High availability of SAP HANA on Azure VMs on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
For on-premises development, you can use either HANA System Replication or shared storage to establish high availability (HA) for SAP HANA. On Azure Virtual Machines, HANA System Replication on Azure is currently the only supported HA function.
SAP HANA Replication consists of one primary node and at least one secondary node. Changes to the data on the primary node are replicated to the secondary node synchronously or asynchronously.
This article describes how to deploy and configure virtual machines (VMs), install the cluster framework, and install and configure SAP HANA System Replication.
In the example configurations, installation commands, instance number 03, and HANA System ID HN1 are used.
Prerequisites
Read the following SAP Notes and papers first:
- SAP Note 1928533, which has:
- The list of Azure VM sizes that are supported for the deployment of SAP software.
- Important capacity information for Azure VM sizes.
- The supported SAP software and operating system (OS) and database combinations.
- The required SAP kernel version for Windows and Linux on Microsoft Azure.
- SAP Note 2015553 lists prerequisites for SAP-supported SAP software deployments in Azure.
- SAP Note 2002167 has recommended OS settings for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- SAP Note 2009879 has SAP HANA Guidelines for Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
- SAP Note 3108302 has SAP HANA Guidelines for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 9.x.
- SAP Note 2178632 has detailed information about all monitoring metrics reported for SAP in Azure.
- SAP Note 2191498 has the required SAP Host Agent version for Linux in Azure.
- SAP Note 2243692 has information about SAP licensing on Linux in Azure.
- SAP Note 1999351 has more troubleshooting information for the Azure Enhanced Monitoring Extension for SAP.
- SAP Community WIKI has all required SAP Notes for Linux.
- Azure Virtual Machines planning and implementation for SAP on Linux
- Azure Virtual Machines deployment for SAP on Linux (this article)
- Azure Virtual Machines DBMS deployment for SAP on Linux
- SAP HANA System Replication in a Pacemaker cluster
- General RHEL documentation:
- Azure-specific RHEL documentation:
Overview
To achieve HA, SAP HANA is installed on two VMs. The data is replicated by using HANA System Replication.
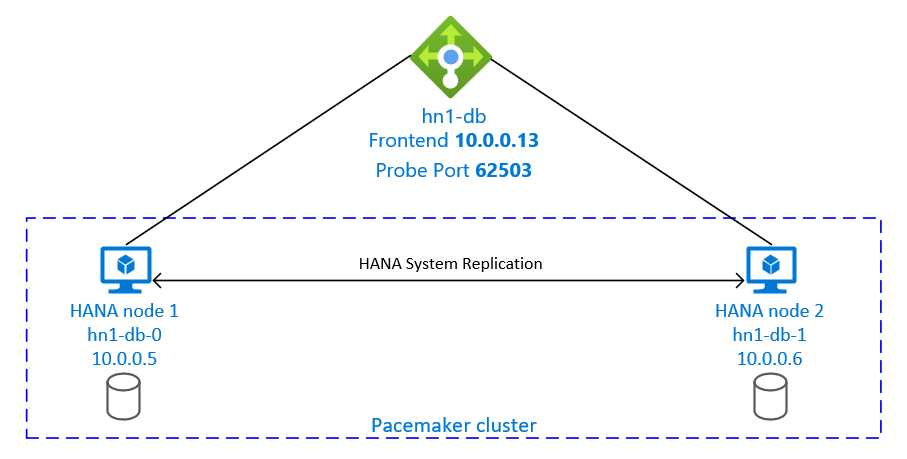
The SAP HANA System Replication setup uses a dedicated virtual hostname and virtual IP addresses. On Azure, a load balancer is required to use a virtual IP address. The presented configuration shows a load balancer with:
- Front-end IP address: 10.0.0.13 for hn1-db
- Probe port: 62503
Prepare the infrastructure
Azure Marketplace contains images qualified for SAP HANA with the High Availability add-on, which you can use to deploy new VMs by using various versions of Red Hat.
Deploy Linux VMs manually via the Azure portal
This document assumes that you've already deployed a resource group, an Azure virtual network, and a subnet.
Deploy VMs for SAP HANA. Choose a suitable RHEL image that's supported for the HANA system. You can deploy a VM in any one of the availability options: virtual machine scale set, availability zone, or availability set.
