Configure Apache Ranger policies for Spark SQL in HDInsight with Enterprise Security Package
This article describes how to configure Apache Ranger policies for Spark SQL with Enterprise Security Package in HDInsight.
In this article, you learn how to:
- Create Apache Ranger policies.
- Verify the applied Ranger policies.
- Apply guidelines for setting Apache Ranger for Spark SQL.
Prerequisites
- An Apache Spark cluster in HDInsight version 5.1 with Enterprise Security Package
Connect to the Apache Ranger admin UI
From a browser, connect to the Ranger admin user interface by using the URL
https://ClusterName.azurehdinsight.net/Ranger/.Change
ClusterNameto the name of your Spark cluster.Sign in by using your Microsoft Entra admin credentials. The Microsoft Entra admin credentials aren't the same as HDInsight cluster credentials or Linux HDInsight node Secure Shell (SSH) credentials.
Create domain users
For information on how to create sparkuser domain users, see Create an HDInsight cluster with ESP. In a production scenario, domain users come from your Microsoft Entra tenant.
Create a Ranger policy
In this section, you create two Ranger policies:
- An access policy for accessing
hivesampletablefrom Spark SQL - A masking policy for obfuscating the columns in
hivesampletable
Create a Ranger access policy
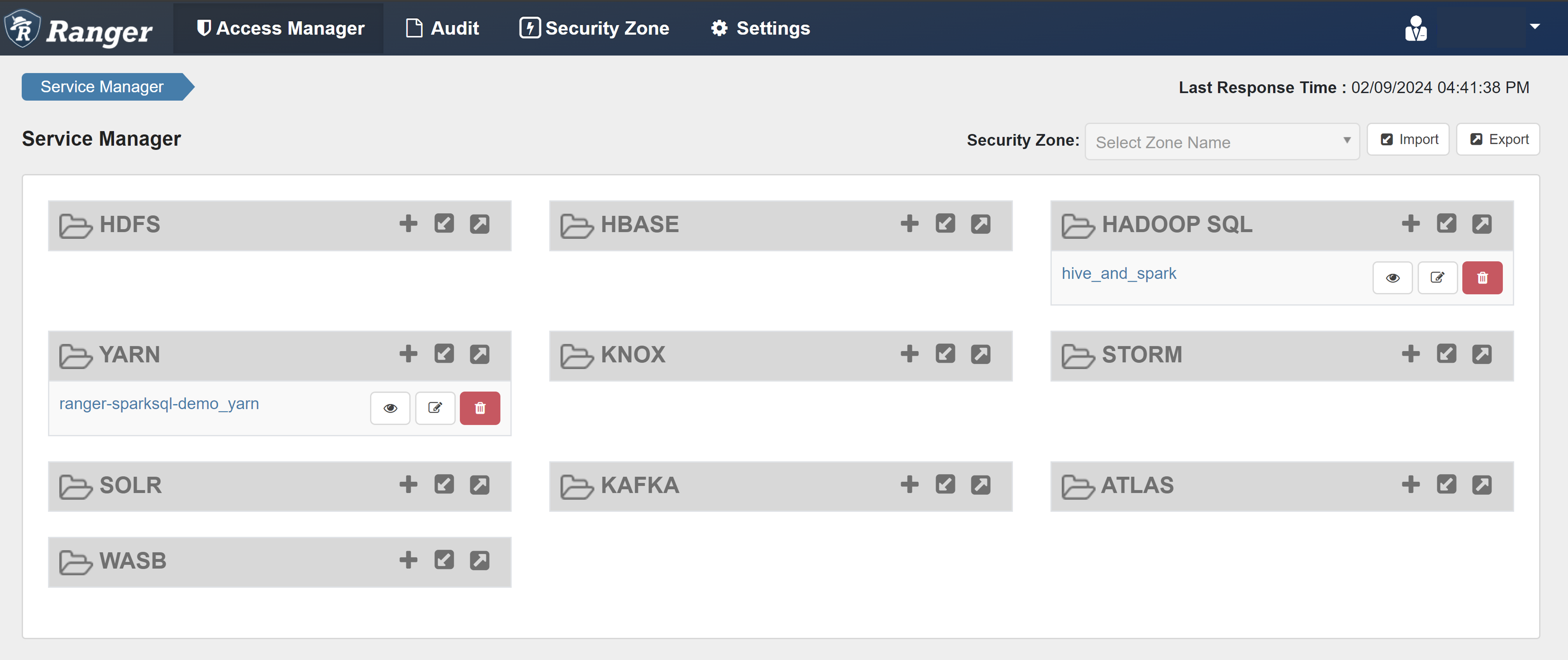
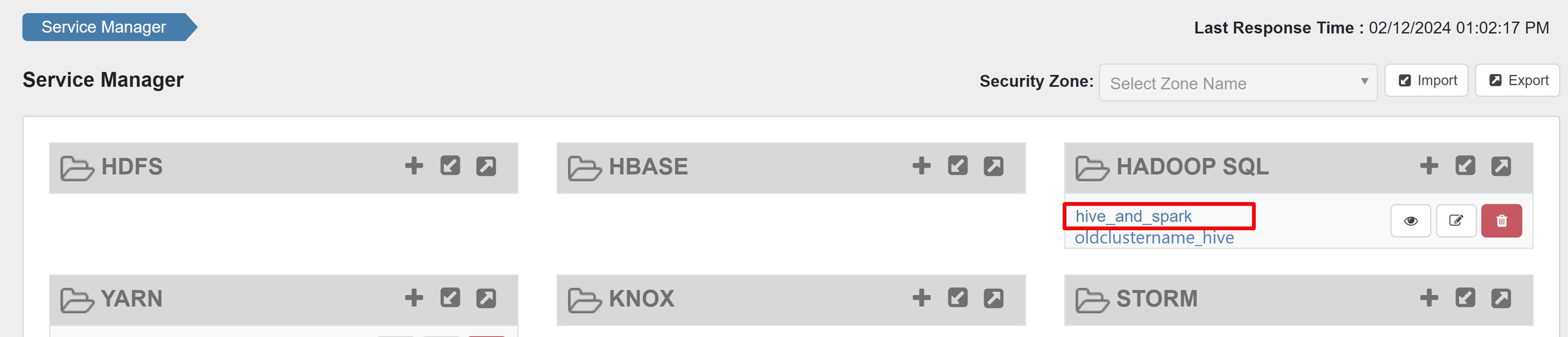
Open the Ranger admin UI.
