App lifecycle
.NET Multi-platform App UI (.NET MAUI) apps generally have four execution states: not running, running, deactivated, and stopped. .NET MAUI raises cross-platform lifecycle events on the Window class when an app transitions from the not running state to the running state, the running state to the deactivated state, the deactivated state to the stopped state, the stopped state to the running state, and the stopped state to the not running state.
The following diagram shows an overview of the .NET MAUI app lifecycle:
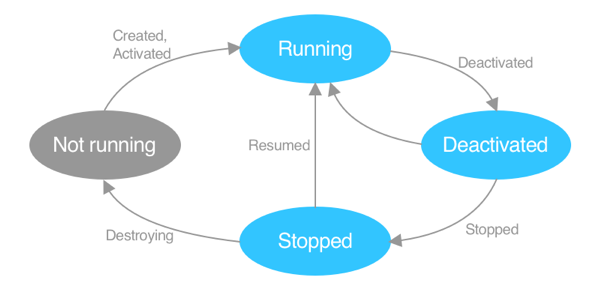
In the diagram, the gray oval indicates that the app isn't loaded into memory. The light blue ovals indicate that the app is in memory. Text on arcs indicates events that are raised by .NET MAUI, that provide notifications to the running app.
The execution state of an app depends on the app's history. For example, when an app is installed for the first time, or a device is started, the app can be considered to be not running. When the app is started, the Created and Activated events are raised and the app is running. If a different app window gains focus, the Deactivated event is raised and the app is deactivated. If the user switches to a different app or returns to the device's Home screen, so that the app window is no longer visible, the Deactivated and Stopped events are raised and the app is stopped. If the user returns to the app, the Resuming event is raised and app is running. Alternatively, an app might be terminated by a user while it's running. In this situation the app is deactivated then stopped, the Destroying event is raised, and the app is not running. Similarly, a device might terminate an app while it's stopped, due to resource restrictions, and the Destroying event is raised and the app is not running.
In addition, .NET MAUI enables apps to be notified when platform lifecycle events are raised. For more information, see Platform lifecycle events.
Cross-platform lifecycle events
The Window class defines the following cross-platform lifecycle events:
| Event | Description | Action to take |
|---|---|---|
Created |
This event is raised after the native window has been created. At this point the cross-platform window will have a native window handler, but the window might not be visible yet. | |
Activated |
This event is raised when the window has been activated, and is, or will become, the focused window. | |
Deactivated |
This event is raised when the window is no longer the focused window. However, the window might still be visible. | |
Stopped |
This event is raised when the window is no longer visible. There's no guarantee that an app will resume from this state, because it may be terminated by the operating system. | Disconnect from any long running processes, or cancel any pending requests that might consume device resources. |
Resumed |
This event is raised when an app resumes after being stopped. This event won't be raised the first time your app launches, and can only be raised if the Stopped event has previously been raised. |
Subscribe to any required events, and refresh any content that's on the visible page. |
Destroying |
This event is raised when the native window is being destroyed and deallocated. The same cross-platform window might be used against a new native window when the app is reopened. | Remove any event subscriptions that you've attached to the native window. |
These cross-platform events map to different platform events, and the following table shows this mapping:
| Event | Android | iOS | Windows |
|---|---|---|---|
Created |
OnPostCreate |
FinishedLaunching |
Created |
Activated |
OnResume |
OnActivated |
Activated (CodeActivated and PointerActivated) |
Deactivated |
OnPause |
OnResignActivation |
Activated (Deactivated) |
Stopped |
OnStop |
DidEnterBackground |
VisibilityChanged |
Resumed |
OnRestart |
WillEnterForeground |
Resumed |
Destroying |
OnDestroy |
WillTerminate |
Closed |
In addition, the Window class also defines a Backgrounding event that's raised on iOS and Mac Catalyst when the Window is closed or enters a background state. A BackgroundingEventArgs object accompanies this event, and any string state should be persisted to the State property of the BackgroundingEventArgs object, which the OS will preserve until it's time to resume the window. When the window is resumed the state is provided by the IActivationState argument to the CreateWindow override.
In addition to these events, the Window class also has the following overridable lifecycle methods:
OnCreated, which is invoked when theCreatedevent is raised.OnActivated, which is invoked when theActivatedevent is raised.OnDeactivated, which is invoked when theDeactivatedevent is raised.OnStopped, which is invoked when theStoppedevent is raised.OnResumed, which is invoked when theResumedevent is raised.OnDestroying, which is invoked when theDestroyingevent is raised.OnBackgrounding, which is invoked when theBackgroundingevent is raised.