Important
Make sure that the OS you select is SAP certified for SAP HANA on the specific VM types that you plan to use in your deployment. You can look up SAP HANA-certified VM types and their OS releases in SAP HANA Certified IaaS Platforms. Make sure that you look at the details of the VM type to get the complete list of SAP HANA-supported OS releases for the specific VM type.
Configure Azure load balancer
During VM configuration, you have an option to create or select exiting load balancer in networking section. Follow below steps, to setup standard load balancer for high availability setup of HANA database.
Follow the steps in Create load balancer to set up a standard load balancer for a high-availability SAP system by using the Azure portal. During the setup of the load balancer, consider the following points:
- Frontend IP Configuration: Create a front-end IP. Select the same virtual network and subnet name as your database virtual machines.
- Backend Pool: Create a back-end pool and add database VMs.
- Inbound rules: Create a load-balancing rule. Follow the same steps for both load-balancing rules.
- Frontend IP address: Select a front-end IP.
- Backend pool: Select a back-end pool.
- High-availability ports: Select this option.
- Protocol: Select TCP.
- Health Probe: Create a health probe with the following details:
- Protocol: Select TCP.
- Port: For example, 625<instance-no.>.
- Interval: Enter 5.
- Probe Threshold: Enter 2.
- Idle timeout (minutes): Enter 30.
- Enable Floating IP: Select this option.
Note
The health probe configuration property numberOfProbes, otherwise known as Unhealthy threshold in the portal, isn't respected. To control the number of successful or failed consecutive probes, set the property probeThreshold to 2. It's currently not possible to set this property by using the Azure portal, so use either the Azure CLI or the PowerShell command.
For more information about the required ports for SAP HANA, read the chapter Connections to Tenant Databases in the SAP HANA Tenant Databases guide or SAP Note 2388694.
Note
When VMs without public IP addresses are placed in the back-end pool of an internal (no public IP address) instance of Standard Azure Load Balancer, there's no outbound internet connectivity unless more configuration is performed to allow routing to public endpoints. For more information on how to achieve outbound connectivity, see Public endpoint connectivity for VMs using Azure Standard Load Balancer in SAP high-availability scenarios.
Important
Don't enable TCP timestamps on Azure VMs placed behind Azure Load Balancer. Enabling TCP timestamps could cause the health probes to fail. Set the parameter net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps to 0. For more information, see Load Balancer health probes and SAP Note 2382421.
Install SAP HANA
The steps in this section use the following prefixes:
- [A]: The step applies to all nodes.
- [1]: The step applies to node 1 only.
- [2]: The step applies to node 2 of the Pacemaker cluster only.
[A] Set up the disk layout: Logical Volume Manager (LVM).
We recommend that you use LVM for volumes that store data and log files. The following example assumes that the VMs have four data disks attached that are used to create two volumes.
List all the available disks:
ls /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun*Example output:
/dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun0 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun2 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun3Create physical volumes for all the disks that you want to use:
sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun0 sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun1 sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun2 sudo pvcreate /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun3Create a volume group for the data files. Use one volume group for the log files and one for the shared directory of SAP HANA:
sudo vgcreate vg_hana_data_HN1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun0 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun1 sudo vgcreate vg_hana_log_HN1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun2 sudo vgcreate vg_hana_shared_HN1 /dev/disk/azure/scsi1/lun3Create the logical volumes. A linear volume is created when you use
lvcreatewithout the-iswitch. We suggest that you create a striped volume for better I/O performance. Align the stripe sizes to the values documented in SAP HANA VM storage configurations. The-iargument should be the number of the underlying physical volumes, and the-Iargument is the stripe size.In this document, two physical volumes are used for the data volume, so the
-iswitch argument is set to 2. The stripe size for the data volume is 256KiB. One physical volume is used for the log volume, so no-ior-Iswitches are explicitly used for the log volume commands.Important
Use the
-iswitch and set it to the number of the underlying physical volume when you use more than one physical volume for each data, log, or shared volumes. Use the-Iswitch to specify the stripe size when you're creating a striped volume. See SAP HANA VM storage configurations for recommended storage configurations, including stripe sizes and number of disks. The following layout examples don't necessarily meet the performance guidelines for a particular system size. They're for illustration only.sudo lvcreate -i 2 -I 256 -l 100%FREE -n hana_data vg_hana_data_HN1 sudo lvcreate -l 100%FREE -n hana_log vg_hana_log_HN1 sudo lvcreate -l 100%FREE -n hana_shared vg_hana_shared_HN1 sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_hana_data_HN1/hana_data sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_hana_log_HN1/hana_log sudo mkfs.xfs /dev/vg_hana_shared_HN1/hana_sharedDon't mount the directories by issuing mount commands. Instead, enter the configurations into the
fstaband issue a finalmount -ato validate the syntax. Start by creating the mount directories for each volume:sudo mkdir -p /hana/data sudo mkdir -p /hana/log sudo mkdir -p /hana/sharedNext, create
fstabentries for the three logical volumes by inserting the following lines in the/etc/fstabfile:/dev/mapper/vg_hana_data_HN1-hana_data /hana/data xfs defaults,nofail 0 2 /dev/mapper/vg_hana_log_HN1-hana_log /hana/log xfs defaults,nofail 0 2 /dev/mapper/vg_hana_shared_HN1-hana_shared /hana/shared xfs defaults,nofail 0 2
Finally, mount the new volumes all at once:
sudo mount -a[A] Set up hostname resolution for all hosts.
