Interpretability: Model explainability in automated ML (preview)
APPLIES TO:  Python SDK azureml v1
Python SDK azureml v1
In this article, you learn how to get explanations for automated machine learning (automated ML) models in Azure Machine Learning using the Python SDK. Automated ML helps you understand feature importance of the models that are generated.
All SDK versions after 1.0.85 set model_explainability=True by default. In SDK version 1.0.85 and earlier versions users need to set model_explainability=True in the AutoMLConfig object in order to use model interpretability.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Perform interpretability during training for best model or any model.
- Enable visualizations to help you see patterns in data and explanations.
- Implement interpretability during inference or scoring.
Prerequisites
- Interpretability features. Run
pip install azureml-interpretto get the necessary package. - Knowledge of building automated ML experiments. For more information on how to use the Azure Machine Learning SDK, complete this object detection model tutorial or see how to configure automated ML experiments.
Important
This feature is currently in public preview. This preview version is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.
For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Interpretability during training for the best model
Retrieve the explanation from the best_run, which includes explanations for both raw and engineered features.
Note
Interpretability, model explanation, is not available for the TCNForecaster model recommended by Auto ML forecasting experiments.
Download the engineered feature importances from the best run
You can use ExplanationClient to download the engineered feature explanations from the artifact store of the best_run.
from azureml.interpret import ExplanationClient
client = ExplanationClient.from_run(best_run)
engineered_explanations = client.download_model_explanation(raw=False)
print(engineered_explanations.get_feature_importance_dict())
Download the raw feature importances from the best run
You can use ExplanationClient to download the raw feature explanations from the artifact store of the best_run.
from azureml.interpret import ExplanationClient
client = ExplanationClient.from_run(best_run)
raw_explanations = client.download_model_explanation(raw=True)
print(raw_explanations.get_feature_importance_dict())
Interpretability during training for any model
When you compute model explanations and visualize them, you're not limited to an existing model explanation for an AutoML model. You can also get an explanation for your model with different test data. The steps in this section show you how to compute and visualize engineered feature importance based on your test data.
Retrieve any other AutoML model from training
automl_run, fitted_model = local_run.get_output(metric='accuracy')
Set up the model explanations
Use automl_setup_model_explanations to get the engineered and raw explanations. The fitted_model can generate the following items:
- Featured data from trained or test samples
- Engineered feature name lists
- Findable classes in your labeled column in classification scenarios
The automl_explainer_setup_obj contains all the structures from above list.
from azureml.train.automl.runtime.automl_explain_utilities import automl_setup_model_explanations
automl_explainer_setup_obj = automl_setup_model_explanations(fitted_model, X=X_train,
X_test=X_test, y=y_train,
task='classification')
Initialize the Mimic Explainer for feature importance
To generate an explanation for automated ML models, use the MimicWrapper class. You can initialize the MimicWrapper with these parameters:
- The explainer setup object
- Your workspace
- A surrogate model to explain the
fitted_modelautomated ML model
The MimicWrapper also takes the automl_run object where the engineered explanations will be uploaded.
from azureml.interpret import MimicWrapper
# Initialize the Mimic Explainer
explainer = MimicWrapper(ws, automl_explainer_setup_obj.automl_estimator,
explainable_model=automl_explainer_setup_obj.surrogate_model,
init_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_transform, run=automl_run,
features=automl_explainer_setup_obj.engineered_feature_names,
feature_maps=[automl_explainer_setup_obj.feature_map],
classes=automl_explainer_setup_obj.classes,
explainer_kwargs=automl_explainer_setup_obj.surrogate_model_params)
Use Mimic Explainer for computing and visualizing engineered feature importance
You can call the explain() method in MimicWrapper with the transformed test samples to get the feature importance for the generated engineered features. You can also sign in to Azure Machine Learning studio to view the explanations dashboard visualization of the feature importance values of the generated engineered features by automated ML featurizers.
engineered_explanations = explainer.explain(['local', 'global'], eval_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform)
print(engineered_explanations.get_feature_importance_dict())
For models trained with automated ML, you can get the best model using the get_output() method and compute explanations locally. You can visualize the explanation results with ExplanationDashboard from the raiwidgets package.
best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output()
from azureml.train.automl.runtime.automl_explain_utilities import AutoMLExplainerSetupClass, automl_setup_model_explanations
automl_explainer_setup_obj = automl_setup_model_explanations(fitted_model, X=X_train,
X_test=X_test, y=y_train,
task='regression')
from interpret.ext.glassbox import LGBMExplainableModel
from azureml.interpret.mimic_wrapper import MimicWrapper
explainer = MimicWrapper(ws, automl_explainer_setup_obj.automl_estimator, LGBMExplainableModel,
init_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_transform, run=best_run,
features=automl_explainer_setup_obj.engineered_feature_names,
feature_maps=[automl_explainer_setup_obj.feature_map],
classes=automl_explainer_setup_obj.classes)
pip install interpret-community[visualization]
engineered_explanations = explainer.explain(['local', 'global'], eval_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform)
print(engineered_explanations.get_feature_importance_dict()),
from raiwidgets import ExplanationDashboard
ExplanationDashboard(engineered_explanations, automl_explainer_setup_obj.automl_estimator, datasetX=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform)
raw_explanations = explainer.explain(['local', 'global'], get_raw=True,
raw_feature_names=automl_explainer_setup_obj.raw_feature_names,
eval_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform)
print(raw_explanations.get_feature_importance_dict()),
from raiwidgets import ExplanationDashboard
ExplanationDashboard(raw_explanations, automl_explainer_setup_obj.automl_pipeline, datasetX=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_raw)
Use Mimic Explainer for computing and visualizing raw feature importance
You can call the explain() method in MimicWrapper with the transformed test samples to get the feature importance for the raw features. In the Machine Learning studio, you can view the dashboard visualization of the feature importance values of the raw features.
