Security considerations for Azure VMware Solution workloads
This article discusses the security design area of an Azure VMware Solution workload. The discussion covers various measures for helping to secure and protect Azure VMware Solution workloads. These measures help protect infrastructure, data, and applications. This approach to security is holistic and aligns with an organization's core priorities.
Securing Azure VMware Solution requires a shared responsibility model, where Microsoft Azure and VMware are responsible for certain security aspects. To implement appropriate security measures, ensure a clear understanding of the shared responsibility model and collaboration between IT teams, VMware, and Microsoft.
Manage compliance and governance
Impact: Security, Operational Excellence
To avoid deleting the private cloud by mistake, use resource locks to safeguard resources from unwanted deletion or change. They can be set at the subscription, resource group, or resource level and block deletions, modifications, or both.
It's also important to detect noncompliant servers. You can use Azure Arc for this purpose. Azure Arc extends Azure management capabilities and services to on-premises or multicloud environments. Azure Arc gives you a single-pane view for applying updates and hotfixes by providing centralized server management and governance. The result is a consistent experience for managing components from Azure, on-premises systems, and Azure VMware Solution.
Recommendations
- Put a resource lock on the resource group that hosts the private cloud to prevent accidentally deleting it.
- Configure Azure VMware Solution guest virtual machines (VMs) as Azure Arc–enabled servers. For methods that you can use to connect machines, see Azure connected machine agent deployment options.
- Deploy a certified third-party solution or Azure Arc for Azure VMware Solution (preview).
- Use Azure Policy for Azure Arc–enabled servers to audit and enforce security controls on Azure VMware Solution guest VMs.
Protect the guest operating system
Impact: Security
If you don't patch and regularly update your operating system, you make it susceptible to vulnerabilities and put your entire platform at risk. When you apply patches regularly, you keep your system up to date. When you use an endpoint protection solution, you help prevent common attack vectors from targeting your operating system. It's also important to regularly perform vulnerability scans and assessments. These tools help you identify and remediate security weaknesses and vulnerabilities.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud offers unique tools that provide advanced threat protection across Azure VMware Solution and on-premises VMs, including:
- File integrity monitoring.
- Fileless attack detection.
- Operating system patch assessment.
- Security misconfiguration assessment.
- Endpoint protection assessment.
Recommendations
- Install an Azure security agent on Azure VMware Solution guest VMs through Azure Arc for servers to monitor them for security configurations and vulnerabilities.
- Configure Azure Arc machines to automatically create an association with the default data collection rule for Defender for Cloud.
- On the subscription you use to deploy and run the Azure VMware Solution private cloud, use a Defender for Cloud plan that includes server protection.
- If you have guest VMs with extended security benefits in the Azure VMware Solution private cloud, deploy security updates regularly. Use the Volume Activation Management Tool to deploy these updates.
Encrypt data
Impact: Security, Operational Excellence
Data encryption is an important aspect of protecting your Azure VMware Solution workload from unauthorized access and preserving the integrity of sensitive data. Encryption includes data at rest on the systems and data in transit.
Recommendations
- Encrypt VMware vSAN datastores with customer-managed keys to encrypt data at rest.
- Use native encryption tools such as BitLocker to encrypt guest VMs.
- Use native database encryption options for databases that run on Azure VMware Solution private cloud guest VMs. For instance, you can use transparent data encryption (TDE) for SQL Server.
- Monitor database activities for suspicious activity. You can use native database monitoring tools like SQL Server Activity Monitor.
Implement network security
Impact: Operational excellence
A goal of network security is to prevent unauthorized access to Azure VMware Solution components. One method for achieving this goal is to implement boundaries via network segmentation. This practice helps to isolate your applications. As part of segmentation, a virtual LAN operates at your data-link layer. That virtual LAN provides physical separation of your VMs by partitioning the physical network into logical ones to separate traffic.
Segments are then created to provide advanced security capabilities and routing. For example, the application, web, and database tier can have separate segments in a three-tier architecture. The application can add a level of micro-segmentation by using security rules to restrict network communication between the VMs in each segment.