You can either use a DNS server or modify the
/etc/hostsfile on all nodes by creating entries for all nodes like this in/etc/hosts:10.0.0.5 hn1-db-0 10.0.0.6 hn1-db-1
[A] Perform RHEL for HANA configuration.
Configure RHEL as described in the following notes:
- 2447641 - Additional packages required for installing SAP HANA SPS 12 on RHEL 7.X
- 2292690 - SAP HANA DB: Recommended OS settings for RHEL 7
- 2777782 - SAP HANA DB: Recommended OS Settings for RHEL 8
- 2455582 - Linux: Running SAP applications compiled with GCC 6.x
- 2593824 - Linux: Running SAP applications compiled with GCC 7.x
- 2886607 - Linux: Running SAP applications compiled with GCC 9.x
[A] Install SAP HANA, following SAP's documentation.
[A] Configure the firewall.
Create the firewall rule for the Azure Load Balancer probe port.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=62503/tcp sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=62503/tcp --permanent
Configure SAP HANA 2.0 System Replication
The steps in this section use the following prefixes:
- [A]: The step applies to all nodes.
- [1]: The step applies to node 1 only.
- [2]: The step applies to node 2 of the Pacemaker cluster only.
[A] Configure the firewall.
Create firewall rules to allow HANA System Replication and client traffic. The required ports are listed on TCP/IP Ports of All SAP Products. The following commands are just an example to allow HANA 2.0 System Replication and client traffic to database SYSTEMDB, HN1, and NW1.
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={40302,40301,40307,40303,40340,30340,30341,30342}/tcp --permanent sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port={40302,40301,40307,40303,40340,30340,30341,30342}/tcp[1] Create the tenant database.
Run the following command as <hanasid>adm:
hdbsql -u SYSTEM -p "[passwd]" -i 03 -d SYSTEMDB 'CREATE DATABASE NW1 SYSTEM USER PASSWORD "<passwd>"'[1] Configure system replication on the first node.
Back up the databases as <hanasid>adm:
hdbsql -d SYSTEMDB -u SYSTEM -p "<passwd>" -i 03 "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('initialbackupSYS')" hdbsql -d HN1 -u SYSTEM -p "<passwd>" -i 03 "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('initialbackupHN1')" hdbsql -d NW1 -u SYSTEM -p "<passwd>" -i 03 "BACKUP DATA USING FILE ('initialbackupNW1')"Copy the system PKI files to the secondary site:
scp /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/SSFS_HN1.DAT hn1-db-1:/usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/data/ scp /usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/SSFS_HN1.KEY hn1-db-1:/usr/sap/HN1/SYS/global/security/rsecssfs/key/Create the primary site:
hdbnsutil -sr_enable --name=SITE1[2] Configure system replication on the second node.
Register the second node to start the system replication. Run the following command as <hanasid>adm:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10 hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hn1-db-0 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=SITE2[2] Start HANA.
Run the following command as <hanasid>adm to start HANA:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StartSystem[1] Check replication status.