Under HADOOP SQL, select hive_and_spark.
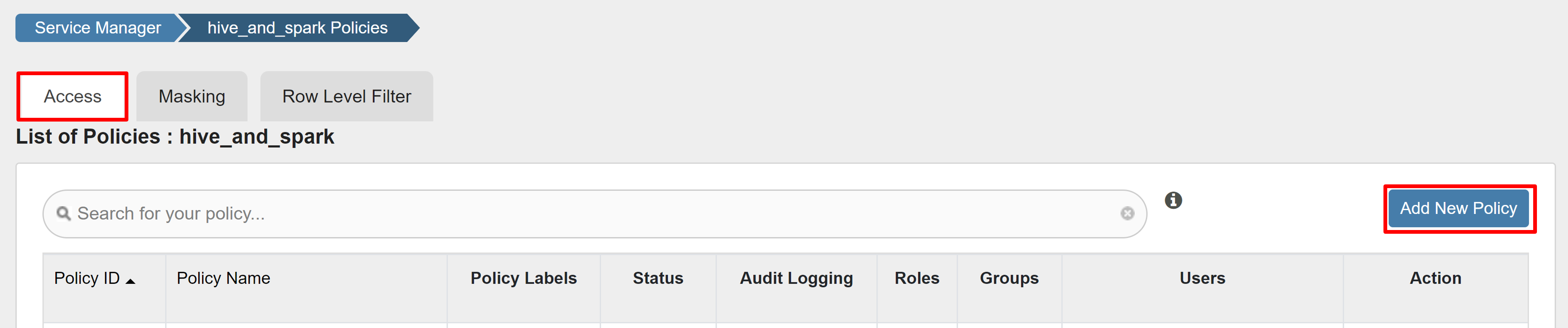
On the Access tab, select Add New Policy.
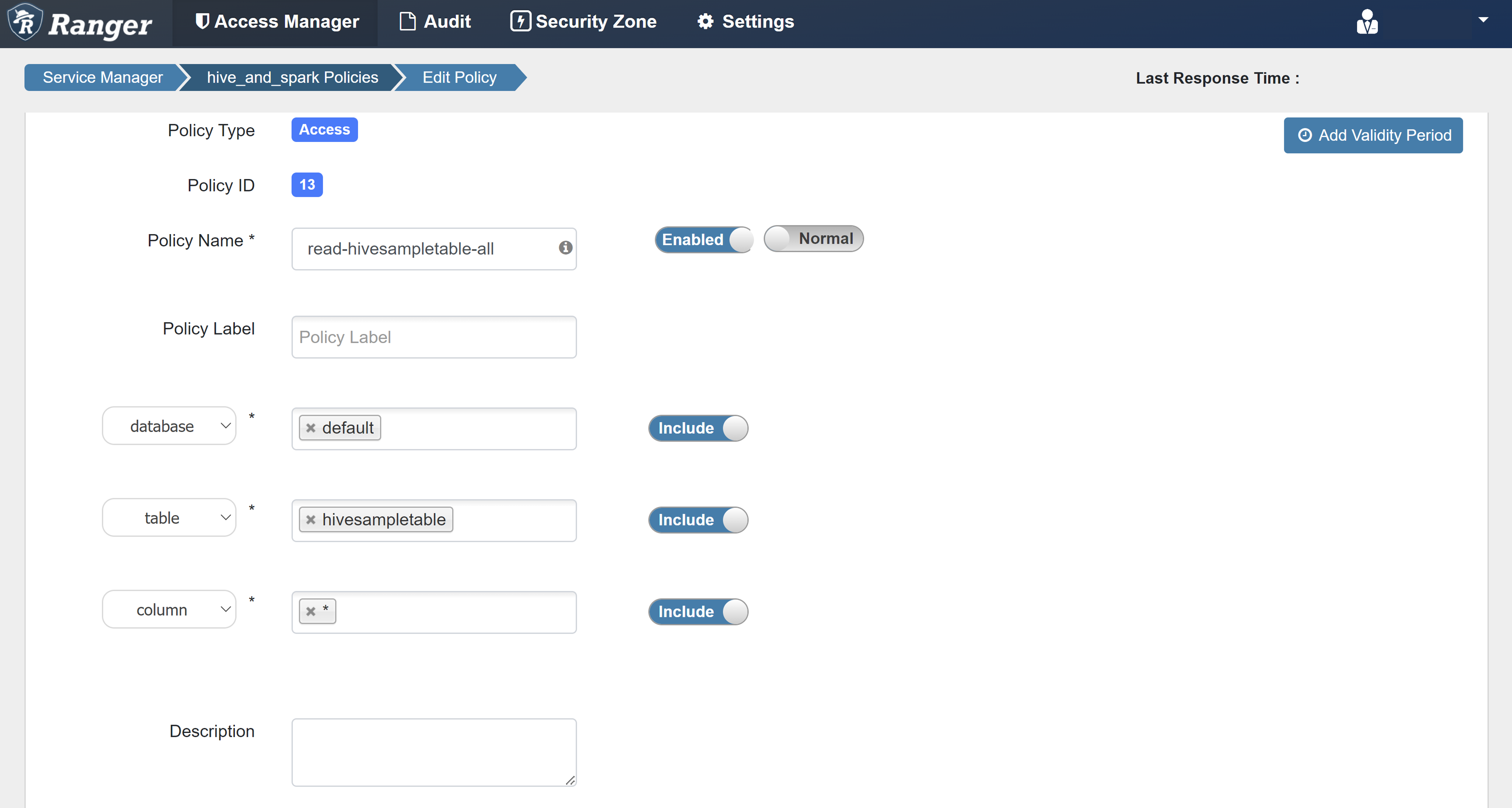
Enter the following values:
Property Value Policy Name read-hivesampletable-all database default table hivesampletable column * Select User sparkuserPermissions select If a domain user isn't automatically populated for Select User, wait a few moments for Ranger to sync with Microsoft Entra ID.