raw_explanations = explainer.explain(['local', 'global'], get_raw=True,
raw_feature_names=automl_explainer_setup_obj.raw_feature_names,
eval_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform,
raw_eval_dataset=automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_raw)
print(raw_explanations.get_feature_importance_dict())
Interpretability during inference
In this section, you learn how to operationalize an automated ML model with the explainer that was used to compute the explanations in the previous section.
Register the model and the scoring explainer
Use the TreeScoringExplainer to create the scoring explainer that'll compute the engineered feature importance values at inference time. You initialize the scoring explainer with the feature_map that was computed previously.
Save the scoring explainer, and then register the model and the scoring explainer with the Model Management Service. Run the following code:
from azureml.interpret.scoring.scoring_explainer import TreeScoringExplainer, save
# Initialize the ScoringExplainer
scoring_explainer = TreeScoringExplainer(explainer.explainer, feature_maps=[automl_explainer_setup_obj.feature_map])
# Pickle scoring explainer locally
save(scoring_explainer, exist_ok=True)
# Register trained automl model present in the 'outputs' folder in the artifacts
original_model = automl_run.register_model(model_name='automl_model',
model_path='outputs/model.pkl')
# Register scoring explainer
automl_run.upload_file('scoring_explainer.pkl', 'scoring_explainer.pkl')
scoring_explainer_model = automl_run.register_model(model_name='scoring_explainer', model_path='scoring_explainer.pkl')
Create the conda dependencies for setting up the service
Next, create the necessary environment dependencies in the container for the deployed model. Please note that azureml-defaults with version >= 1.0.45 must be listed as a pip dependency, because it contains the functionality needed to host the model as a web service.
from azureml.core.conda_dependencies import CondaDependencies
azureml_pip_packages = [
'azureml-interpret', 'azureml-train-automl', 'azureml-defaults'
]
myenv = CondaDependencies.create(conda_packages=['scikit-learn', 'pandas', 'numpy', 'py-xgboost<=0.80'],
pip_packages=azureml_pip_packages,
pin_sdk_version=True)
with open("myenv.yml","w") as f:
f.write(myenv.serialize_to_string())
with open("myenv.yml","r") as f:
print(f.read())
Create the scoring script
Write a script that loads your model and produces predictions and explanations based on a new batch of data.
%%writefile score.py
import joblib
import pandas as pd
from azureml.core.model import Model
from azureml.train.automl.runtime.automl_explain_utilities import automl_setup_model_explanations
def init():
global automl_model
global scoring_explainer
# Retrieve the path to the model file using the model name
# Assume original model is named automl_model
automl_model_path = Model.get_model_path('automl_model')
scoring_explainer_path = Model.get_model_path('scoring_explainer')
automl_model = joblib.load(automl_model_path)
scoring_explainer = joblib.load(scoring_explainer_path)
def run(raw_data):
data = pd.read_json(raw_data, orient='records')
# Make prediction
predictions = automl_model.predict(data)
# Setup for inferencing explanations
automl_explainer_setup_obj = automl_setup_model_explanations(automl_model,
X_test=data, task='classification')
# Retrieve model explanations for engineered explanations
engineered_local_importance_values = scoring_explainer.explain(automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform)
# Retrieve model explanations for raw explanations
raw_local_importance_values = scoring_explainer.explain(automl_explainer_setup_obj.X_test_transform, get_raw=True)
# You can return any data type as long as it is JSON-serializable
return {'predictions': predictions.tolist(),
'engineered_local_importance_values': engineered_local_importance_values,
'raw_local_importance_values': raw_local_importance_values}
Deploy the service
Deploy the service using the conda file and the scoring file from the previous steps.
from azureml.core.webservice import Webservice
from azureml.core.webservice import AciWebservice
from azureml.core.model import Model, InferenceConfig
from azureml.core.environment import Environment
aciconfig = AciWebservice.deploy_configuration(cpu_cores=1,
memory_gb=1,
tags={"data": "Bank Marketing",
"method" : "local_explanation"},
description='Get local explanations for Bank marketing test data')
myenv = Environment.from_conda_specification(name="myenv", file_path="myenv.yml")
inference_config = InferenceConfig(entry_script="score_local_explain.py", environment=myenv)
# Use configs and models generated above
service = Model.deploy(ws,
'model-scoring',
[scoring_explainer_model, original_model],
inference_config,
aciconfig)
service.wait_for_deployment(show_output=True)
Inference with test data
Inference with some test data to see the predicted value from AutoML model, currently supported only in Azure Machine Learning SDK. View the feature importances contributing towards a predicted value.