Check the replication status and wait until all databases are in sync. If the status remains UNKNOWN, check your firewall settings.
sudo su - hn1adm -c "python /usr/sap/HN1/HDB03/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py" # | Database | Host | Port | Service Name | Volume ID | Site ID | Site Name | Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Secondary | Replication | Replication | Replication | # | | | | | | | | Host | Port | Site ID | Site Name | Active Status | Mode | Status | Status Details | # | -------- | -------- | ----- | ------------ | --------- | ------- | --------- | --------- | --------- | --------- | --------- | ------------- | ----------- | ----------- | -------------- | # | SYSTEMDB | hn1-db-0 | 30301 | nameserver | 1 | 1 | SITE1 | hn1-db-1 | 30301 | 2 | SITE2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | HN1 | hn1-db-0 | 30307 | xsengine | 2 | 1 | SITE1 | hn1-db-1 | 30307 | 2 | SITE2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | NW1 | hn1-db-0 | 30340 | indexserver | 2 | 1 | SITE1 | hn1-db-1 | 30340 | 2 | SITE2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # | HN1 | hn1-db-0 | 30303 | indexserver | 3 | 1 | SITE1 | hn1-db-1 | 30303 | 2 | SITE2 | YES | SYNC | ACTIVE | | # # status system replication site "2": ACTIVE # overall system replication status: ACTIVE # # Local System Replication State # ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ # # mode: PRIMARY # site id: 1 # site name: SITE1
Create a Pacemaker cluster
Follow the steps in Setting up Pacemaker on Red Hat Enterprise Linux in Azure to create a basic Pacemaker cluster for this HANA server.
Important
With the systemd based SAP Startup Framework, SAP HANA instances can now be managed by systemd. The minimum required Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) version is RHEL 8 for SAP. As outlined in SAP Note 3189534, any new installations of SAP HANA SPS07 revision 70 or above, or updates to HANA systems to HANA 2.0 SPS07 revision 70 or above, SAP Startup framework will be automatically registered with systemd.
When using HA solutions to manage SAP HANA system replication in combination with systemd-enabled SAP HANA instances (refer to SAP Note 3189534), additional steps are necessary to ensure that the HA cluster can manage the SAP instance without systemd interference. So, for SAP HANA system integrated with systemd, additional steps outlined in Red Hat KBA 7029705 must be followed on all cluster nodes.
Implement SAP HANA system replication hooks
This important step optimizes the integration with the cluster and improves the detection when a cluster failover is needed. It is mandatory for correct cluster operation to enable the SAPHanaSR hook. We highly recommend that you configure both SAPHanaSR and ChkSrv Python hooks.
[A] Install the SAP HANA resource agents on all nodes. Make sure to enable a repository that contains the package. You don't need to enable more repositories, if you're using an RHEL 8.x or higher HA-enabled image.
# Enable repository that contains SAP HANA resource agents sudo subscription-manager repos --enable="rhel-sap-hana-for-rhel-7-server-rpms" sudo dnf install -y resource-agents-sap-hanaNote
For RHEL 8.x and RHEL 9.x, verify that the installed resource-agents-sap-hana package is version 0.162.3-5 or later.
[A] Install the HANA
system replication hooks. The configuration for the replication hooks needs to be installed on both HANA DB nodes.Stop HANA on both nodes. Run as <sid>adm.
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopSystemAdjust
global.inion each cluster node.[ha_dr_provider_SAPHanaSR] provider = SAPHanaSR path = /usr/share/SAPHanaSR/srHook execution_order = 1 [ha_dr_provider_chksrv] provider = ChkSrv path = /usr/share/SAPHanaSR/srHook execution_order = 2 action_on_lost = kill [trace] ha_dr_saphanasr = info ha_dr_chksrv = info
If you point parameter
pathto the default/usr/share/SAPHanaSR/srHooklocation, the Python hook code updates automatically through OS updates or package updates. HANA uses the hook code updates when it next restarts. With an optional own path like/hana/shared/myHooks, you can decouple OS updates from the hook version that HANA will use.You can adjust the behavior of
ChkSrvhook by using theaction_on_lostparameter. Valid values are [ignore|stop|kill].[A] The cluster requires
sudoersconfiguration on each cluster node for <sid>adm. In this example, that's achieved by creating a new file. Use thevisudocommand to edit the20-saphanadrop-in file asroot.sudo visudo -f /etc/sudoers.d/20-saphanaInsert the following lines and then save:
Cmnd_Alias SITE1_SOK = /usr/sbin/crm_attribute -n hana_hn1_site_srHook_SITE1 -v SOK -t crm_config -s SAPHanaSR Cmnd_Alias SITE1_SFAIL = /usr/sbin/crm_attribute -n hana_hn1_site_srHook_SITE1 -v SFAIL -t crm_config -s SAPHanaSR Cmnd_Alias SITE2_SOK = /usr/sbin/crm_attribute -n hana_hn1_site_srHook_SITE2 -v SOK -t crm_config -s SAPHanaSR Cmnd_Alias SITE2_SFAIL = /usr/sbin/crm_attribute -n hana_hn1_site_srHook_SITE2 -v SFAIL -t crm_config -s SAPHanaSR hn1adm ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: SITE1_SOK, SITE1_SFAIL, SITE2_SOK, SITE2_SFAIL Defaults!SITE1_SOK, SITE1_SFAIL, SITE2_SOK, SITE2_SFAIL !requiretty[A] Start SAP HANA on both nodes. Run as <sid>adm.
