Design identity governance
Identity Governance is the management of identity and access rights across multiple applications and services to meet security and regulatory requirements. Identity governance in Microsoft Entra ID allows you to balance security and productivity by ensuring that the right people have the right access to the right resources at the right time.
Identity Governance enables you to manage the following tasks for services and applications both on-premises and in the cloud:
Govern the identity lifecycle. Automate user lifecycle events such as add, move, and leave actions, to meet both security and productivity needs.
Govern access lifecycle. Quickly manage changes to access rights by using self-service requests and monitoring lifecycle events.
Secure privileged access for administration. Govern access to privileged resources to mitigate the risk of excessive, unnecessary, or misused rights.
Identity lifecycle
When your educational organization spans multiple Microsoft Entra tenants, you'll have internal identities such as educators and students, and external identities such as staff from other schools.
- Internal identities are those created in the tenant you're currently managing
- External identities are created outside the current tenant and granted access. They can be added using Microsoft Entra B2B collaboration.
Identity lifecycle management helps to set the foundation for identity governance. You'll need to manage the lifespan of internal and external identities, and their relationships with your resources.
Everyone within the organization has their own subset of resources necessary for their job. Without a defined list of what each role needs for each project, managing access is challenging. As internal or external identities join, move within, or leave an organization, their identity and resource access should adjust with them. Automatic provisioning of users in Microsoft Entra ID can help solve this challenge by facilitating the creation, maintenance, and ultimate deletion of user identities across applications for better collaboration.
User provisioning
Traditional provisioning methods such as uploading CSV files or custom scripts to sync user data are error prone, insecure, and hard to manage.
Automatic provisioning refers to creating user identities and roles in the cloud applications that users need access to. In addition to creating user identities, automatic provisioning includes the maintenance and removal of user identities as status or roles change.
We recommend that large educational organizations use the automated Microsoft Entra user provisioning service. This service offers integration with cloud-based human resources (HR) applications such as Workday and SuccessFactors, and enables you to take advantage of the following benefits:
Maximizes efficiency and accuracy of provisioning processes
Saves on costs associated with hosting and maintaining custom-developed provisioning solutions and scripts
Secures your organization by instantly removing users’ identities from key SaaS apps when they leave the organization
Easily provisions a large number of users to a particular SaaS application or system
Consistent policies that determine who is provisioned and who can sign in to an application
Inbound user provisioning
Inbound user provisioning is the process when user data flows from an organization’s Human Capital Management (HCM) application(s) to Microsoft Entra ID or on-premises Active Directory. Integration is possible when the HCM application supports the SCIM protocol. Integration is also possible with cloud-based HCM systems that provide provisioning API connectors.
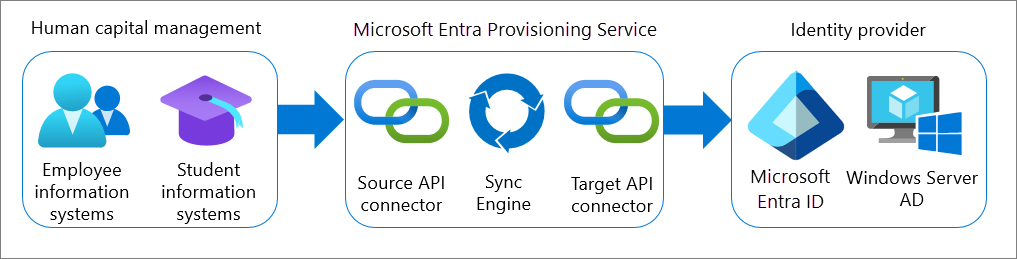
To learn more, see Plan cloud HR application to Microsoft Entra user provisioning.
Outbound user provisioning
Outbound user provisioning, or app provisioning, refers to the automatic creation of user identities and roles in the cloud Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications that users must access. App provisioning is available for pre-integrated applications in the Microsoft Entra SaaS apps gallery and applications that support SCIM 2.0.
