Quickstart: Create and query a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) in Azure synapse Analytics using the Azure portal
Quickly create and query a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) in Azure Synapse Analytics using the Azure portal.
Important
This quickstart helps you to create a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). To create a dedicated SQL pool in Azure Synapse Analytics workspace and take advantage of the latest features and integration in your Azure Synapse Analytics workspace, instead use Quickstart: Create a dedicated SQL pool using Synapse Studio.
Prerequisites
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free Azure account before you begin.
Note
Creating a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) in Azure Synapse may result in a new billable service. For more information, see Azure Synapse Analytics pricing.
Download and install the newest version of SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Note: SSMS is only available on Windows based platforms, see the full list of supported platforms.
Sign in to the Azure portal
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Create a SQL pool
Data warehouses are created using dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) in Azure Synapse Analytics. A dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) is created with a defined set of compute resources. The database is created within an Azure resource group and in a logical SQL server.
Follow these steps to create a dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) that contains the AdventureWorksDW sample data.
Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the Azure portal.
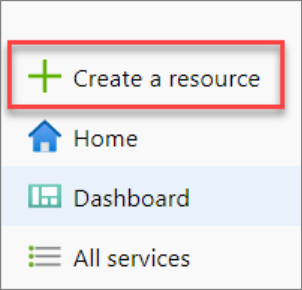
In the search bar, type "dedicated SQL pool" and select dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). Select Create on the page that opens.
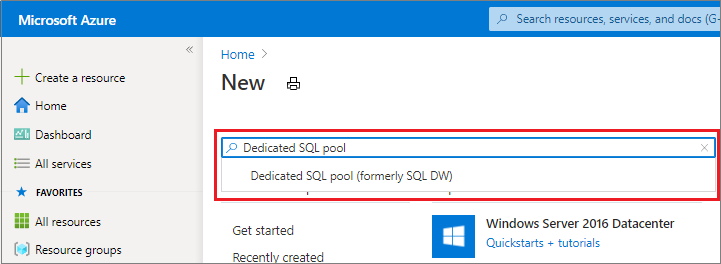
In Basics, provide your subscription, resource group, dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) name, and server name:
Setting Suggested value Description Subscription Your subscription For details about your subscriptions, see Subscriptions. Resource group myResourceGroup For valid resource group names, see Naming rules and restrictions. SQL pool name Any globally unique name (An example is mySampleDataWarehouse) For valid database names, see Database Identifiers. Server Any globally unique name Select existing server, or create a new server name, select Create new. For valid server names, see Naming rules and restrictions. 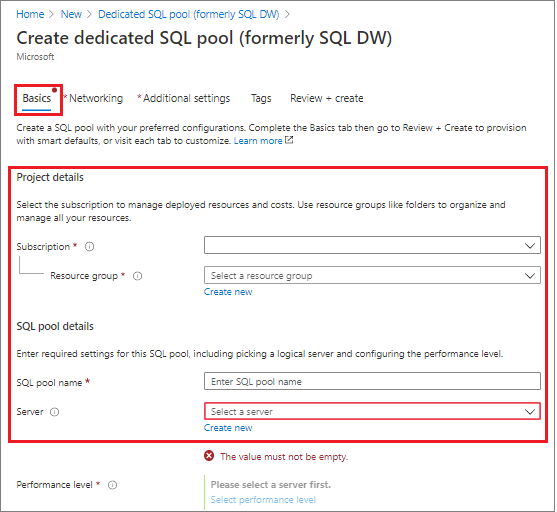
Under Performance level, select Select performance level to optionally change your configuration with a slider.