Select Add to save the policy.
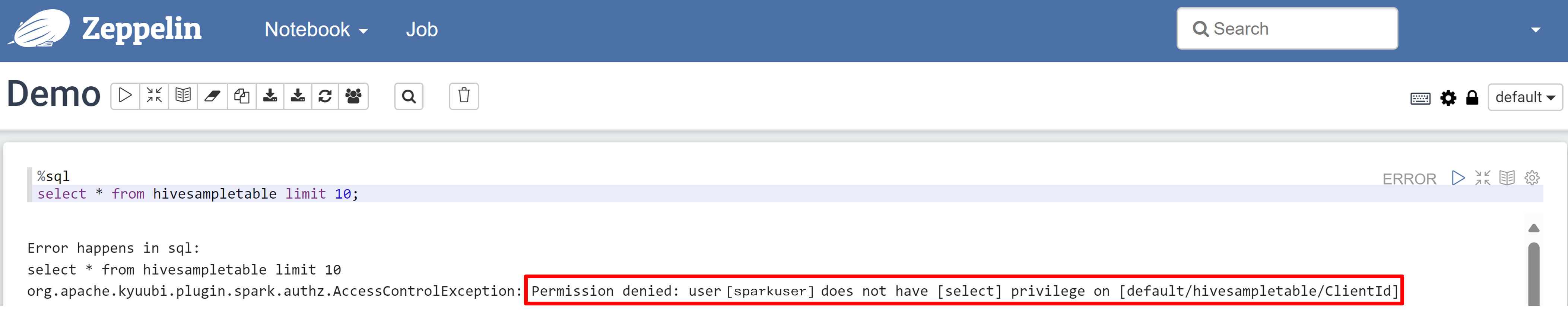
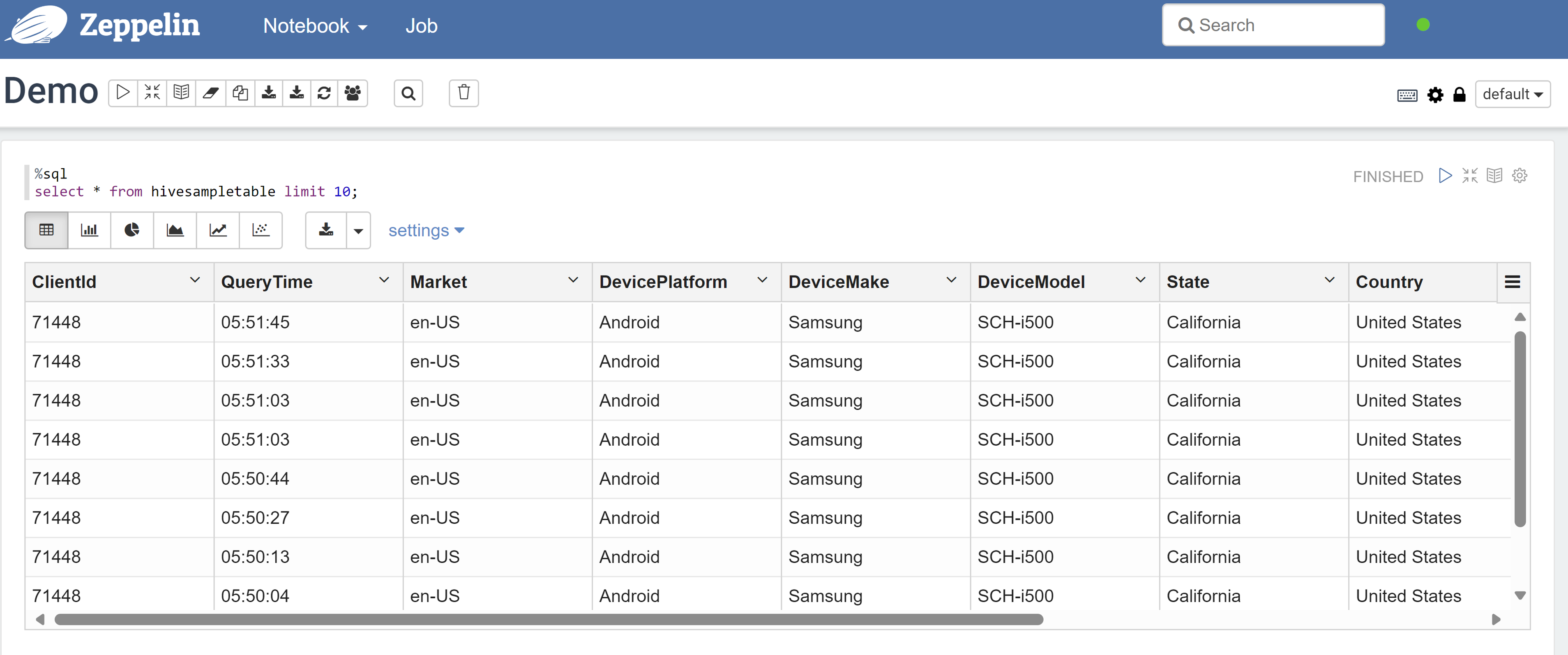
Open a Zeppelin notebook and run the following command to verify the policy:
%sql select * from hivesampletable limit 10;Here's the result before a policy is applied:
Here's the result after a policy is applied:
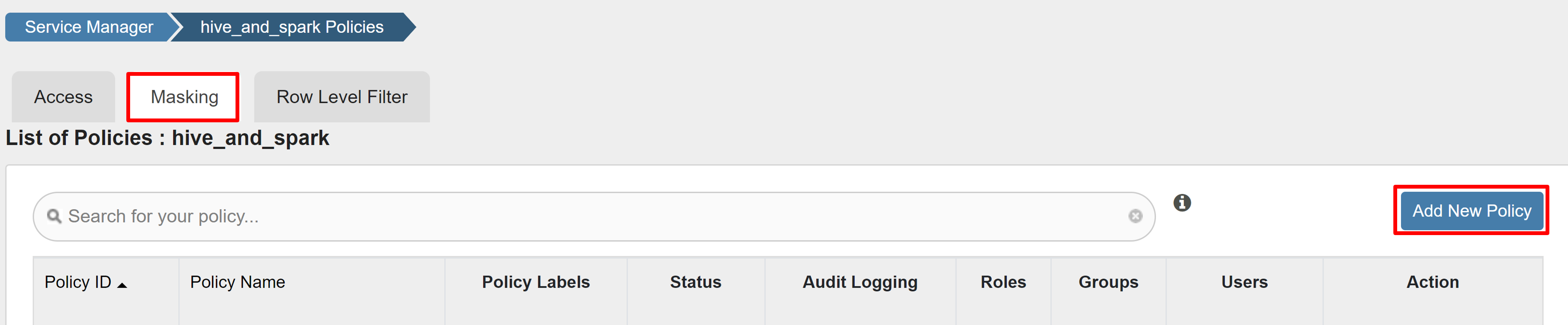
Create a Ranger masking policy
The following example shows how to create a policy to mask a column:
On the Masking tab, select Add New Policy.
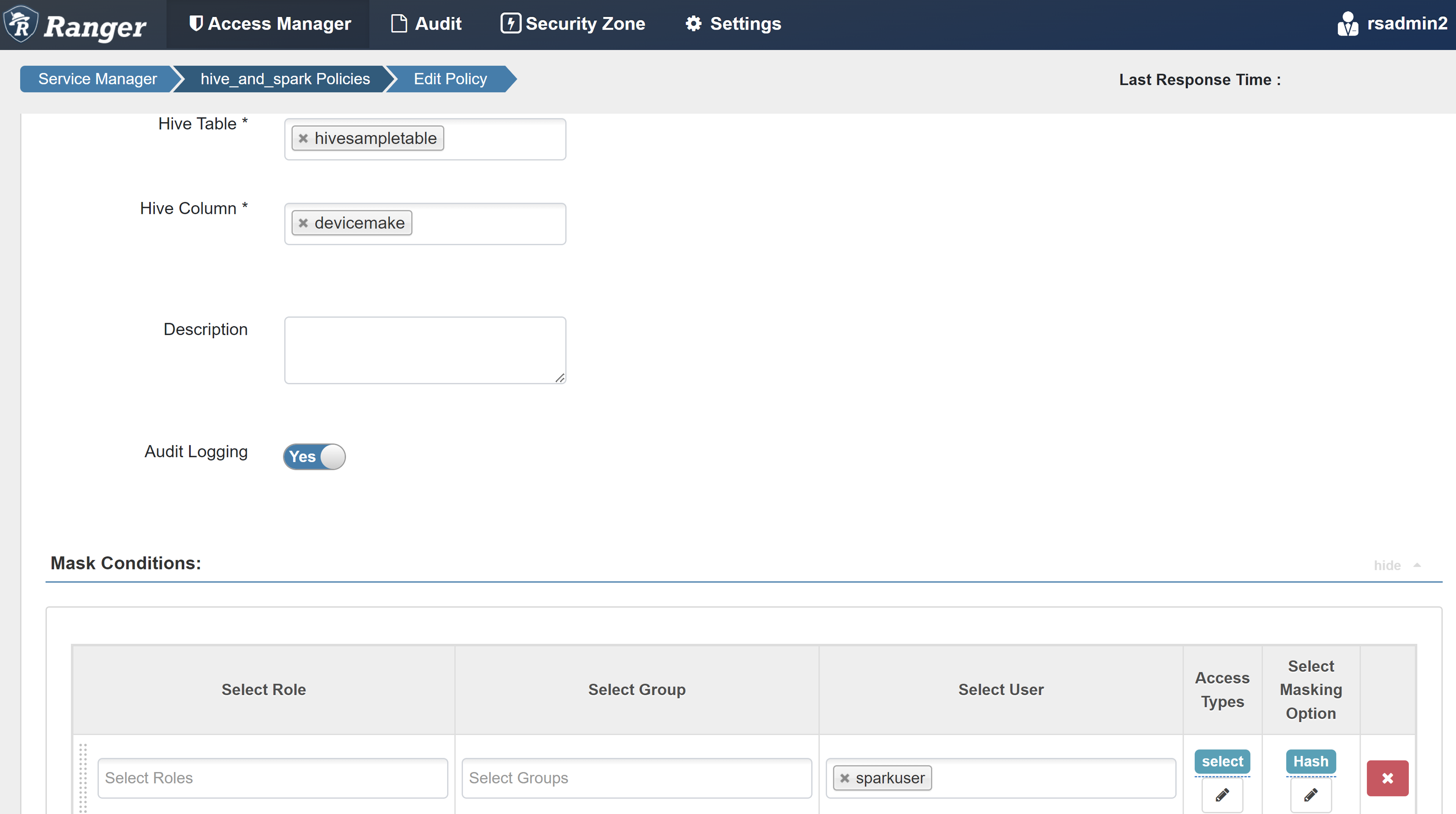