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StartSystem[1] Verify the SRHanaSR hook installation. Run as <sid>adm on the active HANA system replication site.
cdtrace awk '/ha_dr_SAPHanaSR.*crm_attribute/ \ { printf "%s %s %s %s\n",$2,$3,$5,$16 }' nameserver_*# 2021-04-12 21:36:16.911343 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2021-04-12 21:36:29.147808 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SFAIL # 2021-04-12 21:37:04.898680 ha_dr_SAPHanaSR SOK[1] Verify the ChkSrv hook installation. Run as <sid>adm on the active HANA system replication site.
cdtrace tail -20 nameserver_chksrv.trc
For more information on the implementation of the SAP HANA hooks, see Enabling the SAP HANA srConnectionChanged() hook and Enabling the SAP HANA srServiceStateChanged() hook for hdbindexserver process failure action (optional).
Create SAP HANA cluster resources
Create the HANA topology. Run the following commands on one of the Pacemaker cluster nodes. Throughout these instructions, be sure to substitute your instance number, HANA system ID, IP addresses, and system names, where appropriate.
sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
sudo pcs resource create SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03 SAPHanaTopology SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 \
op start timeout=600 op stop timeout=300 op monitor interval=10 timeout=600 \
clone clone-max=2 clone-node-max=1 interleave=true
Next, create the HANA resources.
Note
This article contains references to a term that Microsoft no longer uses. When the term is removed from the software, we'll remove it from this article.
If you're building a cluster on RHEL 7.x, use the following commands:
sudo pcs resource create SAPHana_HN1_03 SAPHana SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 PREFER_SITE_TAKEOVER=true DUPLICATE_PRIMARY_TIMEOUT=7200 AUTOMATED_REGISTER=false \
op start timeout=3600 op stop timeout=3600 \
op monitor interval=61 role="Slave" timeout=700 \
op monitor interval=59 role="Master" timeout=700 \
op promote timeout=3600 op demote timeout=3600 \
master notify=true clone-max=2 clone-node-max=1 interleave=true
sudo pcs resource create vip_HN1_03 IPaddr2 ip="10.0.0.13"
sudo pcs resource create nc_HN1_03 azure-lb port=62503
sudo pcs resource group add g_ip_HN1_03 nc_HN1_03 vip_HN1_03
sudo pcs constraint order SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone then SAPHana_HN1_03-master symmetrical=false
sudo pcs constraint colocation add g_ip_HN1_03 with master SAPHana_HN1_03-master 4000
sudo pcs resource defaults resource-stickiness=1000
sudo pcs resource defaults migration-threshold=5000
sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
If you're building a cluster on RHEL 8.x/9.x, use the following commands:
sudo pcs resource create SAPHana_HN1_03 SAPHana SID=HN1 InstanceNumber=03 PREFER_SITE_TAKEOVER=true DUPLICATE_PRIMARY_TIMEOUT=7200 AUTOMATED_REGISTER=false \
op start timeout=3600 op stop timeout=3600 \
op monitor interval=61 role="Slave" timeout=700 \
op monitor interval=59 role="Master" timeout=700 \
op promote timeout=3600 op demote timeout=3600 \
promotable notify=true clone-max=2 clone-node-max=1 interleave=true
sudo pcs resource create vip_HN1_03 IPaddr2 ip="10.0.0.13"
sudo pcs resource create nc_HN1_03 azure-lb port=62503
sudo pcs resource group add g_ip_HN1_03 nc_HN1_03 vip_HN1_03
sudo pcs constraint order SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone then SAPHana_HN1_03-clone symmetrical=false
sudo pcs constraint colocation add g_ip_HN1_03 with master SAPHana_HN1_03-clone 4000
sudo pcs resource defaults update resource-stickiness=1000
sudo pcs resource defaults update migration-threshold=5000
sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
To configure priority-fencing-delay for SAP HANA (applicable only as of pacemaker-2.0.4-6.el8 or higher), the following commands need to be executed.