To subscribe to the Window lifecycle events, override the CreateWindow method in your App class to create a Window instance on which you can subscribe to events:
namespace MyMauiApp
{
public partial class App : Application
{
public App()
{
InitializeComponent();
MainPage = new MainPage();
}
protected override Window CreateWindow(IActivationState? activationState)
{
Window window = new Window(new AppShell());
window.Created += (s, e) =>
{
// Custom logic
};
return window;
}
}
}
namespace MyMauiApp
{
public partial class App : Application
{
public App()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override Window CreateWindow(IActivationState activationState)
{
Window window = base.CreateWindow(activationState);
window.Created += (s, e) =>
{
// Custom logic
};
return window;
}
}
}
Alternatively, to consume the lifecycle overrides, create a class that derives from the Window class
namespace MyMauiApp
{
public class MyWindow : Window
{
public MyWindow() : base()
{
}
public MyWindow(Page page) : base(page)
{
}
protected override void OnCreated()
{
// Register services
}
}
}
The Window-derived class can then be consumed by overriding the CreateWindow method in your App class to return a MyWindow instance.
Warning
An InvalidOperationException will be thrown if the App.MainPage property is set and the CreateWindow method creates a Window object using the override that accepts a Page argument.
Platform lifecycle events
.NET MAUI defines delegates that are invoked in response to platform lifecycle events being raised. Handlers can be specified for these delegates, using named methods or anonymous functions, which are executed when the delegate is invoked. This mechanism enables apps to be notified when common platform lifecycle events are raised.
Important
The ConfigureLifecycleEvents method is in the Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents namespace.
Android
The following table lists the .NET MAUI delegates that are invoked in response to Android lifecycle events being raised:
| Delegate | Arguments | Description | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
OnActivityResult |
Android.App.Activity, int, Android.App.Result, Android.Content.Intent? |
Invoked when an activity you launched exits. | |
OnApplicationConfigurationChanged |
Android.App.Application, Android.Content.Res.Configuration |
Invoked when the device configuration changes while your component is running. | |
OnApplicationCreate |
Android.App.Application |
Invoked when the app has started, before an activity, service, or receiver objects (excluding content providers) have been created. | |
OnApplicationCreating |
Android.App.Application |
Invoked when the app is starting, before an activity, service, or receiver objects (excluding content providers) have been created. | |
OnApplicationLowMemory |
Android.App.Application |
Invoked when the system is running low on memory, and actively running processes should trim their memory usage. | |
OnApplicationTrimMemory |
Android.App.Application, Android.Content.TrimMemory |
Invoked when the operating system has determined that it's a good time for a process to trim unneeded memory from its process. | |
OnBackPressed |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked when the activity has detected a press of the back key. | |
OnConfigurationChanged |
Android.App.Activity, Android.Content.Res.Configuration |
Invoked when the device configuration changes while your activity is running. | |
OnCreate |
Android.App.Activity, Android.OS.Bundle? |
Raised when the activity is created. | |
OnDestroy |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked when the activity is finishing, or because the system is temporarily destroying the activity instance to save space. | Always call the super class's implementation. |
OnNewIntent |
Android.App.Activity, Android.Content.Intent? |
Invoked when the activity is relaunched while at the top of the activity stack instead of a new instance of the activity being started. | |
OnPause |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked when an activity is going into the background, but has not yet been killed. | Always call the super class's implementation. |
OnPostCreate |
Android.App.Activity, Android.OS.Bundle? |
Invoked when activity startup is complete, after OnStart and OnRestoreInstanceState have been called. |
Always call the super class's implementation. This is a system-only event that generally shouldn't be used by apps. |
OnPostResume |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked when activity resume is complete, after OnResume has been called. |
Always call the super class's implementation. This is a system-only event that generally shouldn't be used by apps. |
OnRequestPermissionsResult |
Android.App.Activity, int, string[], Android.Content.PM.Permission[] |
Invoked as a callback for the result from requesting permissions. | |
OnRestart |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked after OnStop when the current activity is being redisplayed to the user (the user has navigated back to it). |
Always call the super class's implementation. |
OnRestoreInstanceState |
Android.App.Activity, Android.OS.Bundle |
Invoked after OnStart when the activity is being reinitialized from a previously saved state. |
|
OnResume |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked after OnRestoreInstanceState, OnRestart, or OnPause, to indicate that the activity is active and is ready to receive input. |
|
OnSaveInstanceState |
Android.App.Activity, Android.OS.Bundle |
Invoked to retrieve per-instance state from an activity being killed so that the state can be restored in OnCreate or OnRestoreInstanceState. |
|
OnStart |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked after OnCreate or OnRestart when the activity has been stopped, but is now being displayed to the user. |
Always call the super class's implementation. |
OnStop |
Android.App.Activity |
Invoked when the activity is no longer visible to the user. | Always call the super class's implementation. |
Important
Each delegate has a corresponding identically named extension method, that can be called to register a handler for the delegate.
