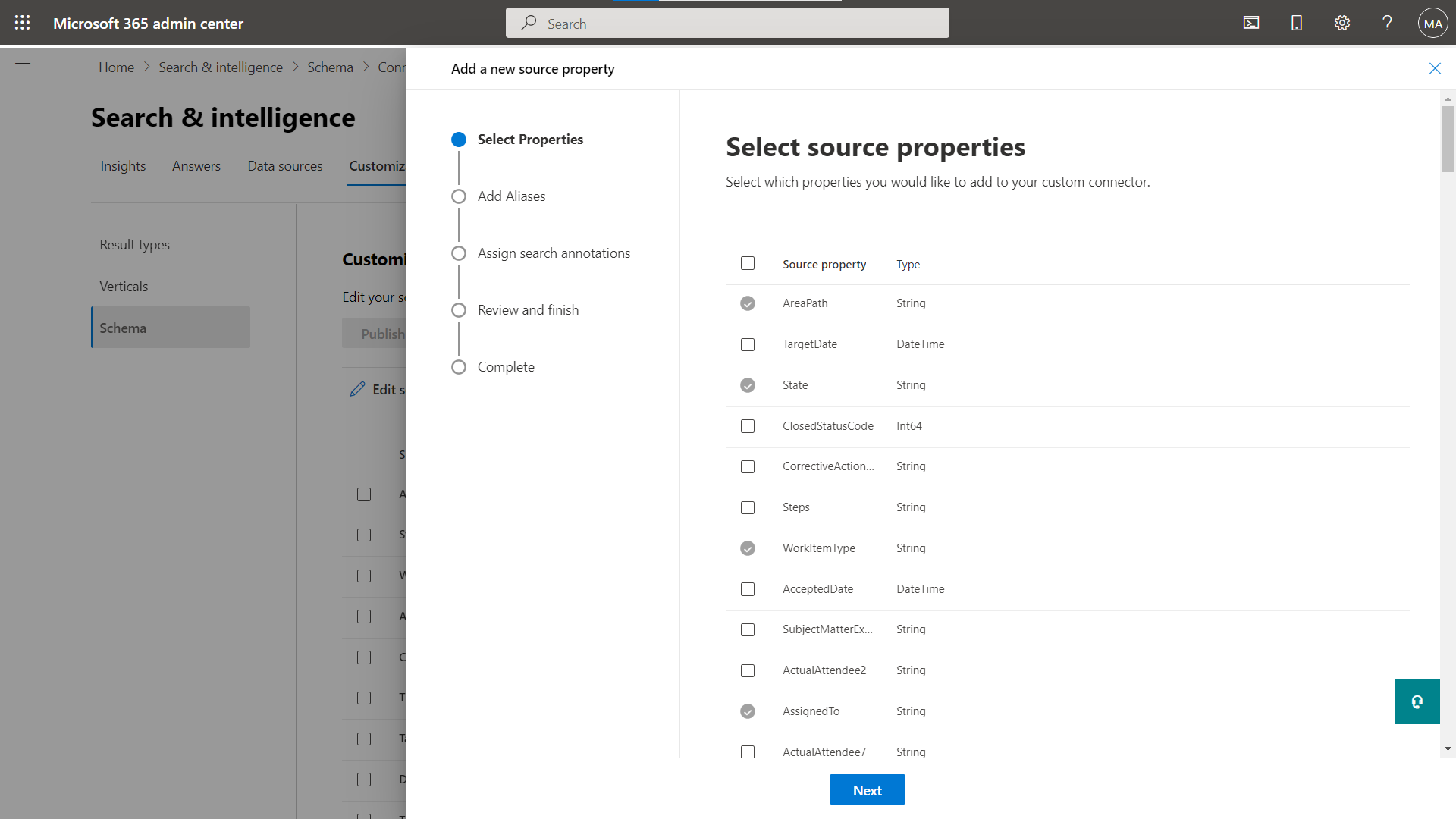
Add a new source property from the list of supported properties by connector.
Important
You cannot delete an existing property for a published connection. To remove a property, you must delete and recreate a connection.
Add/remove a search capability
You can add or remove specific search attributes to a property. Adding a search capability requires a full crawl.