Note
If you have a two-node cluster, you can configure the priority-fencing-delay cluster property. This property introduces a delay in fencing a node that has higher total resource priority when a split-brain scenario occurs. For more information, see Can Pacemaker fence the cluster node with the fewest running resources?.
The property priority-fencing-delay is applicable for pacemaker-2.0.4-6.el8 version or higher. If you're setting up priority-fencing-delay on an existing cluster, make sure to unset the pcmk_delay_max option in the fencing device.
sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
sudo pcs resource defaults update priority=1
sudo pcs resource update SAPHana_HN1_03-clone meta priority=10
sudo pcs property set priority-fencing-delay=15s
sudo pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
Important
It's a good idea to set AUTOMATED_REGISTER to false, while you're performing failover tests, to prevent a failed primary instance to automatically register as secondary. After testing, as a best practice, set AUTOMATED_REGISTER to true so that after takeover, system replication can resume automatically.
Make sure that the cluster status is okay and that all of the resources are started. Which node the resources are running on isn't important.
Note
The timeouts in the preceding configuration are only examples and might need to be adapted to the specific HANA setup. For instance, you might need to increase the start timeout, if it takes longer to start the SAP HANA database.
Use the command sudo pcs status to check the state of the cluster resources created:
# Online: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
#
# Full list of resources:
#
# azure_fence (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started hn1-db-0
# Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
# Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
# Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
# Masters: [ hn1-db-0 ]
# Slaves: [ hn1-db-1 ]
# Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
# nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-0
# vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-0
Configure HANA active/read-enabled system replication in Pacemaker cluster
Starting with SAP HANA 2.0 SPS 01, SAP allows active/read-enabled setups for SAP HANA System Replication, where the secondary systems of SAP HANA System Replication can be used actively for read-intense workloads.
To support such a setup in a cluster, a second virtual IP address is required, which allows clients to access the secondary read-enabled SAP HANA database. To ensure that the secondary replication site can still be accessed after a takeover has occurred, the cluster needs to move the virtual IP address around with the secondary SAPHana resource.
This section describes the other steps that are required to manage HANA active/read-enabled system replication in a Red Hat HA cluster with a second virtual IP.
Before you proceed further, make sure that you've fully configured the Red Hat HA cluster managing an SAP HANA database, as described in preceding segments of the documentation.
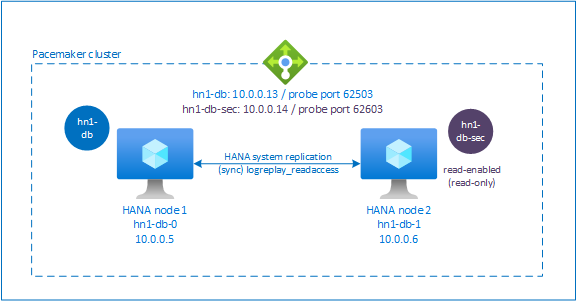
Additional setup in Azure Load Balancer for active/read-enabled setup
To proceed with more steps on provisioning a second virtual IP, make sure that you've configured Azure Load Balancer as described in the Deploy Linux VMs manually via Azure portal section.
For a standard load balancer, follow these steps on the same load balancer that you created in an earlier section.
a. Create a second front-end IP pool:
- Open the load balancer, select frontend IP pool, and select Add.
- Enter the name of the second front-end IP pool (for example, hana-secondaryIP).
- Set Assignment to Static and enter the IP address (for example, 10.0.0.14).
- Select OK.
- After the new front-end IP pool is created, note the pool IP address.
b. Create a health probe:
- Open the load balancer, select health probes, and select Add.
- Enter the name of the new health probe (for example, hana-secondaryhp).
