XAML Hot Reload for .NET MAUI
.NET Multi-platform App UI (.NET MAUI) XAML Hot Reload is a Visual Studio feature that enables you to view the result of XAML changes in your running app, without having to rebuild your project. Without XAML Hot Reload, you have to build and deploy your app every time you want to view the result of a XAML change.
When your .NET MAUI app is running in debug configuration, with the debugger attached, XAML Hot Reload parses your XAML edits and sends those changes to the running app. It preserves your UI state, since it doesn't recreate the UI for the full page, and updates changed properties on controls affected by edits. In addition, your navigate state and data will be maintained, enabling you to quickly iterate on your UI without losing your location in the app. Therefore, you'll spend less time rebuilding and deploying your apps to validate UI changes.
By default, you don't need to save your XAML file to see the results of your edits. Instead, updates are applied immediately as you type. However, on Windows you can change this behavior to update only on file save. This can be accomplished by checking the Apply XAML Hot Reload on document save checkbox in the Hot Reload IDE settings available by selecting Debug > Options> XAML Hot Reload from the Visual Studio menu bar. Only updating on file save can sometimes be useful if you make bigger XAML updates and don't wish them to be displayed until they are complete.
Note
If you're writing a native UWP or WPF app, without using .NET MAUI, see What is XAML Hot Reload for WPF and UWP apps?.
XAML Hot Reload is available in both Visual Studio 2022 and Visual Studio Code. On Windows, XAML Hot Reload is available on Android, iOS, and WinUI on emulators, simulators, and physical devices. On Mac, XAML Hot Reload is available on Android, iOS, and Mac Catalyst on emulators, simulators, and physical devices. In all cases, XAML Hot Reload requires your debug configuration to be named Debug.
Important
XAML Hot Reload doesn't reload C# code. If you add a new event handler in code, it can only be used in XAML after the code is reloaded. In addition, if you add a new XAML element with an x:Name, the name cannot be used in code until the code is reloaded.
Full page reload
There may be cases where XAML Hot Reload doesn't update the running app as expected. For example, you might change a color property on a .NET MAUI control but not see the color change in the running app. To work around such issues you can fully reload the XAML file by clicking the Hot Reload toolbar button, or pressing Alt+F10. Only XAML files that have been edited will be reloaded. The exception to this is if you change a resource dictionary file, in which case all XAML files will be reloaded in order to apply new resources.
Important
When XAML is reloaded some UI state may be lost, such as current focus and selection.
Enable XAML Hot Reload
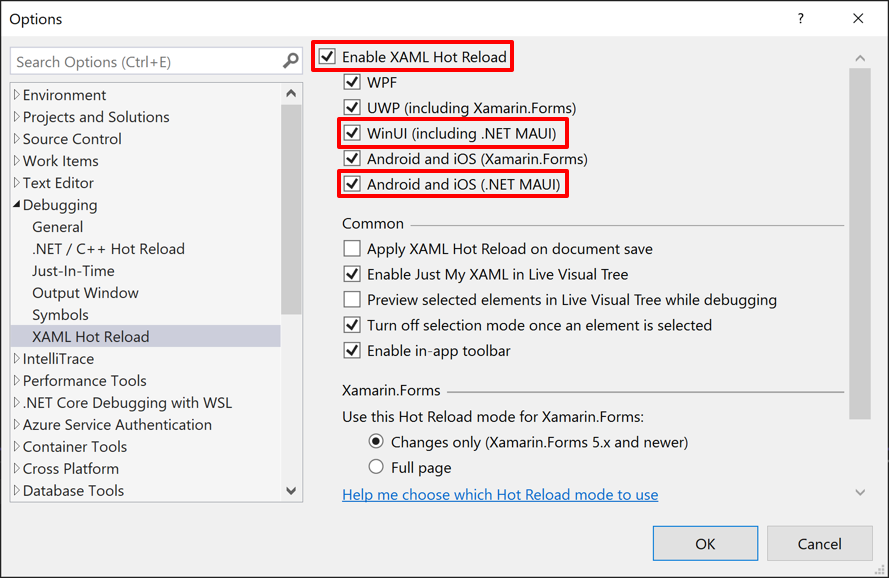
XAML Hot Reload is enabled by default in Visual Studio 2022. If it's been previously disabled, it can be enabled by selecting Debug > Options > XAML Hot Reload from the Visual Studio menu bar. Next, in the Options dialog box, ensure that the Enable XAML Hot Reload, WinUI (including .NET MAUI), and Android and iOS (.NET MAUI) options are checked:
Then, on iOS in your build settings, check that the Linker is set to "Don't Link".
Reload on multiple platforms
XAML Hot Reload supports simultaneous debugging of multiple platforms in Visual Studio, provided that you have separate head projects per platform rather than a single project app. For example, you can deploy an Android and an iOS target at the same time to see your changes reflected on both platforms at once. To debug on multiple platforms on Windows, see How To: Set multiple startup projects.
Troubleshooting
The XAML Hot Reload output displays status messages that can help with troubleshooting. In Visual Studio, these can be displayed by selecting View > Output from the menu bar, and then selecting Hot Reload in the Show output from: drop-down.
If XAML Hot Reload fails to initialize you should ensure that you're using the latest version of .NET MAUI, the latest version of the IDE, and that your iOS linker settings are set to Don't Link in the project's build settings.
XAML Hot Reload requires your debug configuration to be named Debug. If a custom build configuration is used, XAML Hot Reload will stop working if the build configuration isn't named Debug.
If nothing happens when saving your XAML file, ensure that XAML Hot Reload is enabled in the IDE. For more information, see Enable XAML Hot Reload.
If you make a change that the XAML Hot Reload parser sees as invalid, it will show the error underlined in the editor and include it in the Error List window. Hot Reload errors have an error code starting with "XHR" (for XAML Hot Reload). If there are any such errors on the page, XAML Hot Reload won't apply changes to your running app until the errors have been fixed.
You can't add, remove, or rename files or NuGet packages during a XAML Hot Reload session. If you add or remove a file or NuGet package, rebuild and redeploy your app to continue using XAML Hot Reload.
Disabling XAML compilation with [XamlCompilation(XamlCompilationOptions.Skip)] isn't supported and can cause issues with the Live Visual Tree. For more information about Live Visual Tree, see Inspect the visual tree of a .NET MAUI app.