To respond to an Android lifecycle delegate being invoked, call the ConfigureLifecycleEvents method on the MauiAppBuilder object in the CreateMauiapp method of your MauiProgram class. Then, on the ILifecycleBuilder object, call the AddAndroid method and specify the Action that registers handlers for the required delegates:
using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents;
namespace PlatformLifecycleDemo
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events =>
{
#if ANDROID
events.AddAndroid(android => android
.OnActivityResult((activity, requestCode, resultCode, data) => LogEvent(nameof(AndroidLifecycle.OnActivityResult), requestCode.ToString()))
.OnStart((activity) => LogEvent(nameof(AndroidLifecycle.OnStart)))
.OnCreate((activity, bundle) => LogEvent(nameof(AndroidLifecycle.OnCreate)))
.OnBackPressed((activity) => LogEvent(nameof(AndroidLifecycle.OnBackPressed)) && false)
.OnStop((activity) => LogEvent(nameof(AndroidLifecycle.OnStop))));
#endif
static bool LogEvent(string eventName, string type = null)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"Lifecycle event: {eventName}{(type == null ? string.Empty : $" ({type})")}");
return true;
}
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}
For more information about the Android app lifecycle, see Understand the Activity Lifecycle on developer.android.com.
iOS and Mac Catalyst
The following table lists the .NET MAUI delegates that are invoked in response to iOS and Mac Catalyst lifecycle events being raised:
| Delegate | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
ApplicationSignificantTimeChange |
UIKit.UIApplication |
Invoked when a significant time change occurs, such as midnight, carrier-changed time, or the start or stop of daylight savings. |
ContinueUserActivity |
UIKit.UIApplication, Foundation.NSUserActivity, UIKit.UIApplicationRestorationHandler |
Invoked when the app receives data associated with a user activity, such as transferring an activity from a different device using Handoff. |
DidEnterBackground |
UIKit.UIApplication |
Invoked when the app has entered the background. |
FinishedLaunching |
UIKit.UIApplication, Foundation.NSDictionary |
Invoked when the app has launched. |
OnActivated |
UIKit.UIApplication |
Invoked when the app is launched and every time the app returns to the foreground. |
OnResignActivation |
UIKit.UIApplication |
Invoked when the app is about to enter the background, be suspended, or when the user receives an interruption such as a phone call or text. |
OpenUrl |
UIKit.UIApplication, Foundation.NSDictionary |
Invoked when the app should open a specified URL. |
PerformActionForShortcutItem |
UIKit.UIApplication, UIKit.UIApplicationShortcutItem, UIKit.UIOperationHandler |
Invoked when a Home screen quick action is initiated. |
PerformFetch |
UIKit.UIApplication, Action<UIBackgroundFetchResult> |
Invoked to tell the app that it can begin a fetch operation if it has data to download. |
SceneContinueUserActivity |
UIKit.UIScene, Foundation.NSUserActivity |
Invoked to handle the specified Handoff-related activity. |
SceneDidDisconnect |
UIKit.UIScene |
Invoked when a scene is removed from the app. |
SceneDidEnterBackground |
UIKit.UIScene |
Invoked when a scene is running in the background and isn't onscreen. |
SceneDidFailToContinueUserActivity |
UIKit.UIScene, string, Foundation.NSError |
Invoked to inform the user that the activity couldn't be completed. |
SceneDidUpdateUserActivity |
UIKit.UIScene, Foundation.NSUserActivity |
Invoked when the specified activity is updated. |
SceneOnActivated |
UIKit.UIScene |
Invoked when the scene becomes active and able to respond to user events. |
SceneOnResignActivation |
UIKit.UIScene |
Invoked when the scene is about to resign the active state and stop responding to user events. |
SceneOpenUrl |
UIKit.UIScene, Foundation.NSSet<UIKit.UIOpenUrlContext> |
Invoked when a scene asks to open one or more URLs. |
SceneRestoreInteractionState |
UIKit.UIScene, Foundation.NSUserActivity |
Invoked to restore the activity state. |
SceneWillConnect |
UIKit.UIScene, UIKit.UISceneSession, UIKit.UISceneConnectionOptions |
Invoked when a scene is added to the app. |
SceneWillContinueUserActivity |
UIKit.UIScene, string |
Invoked to prepare to receive Handoff-related data. |
SceneWillEnterForeground |
UIKit.UIScene |
Invoked when a scene is about to run in the foreground and become visible to the user. |
WillEnterForeground |
UIKit.UIApplication |
Invoked if the app will be returning from a backgrounded state. |
WillFinishLaunching |
UIKit.UIApplication, Foundation.NSDictionary |
Invoked when app launching has begun, but state restoration has not yet occurred. |
WillTerminate |
UIKit.UIApplication |
Invoked if the app is being terminated due to memory constraints, or directly by the user. |
WindowSceneDidUpdateCoordinateSpace |
UIKit.UIWindowScene, UIKit.IUICoordinateSpace, UIKit.UIInterfaceOrientation, UIKit.UITraitCollection |
Invoked when the size, orientation, or traits of a scene change. |
Important
Each delegate, with the exception of PerformFetch, has a corresponding identically named extension method that can be called to register a handler for the delegate.
