Overview of Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication
Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication (CBA) enables customers to allow or require users to authenticate directly with X.509 certificates against their Microsoft Entra ID for applications and browser sign-in. This feature enables customers to adopt a phishing resistant authentication and authenticate with an X.509 certificate against their Public Key Infrastructure (PKI).
What is Microsoft Entra CBA?
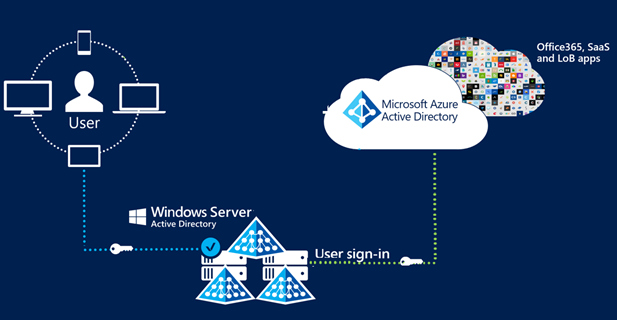
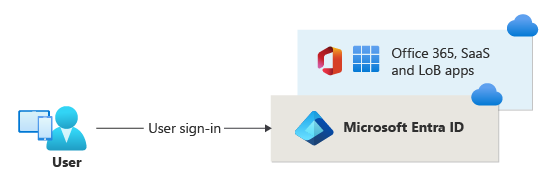
Before cloud-managed support for CBA to Microsoft Entra ID, customers had to implement federated certificate-based authentication, which requires deploying Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) to be able to authenticate using X.509 certificates against Microsoft Entra ID. With Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication, customers can authenticate directly against Microsoft Entra ID and eliminate the need for federated AD FS, with simplified customer environments and cost reduction.
The following images show how Microsoft Entra CBA simplifies the customer environment by eliminating federated AD FS.
Certificate-based authentication with federated AD FS
Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication
Key benefits of using Microsoft Entra CBA
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Great user experience | - Users who need certificate-based authentication can now directly authenticate against Microsoft Entra ID and not have to invest in federated AD FS. - Portal UI enables users to easily configure how to map certificate fields to a user object attribute to look up the user in the tenant (certificate username bindings) - Portal UI to configure authentication policies to help determine which certificates are single-factor versus multifactor. |
| Easy to deploy and administer | - Microsoft Entra CBA is a free feature, and you don't need any paid editions of Microsoft Entra ID to use it. - No need for complex on-premises deployments or network configuration. - Directly authenticate against Microsoft Entra ID. |
| Secure | - On-premises passwords don't need to be stored in the cloud in any form. - Protects your user accounts by working seamlessly with Microsoft Entra Conditional Access policies, including Phishing-Resistant multifactor authentication (MFA requires licensed edition) and blocking legacy authentication. - Strong authentication support where users can define authentication policies through the certificate fields, such as issuer or policy OID (object identifiers), to determine which certificates qualify as single-factor versus multifactor. - The feature works seamlessly with Conditional Access features and authentication strength capability to enforce MFA to help secure your users. |
Supported scenarios
The following scenarios are supported:
- User sign-ins to web browser-based applications on all platforms.
- User sign-ins to Office mobile apps on iOS/Android platforms as well as Office native apps in Windows, including Outlook, OneDrive, and so on.
- User sign-ins on mobile native browsers.
- Support for granular authentication rules for multifactor authentication by using the certificate issuer Subject and policy OIDs.
- Configuring certificate-to-user account bindings by using any of the certificate fields:
- Subject Alternate Name (SAN) PrincipalName and SAN RFC822Name
- Subject Key Identifier (SKI) and SHA1PublicKey
- Issuer + Subject, Subject and Issuer + SerialNumber
- Configuring certificate-to-user account bindings by using any of the user object attributes:
- User Principal Name
- onPremisesUserPrincipalName
- CertificateUserIds
Unsupported scenarios
The following scenarios aren't supported:
- Certificate Authority hints aren't supported, so the list of certificates that appears for users in the certificate picker UI isn't scoped.
- Only one CRL Distribution Point (CDP) for a trusted CA is supported.
- The CDP can be only HTTP URLs. We don't support Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP), or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) URLs.
- Password as an authentication method can't be disabled and the option to sign in using a password is displayed even with Microsoft Entra CBA method available to the user.
Known Limitation with Windows Hello For Business certificates
- While Windows Hello For Business (WHFB) can be used for multifactor authentication in Microsoft Entra ID, WHFB isn't supported for fresh MFA. Customers can choose to enroll certificates for your users using the WHFB key pair. When properly configured, these WHFB certificates can be used for multifactor authentication in Microsoft Entra ID. WHFB certificates are compatible with Microsoft Entra certificate-based authentication (CBA) in Microsoft Edge and Chrome browsers; however, at this time WHFB certificates aren't compatible with Microsoft Entra CBA in non-browser scenarios (such as Office 365 applications). The workaround is to use the "Sign in Windows Hello or security key" option to sign in (when available) as this option doesn't use certificates for authentication and avoids the issue with Microsoft Entra CBA; however, this option may not be available in some older applications.
Out of Scope
The following scenarios are out of scope for Microsoft Entra CBA:
- Public Key Infrastructure for creating client certificates. Customers need to configure their own Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and provision certificates to their users and devices.