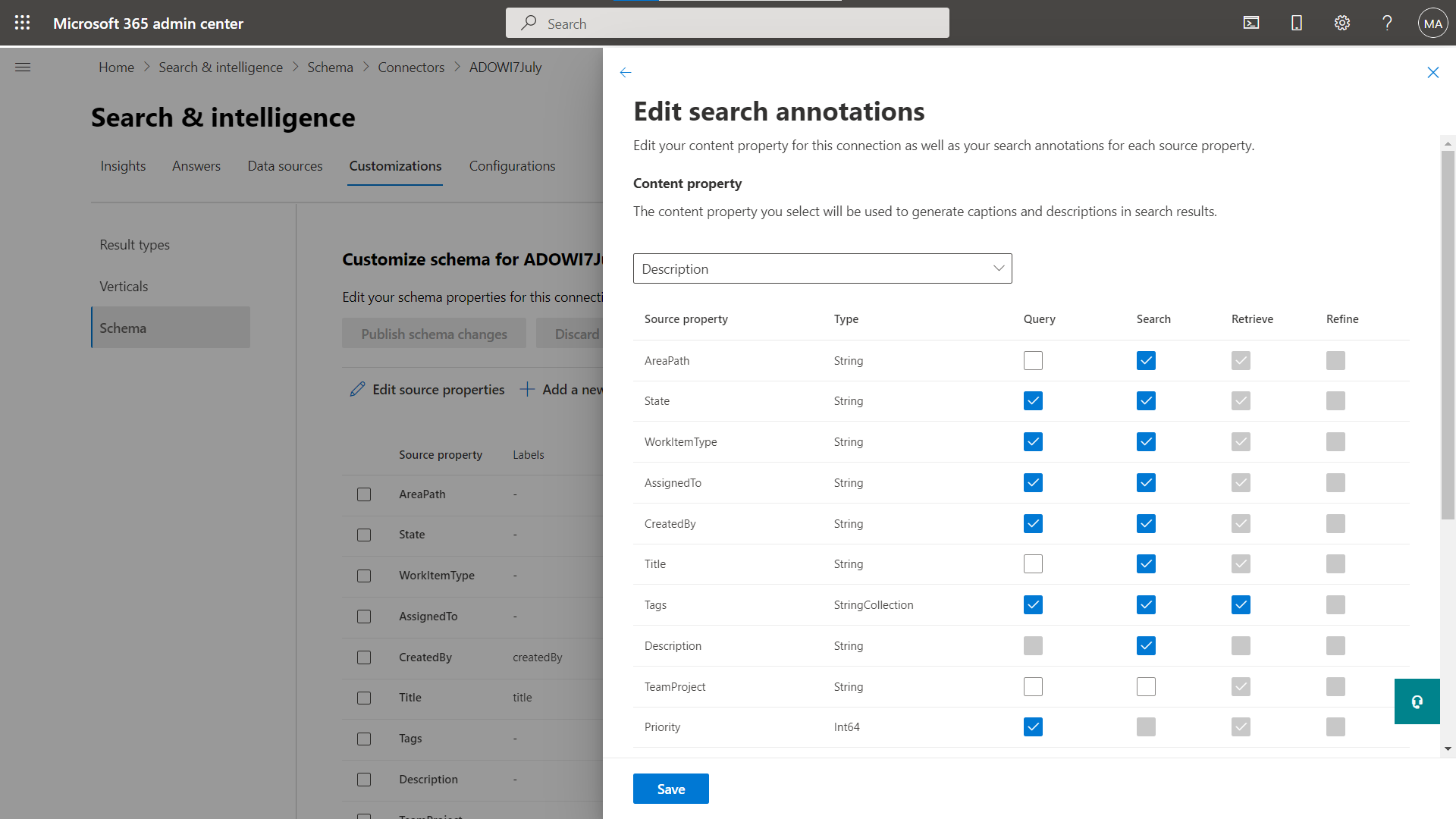
Update the search annotations for crawled properties
Important
- You cannot remove a retrievable search attribute from a property.
- You cannot add or remove a refinable search attribute to a property.