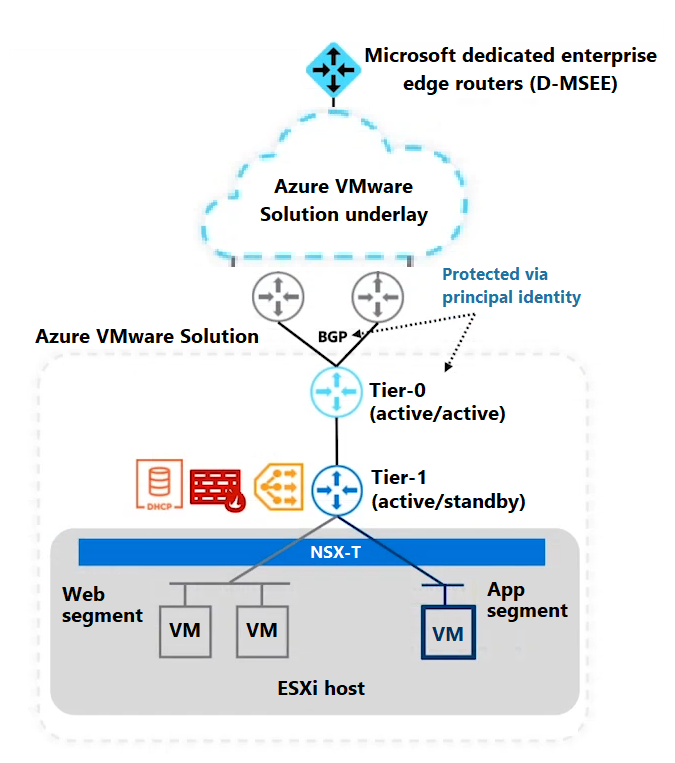
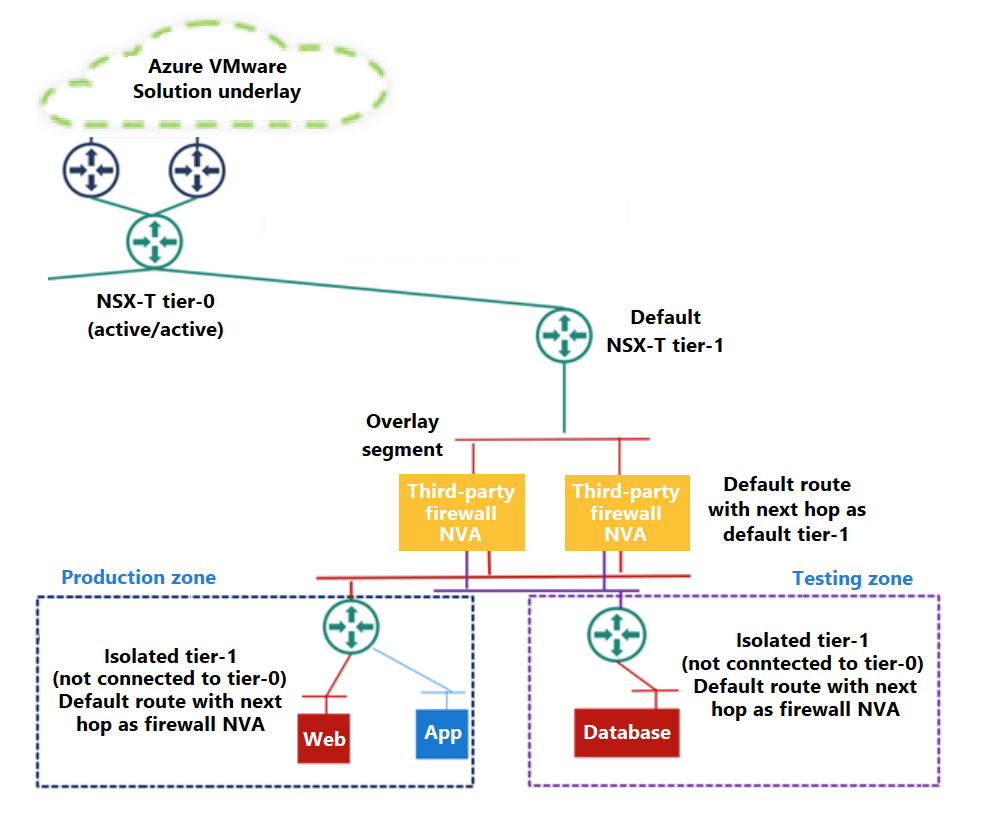
The tier-1 routers are positioned in front of the segments. These routers provide routing capabilities within the software-defined datacenter (SDDC). You can deploy multiple tier-1 routers to segregate different sets of segments or to achieve a specific routing. For example, say you'd like to restrict East-West traffic that flows to and from your production, development, and testing workloads. You can use distributed level-1 tiers to segment and filter that traffic based on specific rules and policies.