if service.state == 'Healthy':
# Serialize the first row of the test data into json
X_test_json = X_test[:1].to_json(orient='records')
print(X_test_json)
# Call the service to get the predictions and the engineered explanations
output = service.run(X_test_json)
# Print the predicted value
print(output['predictions'])
# Print the engineered feature importances for the predicted value
print(output['engineered_local_importance_values'])
# Print the raw feature importances for the predicted value
print('raw_local_importance_values:\n{}\n'.format(output['raw_local_importance_values']))
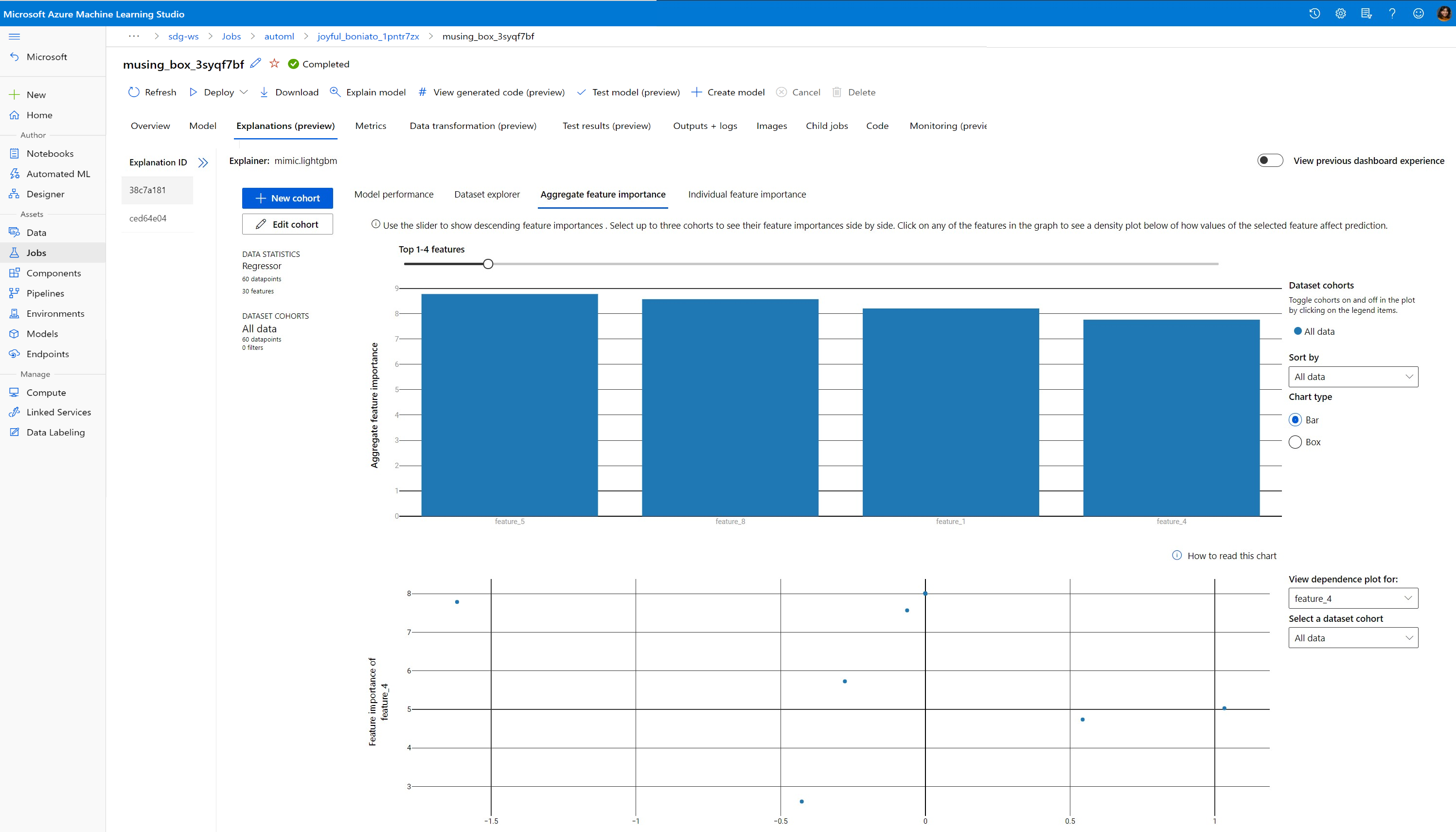
Visualize to discover patterns in data and explanations at training time
You can visualize the feature importance chart in your workspace in Azure Machine Learning studio. After your AutoML run is complete, select View model details to view a specific run. Select the Explanations tab to see the visualizations in the explanation dashboard.
For more information on the explanation dashboard visualizations and specific plots, please refer to the how-to doc on interpretability.
Next steps
For more information about how you can enable model explanations and feature importance in areas other than automated ML, see more techniques for model interpretability.