Authorize users for Apache Ambari Views
Enterprise Security Package (ESP) enabled HDInsight clusters provide enterprise-grade capabilities, including Microsoft Entra ID-based authentication. You can synchronize new users added to Microsoft Entra groups that have been provided access to the cluster, allowing those specific users to perform certain actions. When you work with users, groups, and permissions in Apache Ambari is supported for both ESP HDInsight clusters and standard HDInsight clusters.
Active Directory users can sign in to the cluster nodes using their domain credentials. They can also use their domain credentials to authenticate cluster interactions with other approved endpoints like Hue, Ambari Views, ODBC, JDBC, PowerShell, and REST APIs.
Warning
Do not change the password of the Ambari watchdog (hdinsightwatchdog) on your Linux-based HDInsight cluster. Changing the password breaks the ability to use script actions or perform scaling operations with your cluster.
If you have not already done so, follow these instructions to provision a new ESP cluster.
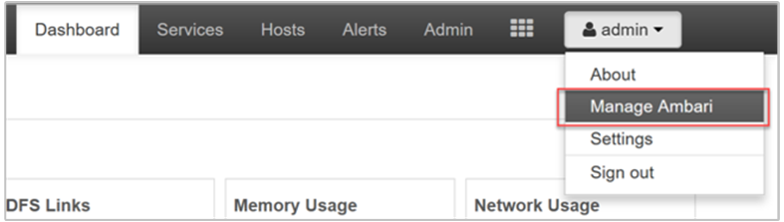
Access the Ambari management page
To get to the Ambari management page on the Apache Ambari Web UI, browse to https://CLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net. Enter the cluster administrator username and password that you defined when creating the cluster. Next, from the Ambari dashboard, select Manage Ambari underneath the admin menu:
Add users
Add users through the portal
From the management page, select Users.
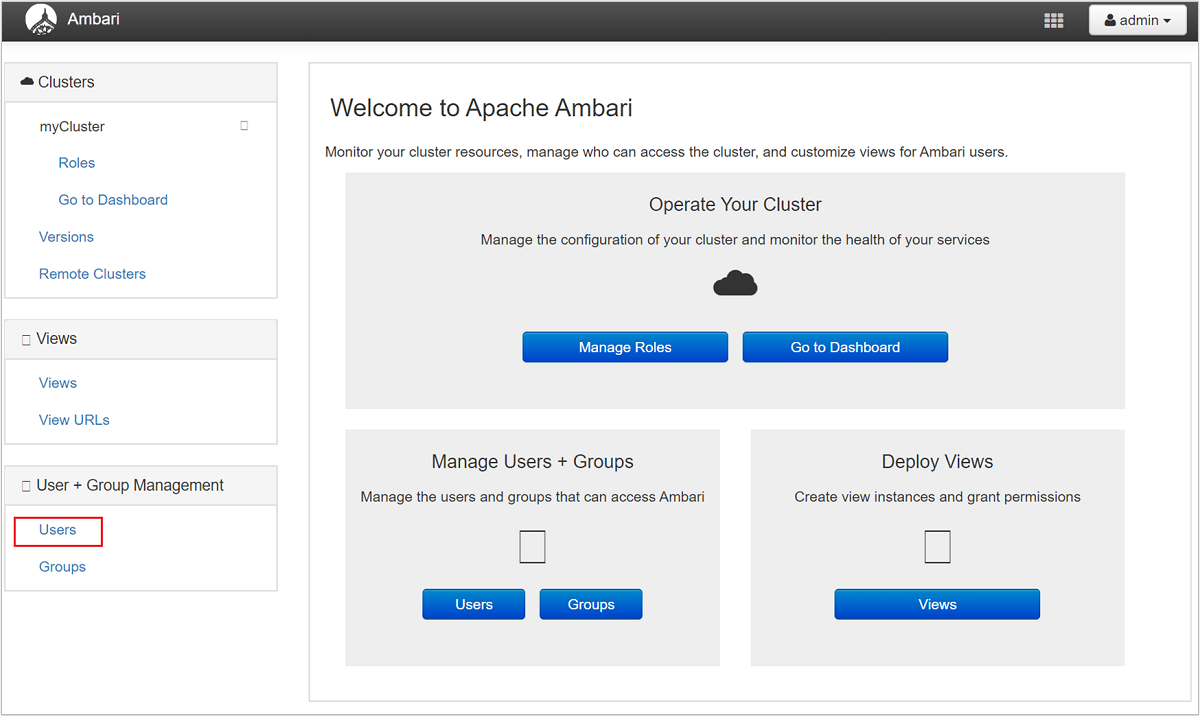
Select + Create Local User.
