How to enable hardware acceleration with Android emulators (Hyper-V & AEHD)
With Visual Studio, you can easily test and debug your .NET MAUI app for Android in emulators for situations where an Android device isn't available. However, if hardware acceleration isn't available or enabled, the emulator will run very slowly. You can significantly improve the performance of the emulator by enabling hardware acceleration and by using virtual device images that are appropriate for your processor architecture. For more information, see Configure hardware acceleration for the Android Emulator on developer.android.com.
The emulator provides versatile networking capabilities that can be used for different purposes, including connecting to an emulator running on a Mac from inside a Windows virtual machine (VM). For more information, see Connect to an Android emulator on a Mac from inside a Windows virtual machine.
On macOS, the Android emulator uses the built-in Hypervisor.Framework. For more information, see Hypervisor on developer.apple.com.
Accelerate Android emulators on Windows
The following virtualization technologies are available for accelerating the Android emulator on Windows:
- The Windows Hypervisor Platform (WHPX). Hyper-V is a virtualization feature of Windows that makes it possible to run virtualized computer systems on a physical host computer.
- The Android Emulator hypervisor driver (AEHD).
Note
The Intel Hardware Accelerated Execution Manager (HAXM) is deprecated from emulator 33.x.x.x, and has been replaced by AEHD on Intel processors. For information about using HAXM on emulator 32.x.x.x and lower, see Configure VM acceleration using Intel HAXM on Windows on developer.android.com.
For the best experience on Windows, it's recommended you use WHPX to accelerate the Android emulator. If WHPX isn't available on your computer, then AEHD can be used. The Android emulator automatically uses hardware acceleration if the following criteria are met:
- Hardware acceleration is available and enabled on your development computer.
- The emulator is running a system image created for an x86-64 or x86-based virtual device.
Important
A Virtual Machine (VM) accelerated emulator can run inside another VM, including Microsoft Dev Box, provided that nested virtualization is enabled in the VM.
For information about launching and debugging with the Android emulator, see Debugging on the Android Emulator.
Accelerate with Hyper-V
Before enabling Hyper-V, read the following section to verify that your computer supports Hyper-V.
Verify support for Hyper-V
Hyper-V runs on the Windows Hypervisor Platform. To use the Android emulator with Hyper-V, your computer must meet the following criteria to support the Windows Hypervisor Platform:
Your computer hardware must meet the following requirements:
- Intel processors with support for Virtualization Technology (VT-x), Extended Page Tables (EPT), and Unrestricted Guest (UG) features. VT-x must be enabled in your computer's BIOS.
- AMD processors: AMD Ryzen processor recommended. Virtualization or SVM must be enabled in your computer's BIOS.
Your computer must be running the Enterprise, Pro, or Education versions of Windows 11 or Windows 10 Version 1909 or later.
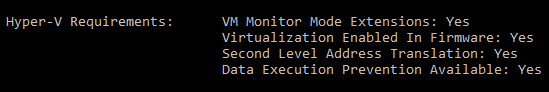
To verify that your computer hardware and software is compatible with Hyper-V, open a command prompt and type the following command:
systeminfo
If all listed Hyper-V requirements have a value of Yes, then your computer can support Hyper-V. For example:
If the Hyper-V result indicates that a hypervisor is currently running, Hyper-V is already enabled.
Important
If Windows is running inside a virtual machine, nested virtualization must be enabled in the host hypervisor.
Enable Hyper-V acceleration in Windows
If your computer meets the above criteria, use the following steps to accelerate the Android emulator with Hyper-V:
Enter windows features in the Windows search box and select Turn Windows features on or off in the search results. In the Windows Features dialog, enable both Hyper-V and Windows Hypervisor Platform:
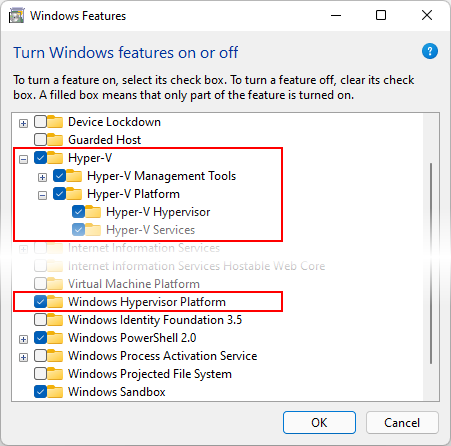
After making these changes, reboot your computer.
Important
On Windows 10 October 2018 Update (RS5) and higher, you only need to enable Hyper-V, as it will use Windows Hypervisor Platform (WHPX) automatically.
Make sure that the virtual device you created in the Android Device Manager is an x86-64 or x86-based system image. If you use an Arm-based system image, the virtual device won't be accelerated and will run slowly.
After Hyper-V is enabled, you'll be able to run your accelerated Android emulator.