To respond to an iOS and Mac Catalyst lifecycle delegate being invoked, call the ConfigureLifecycleEvents method on the MauiAppBuilder object in the CreateMauiapp method of your MauiProgram class. Then, on the ILifecycleBuilder object, call the AddiOS method and specify the Action that registers handlers for the required delegates:
using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents;
namespace PlatformLifecycleDemo
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events =>
{
#if IOS || MACCATALYST
events.AddiOS(ios => ios
.OnActivated((app) => LogEvent(nameof(iOSLifecycle.OnActivated)))
.OnResignActivation((app) => LogEvent(nameof(iOSLifecycle.OnResignActivation)))
.DidEnterBackground((app) => LogEvent(nameof(iOSLifecycle.DidEnterBackground)))
.WillTerminate((app) => LogEvent(nameof(iOSLifecycle.WillTerminate))));
#endif
static bool LogEvent(string eventName, string type = null)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"Lifecycle event: {eventName}{(type == null ? string.Empty : $" ({type})")}");
return true;
}
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}
For more information about the iOS app lifecycle, see Managing Your App's Life Cycle on developer.apple.com.
Windows
The following table lists the .NET MAUI delegates that are invoked in response to Windows lifecycle events being raised:
| Delegate | Arguments | Description |
|---|---|---|
OnActivated |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.WindowActivatedEventArgs |
Invoked when the platform Activated event is raised, if the app isn't resuming. |
OnClosed |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.WindowEventArgs |
Invoked when the platform Closed event is raised. |
OnLaunched |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.LaunchActivatedEventArgs |
Invoked by .NET MAUI's Application.OnLaunched override once the native window has been created and activated. |
OnLaunching |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.LaunchActivatedEventArgs |
Invoked by .NET MAUI's Application.OnLaunched override before the native window has been created and activated. |
OnPlatformMessage |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, WindowsPlatformMessageEventArgs |
Invoked when .NET MAUI receives specific native Windows messages. |
OnPlatformWindowSubclassed |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, WindowsPlatformWindowSubclassedEventArgs |
Invoked by .NET MAUI when the Win32 window is subclassed. |
OnResumed |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window |
Invoked when the platform Activated event is raised, if the app is resuming. |
OnVisibilityChanged |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.WindowVisibilityChangedEventArgs |
Invoked when the platform VisibilityChanged event is raised. |
OnWindowCreated |
Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window |
Invoked when the native window is created for the cross-platform Window. |
.NET MAUI exposes specific native Windows messages as a lifecycle event with the OnPlatformMessage delegate. The WindowsPlatformMessageEventArgs object that accompanies this delegate includes a MessageId property, of type uint. The value of this property can be examined to determine which message has been passed to your app window. For more information about windows messages, see Windows Messages (Get Started with Win32 and C++). For a list of window message constants, see Window notifications.
Important
Each delegate has a corresponding identically named extension method, that can be called to register a handler for the delegate.