Enter the following values:
Property Value Policy Name mask-hivesampletable Hive Database default Hive Table hivesampletable Hive Column devicemake Select User sparkuserAccess Types select Select Masking Option Hash Select Save to save the policy.
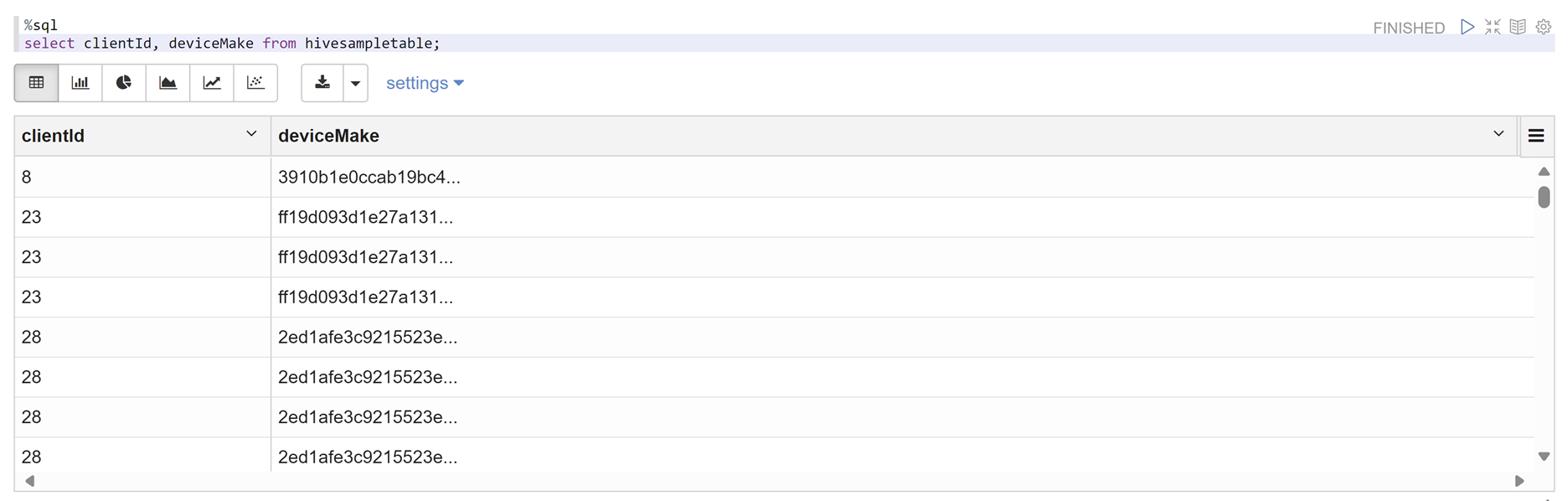
Open a Zeppelin notebook and run the following command to verify the policy:
%sql select clientId, deviceMake from hivesampletable;
Note
By default, the policies for Hive and Spark SQL are common in Ranger.
Apply guidelines for setting up Apache Ranger for Spark SQL
The following scenarios explore guidelines for creating an HDInsight 5.1 Spark cluster by using a new Ranger database and by using an existing Ranger database.
Scenario 1: Use a new Ranger database while creating an HDInsight 5.1 Spark cluster
When you use a new Ranger database to create a cluster, the relevant Ranger repo that contains the Ranger policies for Hive and Spark is created under the name hive_and_spark in the Hadoop SQL service on the Ranger database.
If you edit the policies, they're applied to both Hive and Spark.