- Select TCP as the protocol and port 62603. Keep the Interval value set to 5 and the Unhealthy threshold value set to 2.
- Select OK.
c. Create the load-balancing rules:
- Open the load balancer, select load balancing rules, and select Add.
- Enter the name of the new load balancer rule (for example, hana-secondarylb).
- Select the front-end IP address, the back-end pool, and the health probe that you created earlier (for example, hana-secondaryIP, hana-backend, and hana-secondaryhp).
- Select HA Ports.
- Make sure to enable Floating IP.
- Select OK.
Configure HANA active/read-enabled system replication
The steps to configure HANA System Replication are described in the Configure SAP HANA 2.0 System Replication section. If you're deploying a read-enabled secondary scenario while you're configuring system replication on the second node, run the following command as hanasidadm:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10
hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hn1-db-0 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=SITE2 --operationMode=logreplay_readaccess
Add a secondary virtual IP address resource for an active/read-enabled setup
The second virtual IP and the appropriate colocation constraint can be configured with the following commands:
pcs property set maintenance-mode=true
pcs resource create secvip_HN1_03 ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2 ip="10.40.0.16"
pcs resource create secnc_HN1_03 ocf:heartbeat:azure-lb port=62603
pcs resource group add g_secip_HN1_03 secnc_HN1_03 secvip_HN1_03
pcs constraint location g_secip_HN1_03 rule score=INFINITY hana_hn1_sync_state eq SOK and hana_hn1_roles eq 4:S:master1:master:worker:master
pcs constraint location g_secip_HN1_03 rule score=4000 hana_hn1_sync_state eq PRIM and hana_hn1_roles eq 4:P:master1:master:worker:master
# Set the priority to primary IPaddr2 and azure-lb resource if priority-fencing-delay is configured
sudo pcs resource update vip_HN1_03 meta priority=5
sudo pcs resource update nc_HN1_03 meta priority=5
pcs property set maintenance-mode=false
Make sure that the cluster status is okay and that all the resources are started. The second virtual IP runs on the secondary site along with the SAPHana secondary resource.
sudo pcs status
# Online: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
#
# Full List of Resources:
# rsc_hdb_azr_agt (stonith:fence_azure_arm): Started hn1-db-0
# Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]:
# Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
# Clone Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-clone [SAPHana_HN1_03] (promotable):
# Masters: [ hn1-db-0 ]
# Slaves: [ hn1-db-1 ]
# Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03:
# nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-0
# vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-0
# Resource Group: g_secip_HN1_03:
# secnc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-1
# secvip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-1
In the next section, you can find the typical set of failover tests to run.
Be aware of the second virtual IP behavior while you're testing a HANA cluster configured with read-enabled secondary:
When you migrate the SAPHana_HN1_03 cluster resource to the secondary site hn1-db-1, the second virtual IP continues to run on the same site hn1-db-1. If you've set
AUTOMATED_REGISTER="true"for the resource and HANA system replication is registered automatically on hn1-db-0, your second virtual IP also moves to hn1-db-0.On testing a server crash, the second virtual IP resources (secvip_HN1_03) and the Azure Load Balancer port resource (secnc_HN1_03) run on the primary server alongside the primary virtual IP resources. So, until the time that the secondary server is down, applications that are connected to the read-enabled HANA database connect to the primary HANA database. The behavior is expected because you don't want applications that are connected to the read-enabled HANA database to be inaccessible until the time the secondary server is unavailable.
During failover and fallback of the second virtual IP address, the existing connections on applications that use the second virtual IP to connect to the HANA database might get interrupted.
The setup maximizes the time that the second virtual IP resource is assigned to a node where a healthy SAP HANA instance is running.
Test the cluster setup
This section describes how you can test your setup. Before you start a test, make sure that Pacemaker doesn't have any failed action (via pcs status), there are no unexpected location constraints (for example, leftovers of a migration test), and that HANA is in sync state, for example, with systemReplicationStatus.
sudo su - hn1adm -c "python /usr/sap/HN1/HDB03/exe/python_support/systemReplicationStatus.py"
Test the migration
Resource state before starting the test:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-0
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-0
You can migrate the SAP HANA master node by running the following command as root:
# On RHEL 7.x
pcs resource move SAPHana_HN1_03-master
# On RHEL 8.x
pcs resource move SAPHana_HN1_03-clone --master
The cluster would migrate the SAP HANA master node and the group containing virtual IP address to hn1-db-1.