Recommendations
- Use network segments to separate and monitor components logically.
- Use micro-segmentation capabilities that are native to VMware NSX-T Data Center to restrict network communication between application components.
- Use a centralized routing appliance to secure and optimize routing between segments.
- Use staggered tier-1 routers when network segmentation is driven by organizational security or networking policies, compliance requirements, business units, departments, or environments.
Use an intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS)
Impact: Security
An IDPS can help you detect and prevent network-based attacks and malicious activity in your Azure VMware Solution environment.
Recommendations
- Use the VMware NSX-T Data Center distributed firewall for help with detecting malicious patterns and malware in East-West traffic between your Azure VMware Solution components.
- Use an Azure service such as Azure Firewall or a certified third-party NVA that runs in Azure or in Azure VMware Solution.
Use role-based access control (RBAC) and multifactor authentication
Impact: Security, Operational excellence
Identity security helps control access to Azure VMware Solution private cloud workloads and the applications that run on them. You can use RBAC to assign roles and permissions that are appropriate for specific users and groups. These roles and permissions are granted based on the principle of least privilege.
You can enforce multifactor authentication for user authentication to provide an extra layer of security against unauthorized access. Various multifactor authentication methods, such as mobile push notifications, offer a convenient user experience and also help to ensure strong authentication. You can integrate Azure VMware Solution with Microsoft Entra ID to centralize user management and take advantage of Microsoft Entra advanced security features. Examples of features include privileged identity management, multifactor authentication, and conditional access.
Recommendations
- Use Microsoft Entra Privileged Identity Management to allow time-bound access to the Azure portal and control pane operations. Use privileged identity management audit history to track operations that highly privileged accounts perform.
- Reduce the number of Microsoft Entra accounts that can:
- Access the Azure portal and APIs.
- Navigate to the Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
- Read VMware vCenter Server and VMware NSX-T Data Center admin accounts.
- Rotate local
cloudadminaccount credentials for VMware vCenter Server and VMware NSX-T Data Center to prevent the misuse and abuse of these administrative accounts. Use these accounts only in break glass scenarios. Create server groups and users for VMware vCenter Server, and assign them identities from external identity sources. Use these groups and users for specific VMware vCenter Server and VMware NSX-T Data Center operations. - Use a centralized identity source for configuring authentication and authorization services for guest VMs and applications.
Monitor security and detect threats
Impact: Security, Operational excellence
Security monitoring and threat detection involve detecting and responding to changes in the security posture of Azure VMware Solution private cloud workloads. It's important to follow industry best practices and comply with regulatory requirements, including:
- The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS).
You can use a security information and event management (SIEM) tool or Microsoft Sentinel to aggregate, monitor, and analyze security logs and events. This information helps you detect and respond to potential threats. Regularly conducting audit reviews also helps you avert threats. When you regularly monitor your Azure VMware Solution environment, you're in a better position to ensure it aligns with security standards and policies.
Recommendations
- Automate responses to recommendations from Defender for Cloud by using the following Azure policies:
- Workflow automation for security alerts
- Workflow automation for security recommendations
- Workflow automation for regulatory compliance changes
- Deploy Microsoft Sentinel and set the destination to a Log Analytics workspace to collect logs from Azure VMware Solution private cloud guest VMs.
- Use a data connector to connect Microsoft Sentinel and Defender for Cloud.
- Automate threat responses by using Microsoft Sentinel playbooks and Azure Automation rules.
Establish a security baseline
Impact: Security
The Microsoft cloud security benchmark provides recommendations about how you can secure your cloud solutions on Azure. This security baseline applies controls that are defined by Microsoft cloud security benchmark version 1.0 to Azure Policy.
Recommendations
- To help protect your workload, apply the recommendations that are given in Azure security baseline for Azure VMware Solution.
Next steps
Now that you've looked at best practices for securing Azure VMware Solution, investigate operational management procedures for achieving business excellence.
Use the assessment tool to evaluate your design choices.