Consider these points:
If you have two metastore databases with the same name used for both Hive (for example, DB1) and Spark (for example, DB1) catalogs:
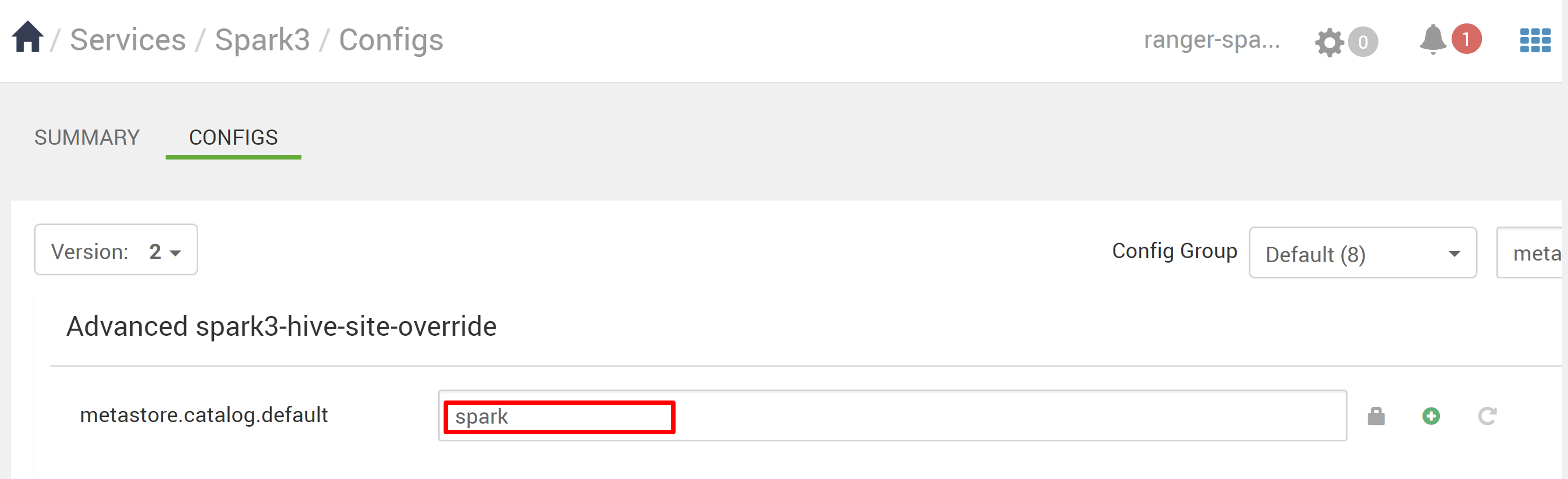
- If Spark uses the Spark catalog (
metastore.catalog.default=spark), the policies are applied to the DB1 database of the Spark catalog. - If Spark uses the Hive catalog (
metastore.catalog.default=hive), the policies are applied to the DB1 database of the Hive catalog.
From the perspective of Ranger, there's no way to differentiate between DB1 of the Hive and Spark catalogs.
In such cases, we recommend that you either:
- Use the Hive catalog for both Hive and Spark.
- Maintain different database, table, and column names for both Hive and Spark catalogs so that the policies aren't applied to databases across catalogs.
- If Spark uses the Spark catalog (
If you use the Hive catalog for both Hive and Spark, consider the following example.
Let's say that you create a table named table1 through Hive with the current xyz user. It creates a Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) file named table1.db whose owner is the xyz user.
Now imagine that you use the user abc to start the Spark SQL session. In this session of user abc, if you try to write anything to table1, it's bound to fail because the table owner is xyz.