After the migration is done, the sudo pcs status output looks like:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Stopped: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-1
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-1
With AUTOMATED_REGISTER="false", the cluster would not restart the failed HANA database or register it against the new primary on hn1-db-0. In this case, configure the HANA instance as secondary by running these commands, as hn1adm:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10
hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hn1-db-1 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=SITE1
The migration creates location constraints that need to be deleted again. Run the following command as root, or via sudo:
pcs resource clear SAPHana_HN1_03-master
Monitor the state of the HANA resource by using pcs status. After HANA is started on hn1-db-0, the output should look like:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-1
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-1
Block network communication
Resource state before starting the test:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-1
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-1
Run the firewall rule to block the communication on one of the nodes.
# Execute iptable rule on hn1-db-1 (10.0.0.6) to block the incoming and outgoing traffic to hn1-db-0 (10.0.0.5)
iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.5 -j DROP; iptables -A OUTPUT -d 10.0.0.5 -j DROP
When cluster nodes can't communicate with each other, there's a risk of a split-brain scenario. In such situations, cluster nodes try to simultaneously fence each other, resulting in a fence race. To avoid such a situation, we recommend that you set the priority-fencing-delay property in cluster configuration (applicable only for pacemaker-2.0.4-6.el8 or higher).
By enabling the priority-fencing-delay property, the cluster introduces a delay in the fencing action specifically on the node hosting the HANA master resource, allowing the node to win the fence race.
Run the following command to delete the firewall rule:
# If the iptables rule set on the server gets reset after a reboot, the rules will be cleared out. In case they have not been reset, please proceed to remove the iptables rule using the following command.
iptables -D INPUT -s 10.0.0.5 -j DROP; iptables -D OUTPUT -d 10.0.0.5 -j DROP
Test the Azure fencing agent
Note
This article contains references to a term that Microsoft no longer uses. When the term is removed from the software, we'll remove it from this article.
Resource state before starting the test:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-1
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-1
You can test the setup of the Azure fencing agent by disabling the network interface on the node where SAP HANA is running as Master. For a description on how to simulate a network failure, see Red Hat Knowledge Base article 79523.
In this example, we use the net_breaker script as root to block all access to the network:
sh ./net_breaker.sh BreakCommCmd 10.0.0.6
The VM should now restart or stop depending on your cluster configuration.
If you set the stonith-action setting to off, the VM is stopped and the resources are migrated to the running VM.
After you start the VM again, the SAP HANA resource fails to start as secondary if you set AUTOMATED_REGISTER="false". In this case, configure the HANA instance as secondary by running this command as the hn1adm user:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10
hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hn1-db-0 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=SITE2
Switch back to root and clean up the failed state:
# On RHEL 7.x
pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_HN1_03-master
# On RHEL 8.x
pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_HN1_03 node=<hostname on which the resource needs to be cleaned>
Resource state after the test:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-0
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-0
Test a manual failover
Resource state before starting the test:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-0
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-0
You can test a manual failover by stopping the cluster on the hn1-db-0 node, as root:
pcs cluster stop
After the failover, you can start the cluster again. If you set AUTOMATED_REGISTER="false", the SAP HANA resource on the hn1-db-0 node fails to start as secondary. In this case, configure the HANA instance as secondary by running this command as root:
pcs cluster start
Run the following as hn1adm:
sapcontrol -nr 03 -function StopWait 600 10
hdbnsutil -sr_register --remoteHost=hn1-db-1 --remoteInstance=03 --replicationMode=sync --name=SITE1
Then as root:
# On RHEL 7.x
pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_HN1_03-master
# On RHEL 8.x
pcs resource cleanup SAPHana_HN1_03 node=<hostname on which the resource needs to be cleaned>
Resource state after the test:
Clone Set: SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03-clone [SAPHanaTopology_HN1_03]
Started: [ hn1-db-0 hn1-db-1 ]
Master/Slave Set: SAPHana_HN1_03-master [SAPHana_HN1_03]
Masters: [ hn1-db-1 ]
Slaves: [ hn1-db-0 ]
Resource Group: g_ip_HN1_03
nc_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:azure-lb): Started hn1-db-1
vip_HN1_03 (ocf::heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started hn1-db-1