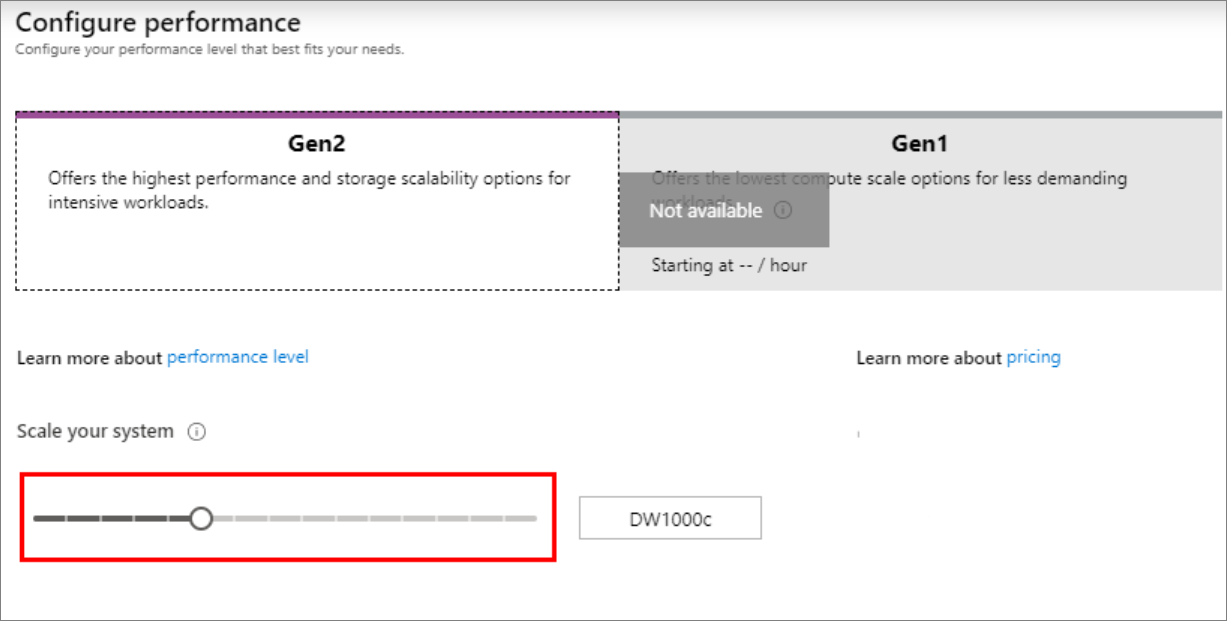
For more information about performance levels, see Manage compute in Azure Synapse Analytics.
Select Additional Settings, under Use existing data, choose Sample so that
AdventureWorksDWwill be created as the sample database.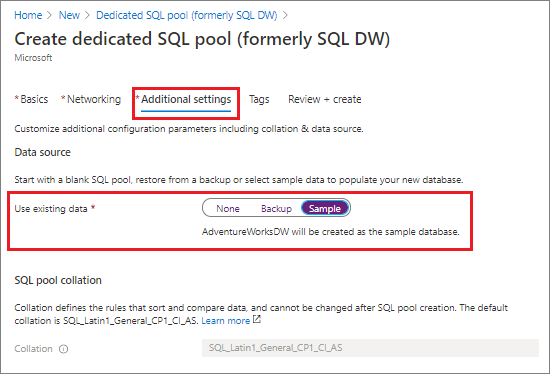
Now that you've completed the Basics tab of the Azure Synapse Analytics form, select Review + Create and then Create to create the SQL pool. Provisioning takes a few minutes.

On the toolbar, select Notifications to monitor the deployment process.
Create a server-level firewall rule
The Azure Synapse service creates a firewall at the server-level. This firewall prevents external applications and tools from connecting to the server or any databases on the server. To enable connectivity, you can add firewall rules that enable connectivity for specific IP addresses. Follow these steps to create a server-level firewall rule for your client's IP address.
Note
Azure Synapse communicates over port 1433. If you are trying to connect from within a corporate network, outbound traffic over port 1433 might not be allowed by your network's firewall. If so, you cannot connect to your server unless your IT department opens port 1433.
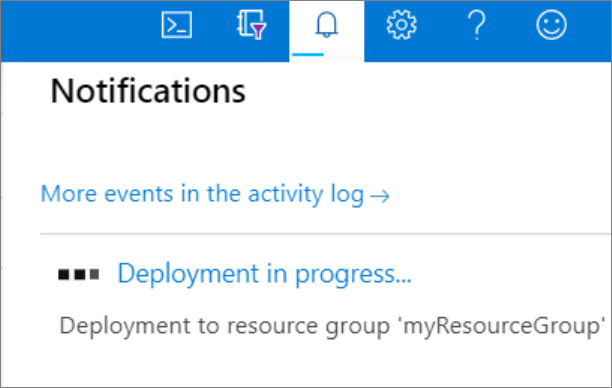
After the deployment completes, select All services from the menu. Select Databases, select the star next to Azure Synapse Analytics to add Azure Synapse Analytics to your favorites.
Select Azure Synapse Analytics from the left-hand menu and then select mySampleDataWarehouse on the Azure Synapse Analytics page. The overview page for your database opens, showing you the fully qualified server name (such as
sqlpoolservername.database.windows.net) and provides options for further configuration.Copy this fully qualified server name for use to connect to your server and its databases in this and other quick starts. To open server settings, select the server name.
Select Show firewall settings.