To respond to a Windows lifecycle delegate being invoked, call the ConfigureLifecycleEvents method on the MauiAppBuilder object in the CreateMauiApp method of your MauiProgram class. Then, on the ILifecycleBuilder object, call the AddWindows method and specify the Action that registers handlers for the required delegates:
using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents;
namespace PlatformLifecycleDemo
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events =>
{
#if WINDOWS
events.AddWindows(windows => windows
.OnActivated((window, args) => LogEvent(nameof(WindowsLifecycle.OnActivated)))
.OnClosed((window, args) => LogEvent(nameof(WindowsLifecycle.OnClosed)))
.OnLaunched((window, args) => LogEvent(nameof(WindowsLifecycle.OnLaunched)))
.OnLaunching((window, args) => LogEvent(nameof(WindowsLifecycle.OnLaunching)))
.OnVisibilityChanged((window, args) => LogEvent(nameof(WindowsLifecycle.OnVisibilityChanged)))
.OnPlatformMessage((window, args) =>
{
if (args.MessageId == Convert.ToUInt32("031A", 16))
{
// System theme has changed
}
}));
#endif
static bool LogEvent(string eventName, string type = null)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"Lifecycle event: {eventName}{(type == null ? string.Empty : $" ({type})")}");
return true;
}
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}
Retrieve the Window object
Platform code can retrieve the app's Window object from platform lifecycle events, with the GetWindow extension method:
using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents;
namespace PlatformLifecycleDemo
{
public static class MauiProgram
{
public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp()
{
var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder();
builder
.UseMauiApp<App>()
.ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events =>
{
#if WINDOWS
events.AddWindows(windows => windows
.OnClosed((window, args) =>
{
IWindow appWindow = window.GetWindow();
}));
#endif
});
return builder.Build();
}
}
}
Custom lifecycle events
While .NET MAUI defines delegates that are invoked in response to platform lifecycle events being raised, it only exposes a common set of platform lifecycle events. However, it also includes a mechanism, typically for library authors, that enables apps to be notified when additional platform lifecycle events are raised. The process for accomplishing this is as follows:
- Register an event handler for a platform lifecycle event that isn't exposed by .NET MAUI.
- In the event handler for the platform lifecycle event, retrieve the
ILifecycleEventServiceinstance and call itsInvokeEventsmethod, specifying the platform event name as its argument.
Then, apps that want to receive notification of the platform lifecycle event should modify the CreateMauiApp method of their MauiProgram class to call the ConfigureLifecycleEvents method on the MauiAppBuilder object. Then, on the ILifecycleBuilder object, call the AddEvent method and specify the platform event name and the Action that will be invoked when the platform event is raised.
Example
The WinUI 3 Window.SizeChanged event occurs when the native app window has first rendered, or has changed its rendering size. .NET MAUI doesn't expose this platform event as a lifecycle event. However, apps can receive notification when this platform event is raised by using the following approach:
Register an event handler for the Window.SizeChanged platform lifecycle event:
using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents; ... public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp() { var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder(); builder .UseMauiApp<App>() .ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events => { #if WINDOWS events.AddWindows(windows => windows .OnWindowCreated(window => { window.SizeChanged += OnSizeChanged; })); #endif }); return builder.Build(); }In the event handler for the platform lifecycle event, retrieve the
ILifecycleEventServiceinstance and call itsInvokeEventsmethod, specifying the platform event name as its argument:using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents; ... #if WINDOWS static void OnSizeChanged(object sender, Microsoft.UI.Xaml.WindowSizeChangedEventArgs args) { ILifecycleEventService service = MauiWinUIApplication.Current.Services.GetRequiredService<ILifecycleEventService>(); service.InvokeEvents(nameof(Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window.SizeChanged)); } #endifThe
MauiWinUIApplicationtype on Windows can be used to access the native app instance via itsCurrentproperty. TheMauiApplicationtype on Android can be used to access the native app instance. Similarly, theMauiUIApplicationDelegatetype on iOS can be used to access the native app instance.Warning
Invoking an unregistered event, with the
InvokeEventsmethod, doesn't throw an exception.In the
CreateMauiAppmethod of yourMauiProgramclass, call theConfigureLifecycleEventsmethod on theMauiAppBuilderobject. Then, on theILifecycleBuilderobject, call theAddEventmethod and specify the platform event name and theActionthat will be invoked when the platform event is raised:using Microsoft.Maui.LifecycleEvents; namespace PlatformLifecycleDemo { public static class MauiProgram { public static MauiApp CreateMauiApp() { var builder = MauiApp.CreateBuilder(); builder .UseMauiApp<App>() .ConfigureLifecycleEvents(events => { #if WINDOWS events.AddWindows(windows => windows .OnWindowCreated(window => { window.SizeChanged += OnSizeChanged; })); events.AddEvent(nameof(Microsoft.UI.Xaml.Window.SizeChanged), () => LogEvent("Window SizeChanged")); #endif static bool LogEvent(string eventName, string type = null) { System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine($"Lifecycle event: {eventName}{(type == null ? string.Empty : $" ({type})")}"); return true; } }); return builder.Build(); } } }
The overall effect is that when a user changes the app window size on Windows, the action specified in the AddEvent method is executed.
Note
The AddEvent method also has an overload that enables a delegate to be specified.