In such a case, we recommend that you use the same user in Hive and Spark SQL for updating the table. That user should have sufficient privileges to perform update operations.
Scenario 2: Use an existing Ranger database (with existing policies) while creating an HDInsight 5.1 Spark cluster
When you create an HDInsight 5.1 cluster by using an existing Ranger database, a new Ranger repo is created again on this database with the name of the new cluster in this format: hive_and_spark.
Let's say that you have the policies defined in the Ranger repo already under the name oldclustername_hive on the existing Ranger database inside the Hadoop SQL service. You want to share the same policies in the new HDInsight 5.1 Spark cluster. To achieve this goal, use the following steps.
Note
A user who has Ambari admin privileges can perform configuration updates.
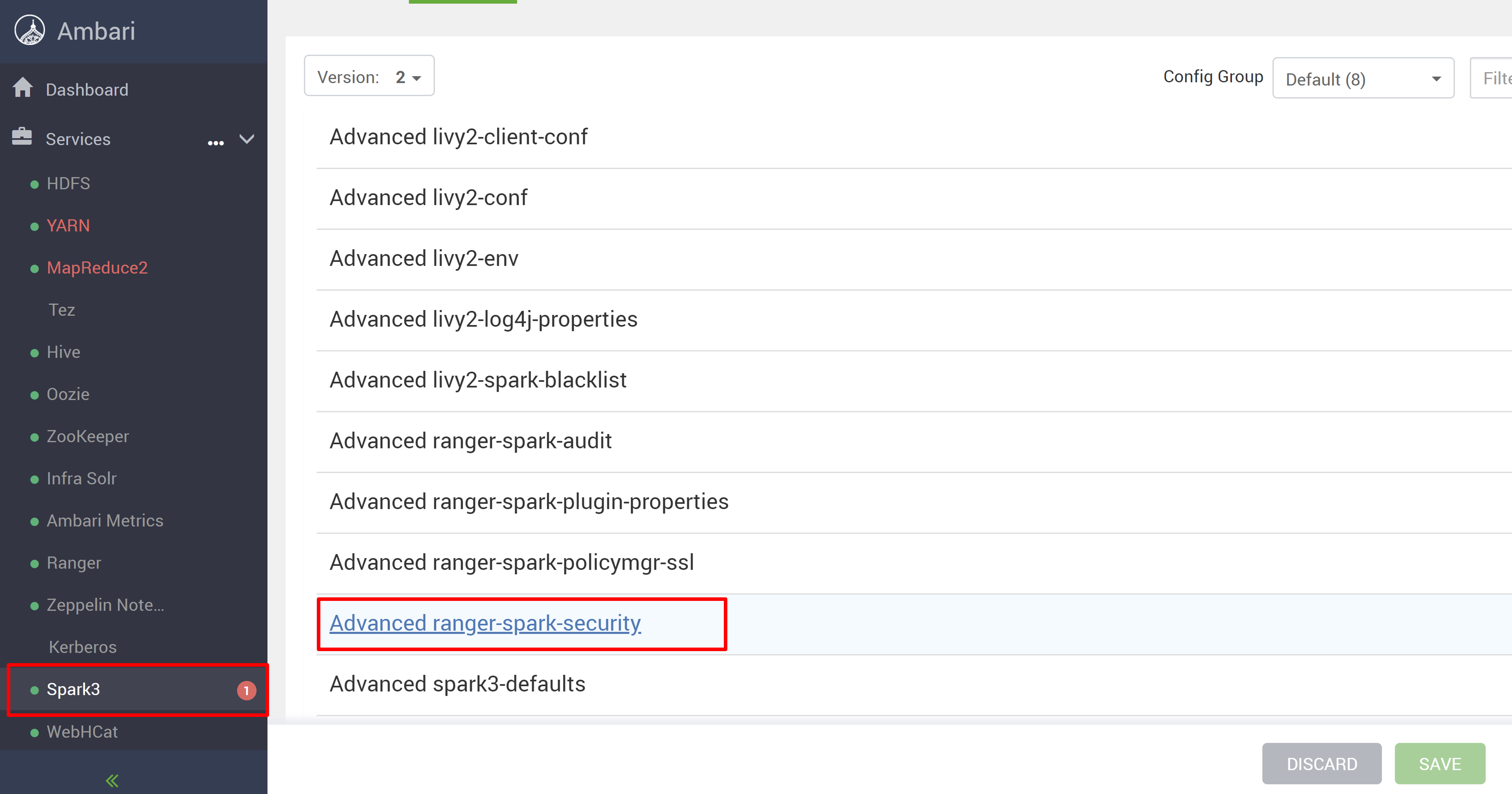
Open the Ambari UI from your new HDInsight 5.1 cluster.
Go to the Spark3 service, and then go to Configs.
Open the Advanced ranger-spark-security configuration.
or You can also open this configuration in /etc/spark3/conf by using SSH.
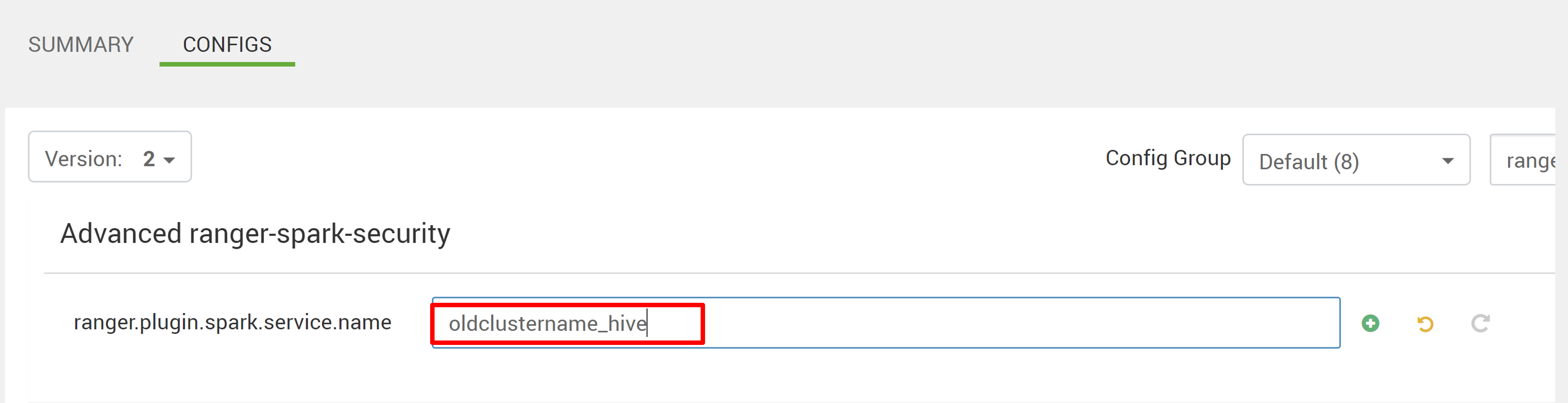
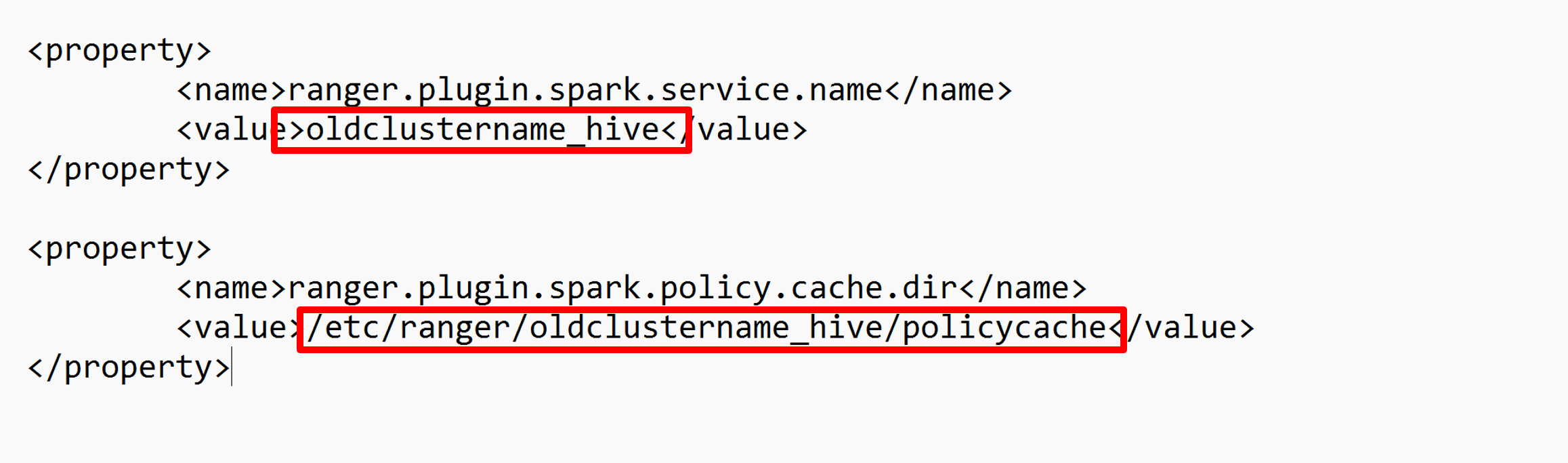
Edit two configurations (ranger.plugin.spark.service.name and ranger.plugin.spark.policy.cache.dir) to point to the old policy repo oldclustername_hive, and then save the configurations.