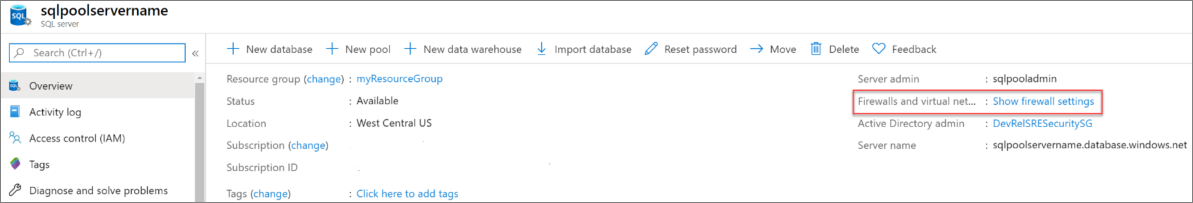
The Firewall settings page for the server opens.
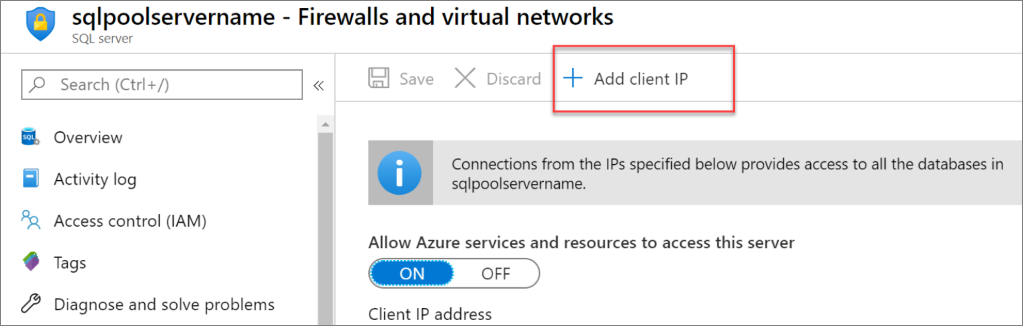
To add your current IP address to a new firewall rule, select Add client IP on the toolbar. A firewall rule can open port 1433 for a single IP address or a range of IP addresses.
Select Save. A server-level firewall rule is created for your current IP address opening port 1433 on the server.
Select OK and then close the Firewall settings page.
You can now connect to the server and its SQL pools using this IP address. The connection works from SQL Server Management Studio or another tool of your choice. When you connect, use the ServerAdmin account you created previously.
Important
By default, access through the SQL Database firewall is enabled for all Azure services. Select OFF on this page and then select Save to disable the firewall for all Azure services.
Get the fully qualified server name
Get the fully qualified server name for your server in the Azure portal. Later you use the fully qualified name when connecting to the server.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Select Azure Synapse Analytics from the left-hand menu, and select your workspace on the Azure Synapse Analytics page.
In the Essentials pane in the Azure portal page for your database, locate and then copy the Server name. In this example, the fully qualified name is
sqlpoolservername.database.windows.net.
Connect to the server as server admin