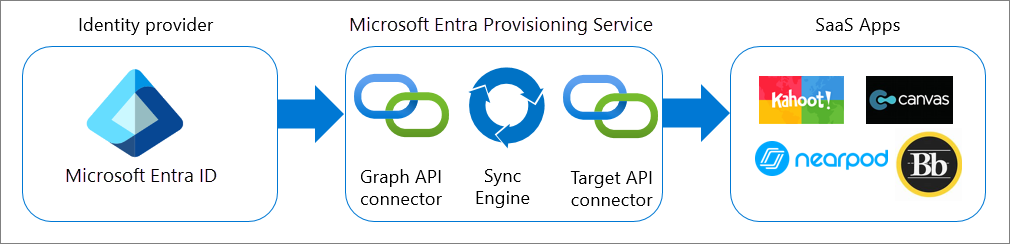
To learn more, see Plan an automatic user provisioning deployment.
Access lifecycle
Your EDU organization needs a process to manage access beyond initial creation and provisioning. Ideally, you should also be able to scale efficiently in order to develop and enforce access policy and controls on an ongoing basis.
Self-service group management
When possible, use self-service group management to take advantage of the following benefits:
Security. Administrators can set rules for groups that are created in Microsoft Entra ID based on user attributes. This allows members to be automatically added to or removed from a security group. These dynamic groups can be used to provide access to applications or cloud resources and to assign licenses to members. Conditional Access policies can further enhance security by ensuring that an app is being accessed by legitimate users. For example, you can select a group that contains all members of the HR department when an HR app is selected as the cloud app.
Cost-effective. Reduces the cost, time, and workload of IT support with self-service group membership. The self-service group management feature gives you the ability to delegate group management to your users. With this feature they can create groups and manage memberships in groups they own.
Self-service. Delegates group management to your users. The self-service group management feature capabilities enable users to create groups and manage memberships in groups they own. These groups can then be used to assign access to applications. For example, if you want to assign access for the faculty department to use five different SaaS applications, you can create a group that contains the users in the faculty department, and then assign that group to those five SaaS applications that are needed by the faculty department.
For a detailed look at self-service group management, download the Microsoft Entra Self-Service Group Management white paper.
Entitlement management
Managing user access to resources in large EDUs is challenging, even more so when you have a combination of internal and external users across tenants. Entitlement Management enables users, including guests, to request access to an access package granting access across groups, applications, and SharePoint sites. It also enables you to manage identity and access lifecycle at scale by automating access request workflows, access assignments, reviews, and expiration.
Here are the types of resources you can manage user's access to with Entitlement Management:
Membership of Microsoft Entra security groups
Membership of Microsoft 365 Groups and Teams
Assignment to Microsoft Entra enterprise applications, including SaaS applications and custom-integrated applications that support federation/single sign-on and/or provisioning
Membership of SharePoint Online sites
Access packages
Entitlement Management allows defining access packages that represent a set of resources that is assigned to users as a unit, establish a validity period, approval workflows, etc. Access packages enable you to do a one-time setup of resources and policies that automatically administers access for the life of the access package.
Access packages must be put in a container called a catalog. A catalog defines what resources you can add to your access package. Catalogs are used for delegation, so that non-administrators can create their own access packages. Catalog owners are enabled to add resources they own to a catalog.
As an educational organization you should consider creating a catalog per school and an access package for every grade that contains policies and access rights to resources specific to that grade. When students advance to a next grade or teachers move to another grade, they can request access to the access package for the new grade while the access related to their former grade will expire.
Access packages must also have at least one policy. Policies specify who can request the access package and the approval and lifecycle settings. We recommend that you use Entitlement Management to delegate to non-administrators the ability to create access packages and define policies with rules for which users can request, who must approve their access, and when access expires.
Access packages are most appropriate in situations such as the following:
Users need time-limited access for a particular task. For example, you might use group-based licensing and a dynamic group to ensure all employees have an Exchange Online mailbox, and then use access packages for situations in which users need additional access, such as to read departmental resources from another department.
Access needs to be approved by a user’s manager or other designated individuals.
