Near-edge compute
Azure Operator Nexus offers a group of on-premises cloud solutions. One of the on-premises offerings allows telco operators to run the network functions in a near-edge environment.
In a near-edge environment (also known as an instance), the compute servers (also known as bare-metal machines) represent the physical machines on the rack. They run the Azure Linux operating system and provide support for running high-performance workloads.
Compute connectivity
This diagram shows the connectivity model followed by computes in the near-edge instances.
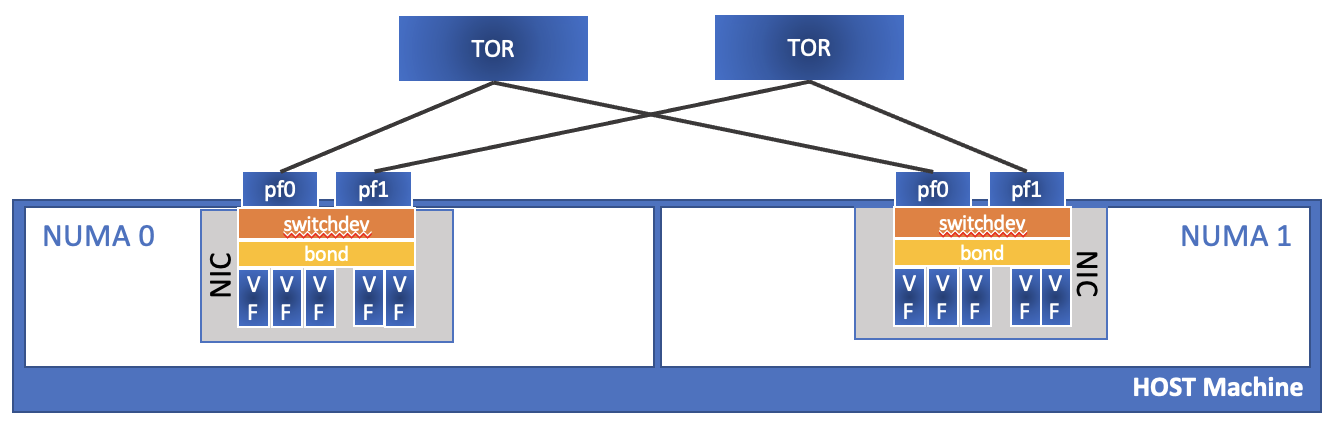
Compute configurations
Azure Operator Nexus supports a range of geometries and configurations. This table specifies the resources available per compute.
Dell R750 (Icelake)
| Property | Specification/Description |
|---|---|
| Number of virtual CPUs (vCPUs) for tenant usage | 96 vCPUs, with hyperthreading enabled per compute server. |
| Number of vCPUs available for workloads | 2 to 48 vCPUs, with an even number of vCPUs only. No cross-NUMA (nonuniform memory access) virtual machines (VMs). |
| CPU pinning | Default. |
| RAM for running tenant workloads | 448 GiB (224 GiB per NUMA). |
| Huge pages for tenant workloads | All VMs are backed by 1GiB (1G) huge pages. |
| Disk (ephemeral) per compute | Up to 3.5 TB (3.18 TiB) per compute host. |
| Data plane traffic path for workloads | Single-root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV). |
| Number of SR-IOV virtual functions (VFs) | Maximum of 32 virtual NICs (vNICs), with 30 VFs available for tenant workloads per NUMA. |
| SR-IOV NIC support | Enabled on all 100G NIC ports on VMs, with VFs assigned out of Mellanox-supported VF link aggregation (VF LAG). The allocated VFs are from the same physical NIC and within the same NUMA boundary. NIC ports that provide VF LAG are connected to two different top-of-rack (ToR) switches for redundancy. Support includes trunked VF receive-side scaling (RSS) with hardware queuing. Support also includes multiple queues on VMs. |
| IPv4/IPv6 support | Dual-stack IPv4/IPv6, IPv4, and IPv6-only virtual machines. |
Dell R760 (Sapphire Rapids)
| Property | Specification/Description |
|---|---|
| Number of virtual CPUs (vCPUs) for tenant usage | 116 vCPUs, with hyperthreading enabled per compute server. |
| Number of vCPUs available for workloads | 2 to 55 vCPUs, with an even number of vCPUs only. No cross-NUMA (nonuniform memory access) virtual machines (VMs). |
| CPU pinning | Default. |
| RAM for running tenant workloads | 960 GiB (480 GiB per NUMA). |
| Huge pages for tenant workloads | All VMs are backed by 1GiB (1G) huge pages. |
| Disk (ephemeral) per compute | Up to 3.84 TB (3.49 TiB) per compute host. |
| Data plane traffic path for workloads | Single-root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV). |
| Number of SR-IOV virtual functions (VFs) | Maximum of 32 virtual NICs (vNICs), with 30 VFs available for tenant workloads per NUMA. |
| SR-IOV NIC support | Enabled on all 100G NIC ports on VMs, with VFs assigned out of Mellanox-supported VF link aggregation (VF LAG). The allocated VFs are from the same physical NIC and within the same NUMA boundary. NIC ports that provide VF LAG are connected to two different top-of-rack (ToR) switches for redundancy. Support includes trunked VF receive-side scaling (RSS) with hardware queuing. Support also includes multiple queues on VMs. |
| IPv4/IPv6 support | Dual-stack IPv4/IPv6, IPv4, and IPv6-only virtual machines. |