This section uses SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to establish a connection to your server.
Open SQL Server Management Studio.
In the Connect to Server dialog box, enter the following information:
Setting Suggested value Description Server type Database engine This value is required Server name The fully qualified server name Here's an example: sqlpoolservername.database.windows.net.Authentication SQL Server Authentication SQL Authentication is the only authentication type that is configured in this tutorial. Login The server admin account Account that you specified when you created the server. Password The password for your server admin account Password that you specified when you created the server. 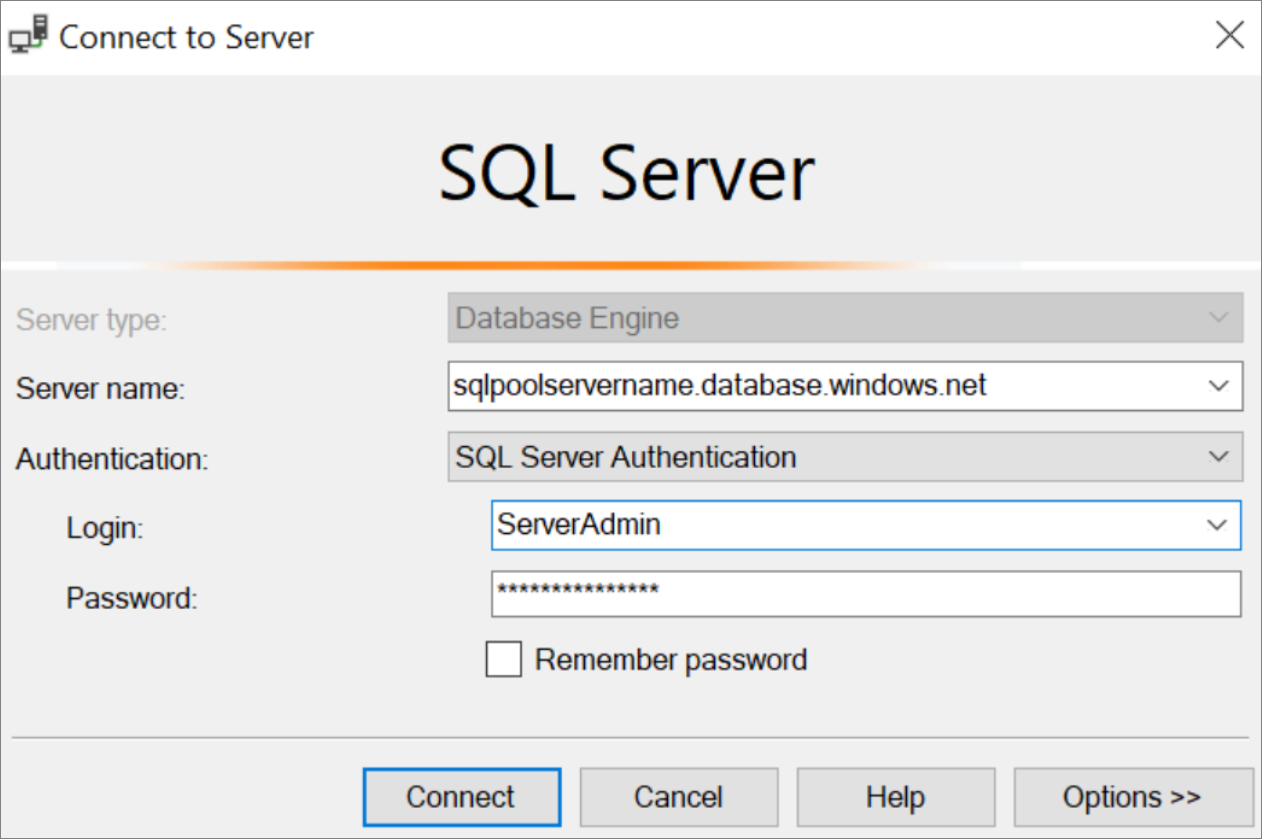
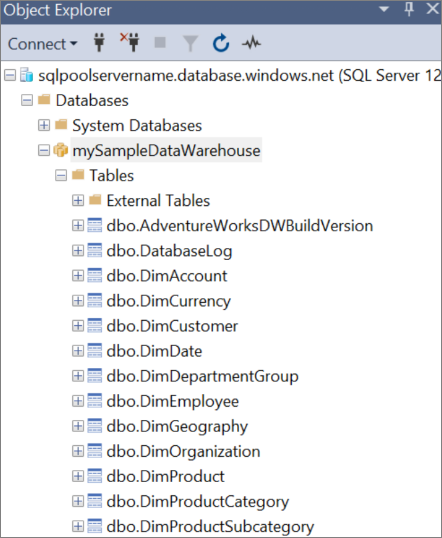
Select Connect. The Object Explorer window opens in SSMS.
In Object Explorer, expand Databases. Then expand mySampleDatabase to view the objects in your new database.
Run some queries
It is not recommended to run large queries while being logged as the server admin, as it uses a limited resource class. Instead configure Workload Isolation as illustrated in the tutorials.
Azure Synapse Analytics uses T-SQL as the query language. To open a query window and run some T-SQL queries, use the following steps in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS):
In Object Explorer, right-click mySampleDataWarehouse and select New Query. A new query window opens.
In the query window, enter the following command to see a list of databases.