Add/remove a semantic label
You can add or update semantic label mapping of your crawled properties.
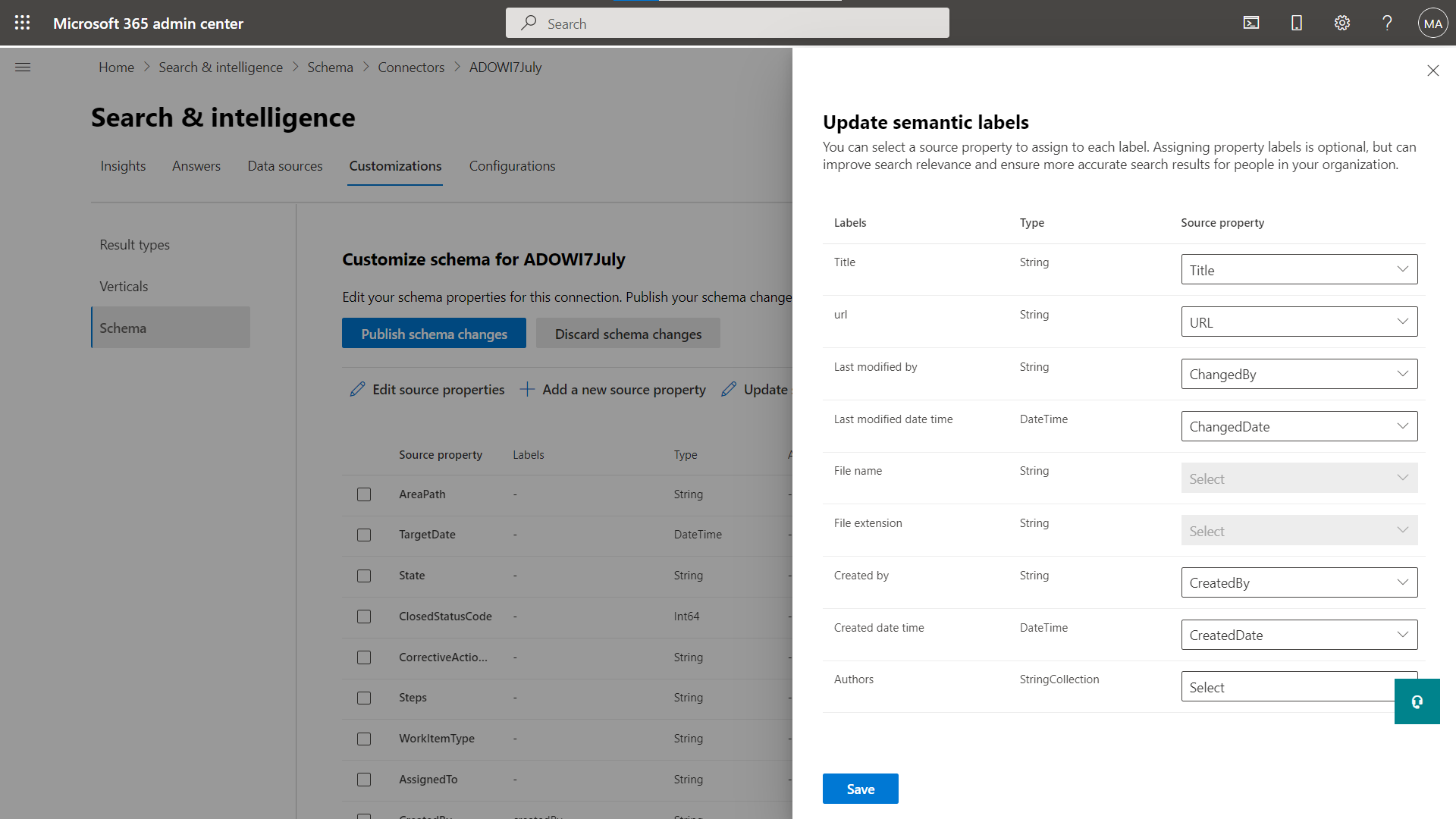
Update semantic labels for crawled properties
Add/remove an alias
You can add or remove aliases, and use them for your search queries.
Add or remove an alias for crawled properties