Accelerate with AEHD
If your computer doesn't support Hyper-V, you should use AEHD to accelerate the Android emulator. Before you can install and use AEHD, read the following section to verify that your computer supports AEHD.
Verify support for AEHD
Your computer must meet the following criteria to support AEHD:
- An Intel or AMD processor with virtualization extension, which must be enabled in your BIOS.
- 64-bit Windows 11 or Windows 10.
- Hyper-V must be turned off.
Note
Several features in Windows enable Hyper-V implicitly. For more information, see Double-check when disabling Hyper-V on developer.android.com.
Enable AEHD acceleration in Windows
If your computer meets the above criteria, use the following steps to accelerate the Android emulator with AEHD:
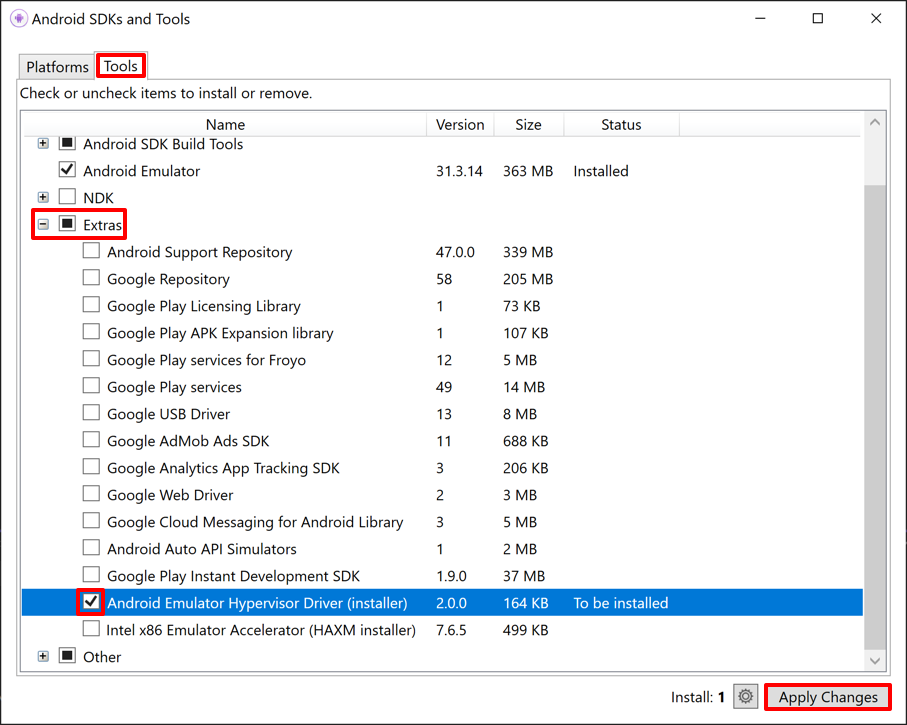
In Visual Studio, select the Tools > Android > Android SDK Manager... menu item.
In the Android SDKs and Tools window, select the Tools tab.
In the Tools tab, expand Extras, tick the checkbox for the Android Emulator Hypervisor Driver (installer) item, and then select the Apply Changes button:
Note
Alternatively, AEHD can be downloaded and installed from GitHub. After unpacking the driver package, run
silent_install.batat a command line with administrator privileges.Make sure that the virtual device you created in the Android Device Manager is an x86-64 or x86-based system image. If you use an Arm-based system image, the virtual device won't be accelerated and will run slowly.
AEHD 2.1 and higher
After installation, confirm that the driver is operating correctly using the following command:
sc query aehd
If the driver is operating correctly, the status message will include the following information:
SERVICE_NAME: aehd
...
STATE : 4 RUNNING
...
The following error message means that the virtualization extension isn't enabled in your BIOS or that Hyper-V isn't disabled:
SERVICE_NAME: aehd
...
STATE : 1 STOPPED
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 4294967201 (0xffffffa1)
...
After AEHD is installed and running, you'll be able to run your accelerated Android emulator.
AEHD 2.0 and lower
After installation, confirm that the driver is operating correctly using the following command:
sc query gvm
If the driver is operating correctly, the status message will include the following information:
SERVICE_NAME: gvm
...
STATE : 4 RUNNING
...
The following error message means that the virtualization extension isn't enabled in your BIOS or that Hyper-V isn't disabled:
SERVICE_NAME: gvm
...
STATE : 1 STOPPED
WIN32_EXIT_CODE : 4294967201 (0xffffffa1)
...
After AEHD is installed and running, you'll be able to run your accelerated Android emulator.
Uninstall AEHD
To uninstall AEHD, use the following commands at a command line with administrator privileges:
AEHD 2.1 and higher
sc stop aehd sc delete aehdAEHD 2.0 and lower
sc stop gvm sc delete gvm
Important
Shut down any x86 emulators before uninstalling AEHD for AMD.
Troubleshoot
For help with troubleshooting hardware acceleration issues, see the Android emulator Troubleshooting guide.