Departments wish to manage their own access policies for their resources without IT involvement.
Two or more schools are collaborating on a project, and as a result, multiple users from one school need to be brought in via Microsoft Entra B2B to access another school’s resources.
For more information, see Create a new access package in Microsoft Entra entitlement management.
License requirements
Using Access Packages requires a Microsoft Entra ID license, and is required for:
Member users who can request an access package.
Member and guest users who request an access package.
Member and guest users who approve requests for an access package.
Member and guest users who have a direct assignment to an access package.
Microsoft Entra ID P2 licenses aren't required for the following tasks:
Users with the Global Administrator role who set up the initial catalogs, access packages, and policies, and delegate administrative tasks to other users.
Users who have been delegated administrative tasks, such as catalog creator, catalog owner, and access package manager.
Guests who can request access packages, but don't request an access package.
Note
For each paid Microsoft Entra ID P2 license that you purchase for your member users, you can use Microsoft Entra B2B to invite up to 5 guest users. These guest users can also use Microsoft Entra ID P2 features. For more information, see Microsoft Entra B2B collaboration licensing guidance.
Access reviews
Once users are onboarded, you'll need a process that enables your users’ access to change as their needs change over time.
Consider the following:
As new users join, how do you ensure they have the right access to be productive?
As people move teams or leave the school, how do you ensure their old access is removed, especially when it involves guests?
Excessive access rights can lead to audit findings and compromises as they indicate a lack of control over access.
You must proactively engage with resource owners to ensure they regularly review who has access to their resources.
We recommend using Microsoft Entra access reviews to efficiently manage group memberships, access to applications, and role assignments. User’s access should be reviewed regularly to make sure only the right people have continued access.
License requirements
Using Access Reviews requires a Microsoft Entra ID license, and is required for:
Member and guest users who are assigned as reviewers.
Member and guest users who perform a self-review.
Group owners who perform an access review.
Application owners who perform an access review.
Microsoft Entra ID P2 licenses aren't required for users with the Global Administrator or User Administrator roles who set up access reviews, configure settings, or apply the decisions from the reviews.
For each paid Microsoft Entra ID P2 license that you assign to one of your own organization's users, you can use Microsoft Entra business-to-business (B2B) to invite up to five guest users under the External User Allowance. These guest users can also use Microsoft Entra ID P2 features. For more information, see Microsoft Entra B2B collaboration licensing guidance.
Privileged access
Another key lifecycle in identity governance is that of users’ privileged access. Minimizing the number of users with access to sensitive resources helps maintain an overall secure environment, but there are still users who need admin rights. Govern admin access to mitigate the risk of excessive, unnecessary, or misused access rights— whether they are from your school or another school.
Privileged Identity Management
Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management (PIM) provides time-based and approval-based role activation to mitigate the risks of excessive, unnecessary, or misused access permissions to resources in Microsoft Entra ID, Azure, and other Microsoft Online Services like Microsoft 365 or Microsoft Intune. It's used to protect privileged accounts by lowering the exposure time of privileges and increasing visibility into their use through reports and alerts.
Here are some of the key features of Privileged Identity Management:
Provide just-in-time privileged access to Microsoft Entra ID and Azure resources
Assign time-bound access to resources using start and end dates
Require approval to activate privileged roles
Enforce multifactor authentication to activate any role
Use justification to understand why users activate
Get notifications when privileged roles are activated
Conduct access reviews to ensure users still need roles
Download audit history for internal or external audit
We recommend using PIM to manage and control the following in your organization:
Enable approval for specific roles
Specify approver users or groups to approve requests
View request and approval history for all privileged roles
Approve or reject requests for role elevation (single and bulk)
Provide justification for an approval or rejection
Request activation of a role that requires approval
License requirements
Using PIM requires a Microsoft Entra ID license, and is required for:
Users assigned as eligible to Microsoft Entra ID or Azure roles managed using PIM.
Users who are assigned as eligible members or owners of privileged access groups.
Users able to approve or reject activation requests in PIM.
Users assigned to an access review.
Users who perform access reviews.