Ambari:
XML file:
Restart the Ranger and Spark services from Ambari.
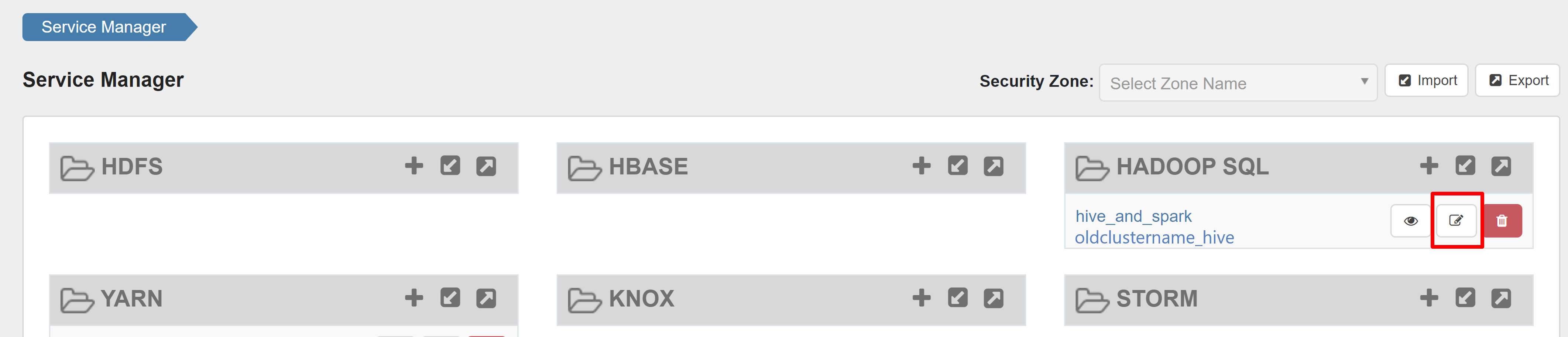
Open the Ranger admin UI and click on edit button under HADOOP SQL service.
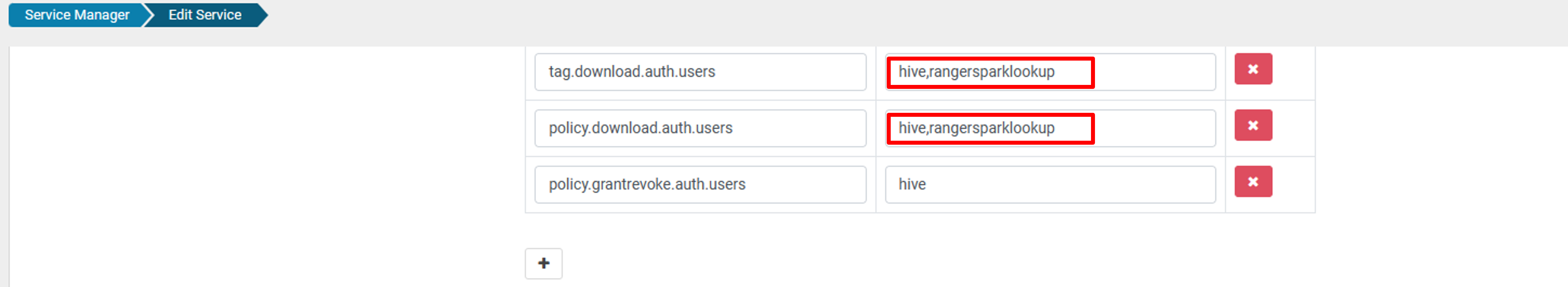
For oldclustername_hive service, add rangersparklookup user in the policy.download.auth.users and tag.download.auth.users list and click save.
The policies are applied on databases in the Spark catalog. If you want to access the databases in the Hive catalog:
Known issues
- Apache Ranger integration with Spark SQL doesn't work if the Ranger admin is down.
- In Ranger audit logs, when you hover over the Resource column, it can't show the entire query that you ran.