SELECT * FROM sys.databasesSelect Execute. The query results show two databases:
masterandmySampleDataWarehouse.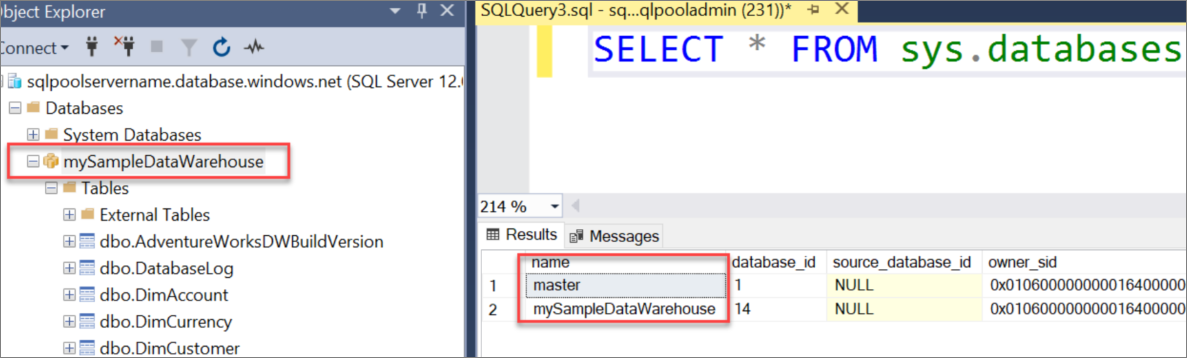
To look at some data, use the following command to see the number of customers with last name of Adams that have three children at home. The results list six customers.
SELECT LastName, FirstName FROM dbo.dimCustomer WHERE LastName = 'Adams' AND NumberChildrenAtHome = 3;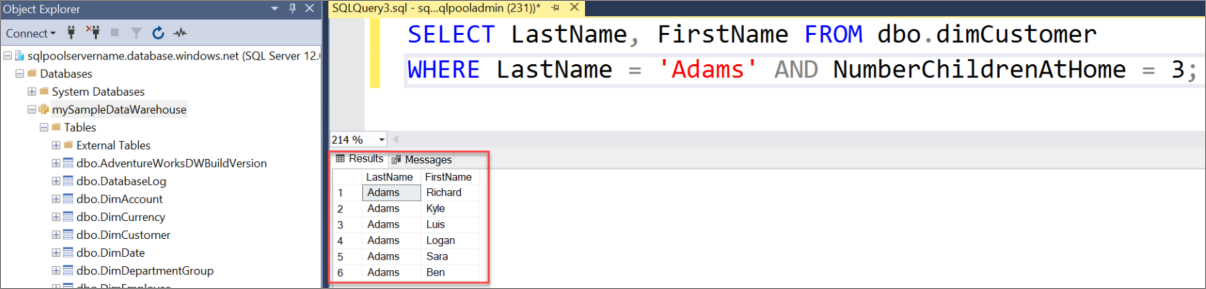
Clean up resources
You're being charged for data warehouse units and data stored your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). These compute and storage resources are billed separately.
If you want to keep the data in storage, you can pause compute when you aren't using the dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW). By pausing compute, you're only charged for data storage. You can resume compute whenever you're ready to work with the data.
If you want to remove future charges, you can delete the dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW).
Follow these steps to clean up resources you no longer need.
Sign in to the Azure portal, select your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW).
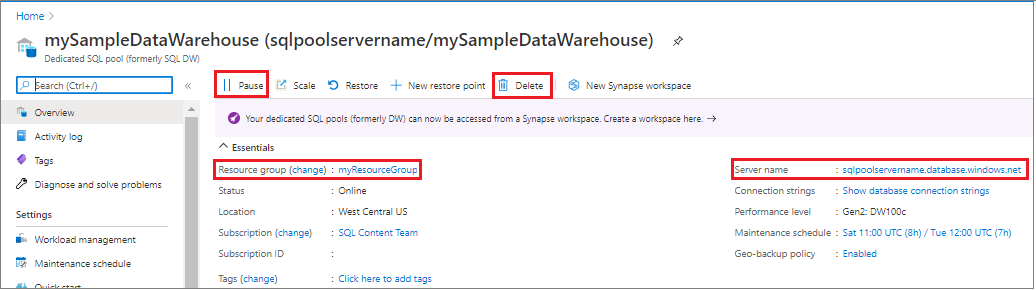
To pause compute, select the Pause button. When the dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) is paused, you see a Resume button. To resume compute, select Resume.
To remove the dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW) so you aren't charged for compute or storage, select Delete.
To remove the server you created, select sqlpoolservername.database.windows.net in the previous image, and then select Delete. Be careful with this deletion, since deleting the server also deletes all databases assigned to the server.
To remove the resource group, select myResourceGroup, and then select Delete resource group.
Want to optimize and save on your cloud spending?
Azure services cost money. Azure Cost Management helps you set budgets and configure alerts to keep spending under control. Analyze, manage, and optimize your Azure costs with Cost Management. To learn more, see the quickstart on analyzing your costs.
Next steps
- To learn more about loading data into your dedicated SQL pool (formerly SQL DW), continue to the Load data into a dedicated SQL pool article.