Provide Username and password. Select save.
Add users through PowerShell
Edit the variables below by replacing CLUSTERNAME, NEWUSER, and PASSWORD with the appropriate values.
# Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
# Begin user input; update values
$clusterName="CLUSTERNAME"
$user="NEWUSER"
$userpass='PASSWORD'
# End user input
$adminCredentials = Get-Credential -UserName "admin" -Message "Enter admin password"
$clusterName = $clusterName.ToLower()
$createUserUrl="https://$($clusterName).azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/users"
$createUserBody=@{
"Users/user_name" = "$user"
"Users/password" = "$userpass"
"Users/active" = "$true"
"Users/admin" = "$false"
} | ConvertTo-Json
# Create user
$statusCode =
Invoke-WebRequest `
-Uri $createUserUrl `
-Credential $adminCredentials `
-Method POST `
-Headers @{"X-Requested-By" = "ambari"} `
-Body $createUserBody | Select-Object -Expand StatusCode
if ($statusCode -eq 201) {
Write-Output "User is created: $user"
}
else
{
Write-Output 'User is not created'
Exit
}
$grantPrivilegeUrl="https://$($clusterName).azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/$($clusterName)/privileges"
$grantPrivilegeBody=@{
"PrivilegeInfo" = @{
"permission_name" = "CLUSTER.USER"
"principal_name" = "$user"
"principal_type" = "USER"
}
} | ConvertTo-Json
# Grant privileges
$statusCode =
Invoke-WebRequest `
-Uri $grantPrivilegeUrl `
-Credential $adminCredentials `
-Method POST `
-Headers @{"X-Requested-By" = "ambari"} `
-Body $grantPrivilegeBody | Select-Object -Expand StatusCode
if ($statusCode -eq 201) {
Write-Output 'Privilege is granted'
}
else
{
Write-Output 'Privilege is not granted'
Exit
}
Write-Host "Pausing for 100 seconds"
Start-Sleep -s 100
$userCredentials = "$($user):$($userpass)"
$encodedUserCredentials = [System.Convert]::ToBase64String([System.Text.Encoding]::ASCII.GetBytes($userCredentials))
$zookeeperUrlHeaders = @{ Authorization = "Basic $encodedUserCredentials" }
$getZookeeperurl="https://$($clusterName).azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/$($clusterName)/services/ZOOKEEPER/components/ZOOKEEPER_SERVER"
# Perform query with new user
$zookeeperHosts =
Invoke-WebRequest `
-Uri $getZookeeperurl `
-Method Get `
-Headers $zookeeperUrlHeaders
Write-Output $zookeeperHosts
Add users through Curl
Edit the variables below by replacing CLUSTERNAME, ADMINPASSWORD, NEWUSER, and USERPASSWORD with the appropriate values. The script is designed to be executed with bash. Slight modifications would be needed for a Windows command prompt.
export CLUSTER_NAME="CLUSTERNAME"
export ADMIN_PASSWORD='ADMINPASSWORD'
export USER="NEWUSER"
export USER_PASSWORD='USERPASSWORD'
# create user
curl -k -u admin:$ADMIN_PASSWORD -H "X-Requested-By: ambari" -X POST \
-d "{\"Users/user_name\":\"$USER\",\"Users/password\":\"$USER_PASSWORD\",\"Users/active\":\"true\",\"Users/admin\":\"false\"}" \
https://$CLUSTER_NAME.azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/users
echo "user created: $USER"
# grant permissions
curl -k -u admin:$ADMIN_PASSWORD -H "X-Requested-By: ambari" -X POST \
-d '[{"PrivilegeInfo":{"permission_name":"CLUSTER.USER","principal_name":"'$USER'","principal_type":"USER"}}]' \
https://$CLUSTER_NAME.azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER_NAME/privileges
echo "Privilege is granted"
echo "Pausing for 100 seconds"
sleep 10s
# perform query using new user account
curl -k -u $USER:$USER_PASSWORD -H "X-Requested-By: ambari" \
-X GET "https://$CLUSTER_NAME.azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/$CLUSTER_NAME/services/ZOOKEEPER/components/ZOOKEEPER_SERVER"
Grant permissions to Apache Hive views
Ambari comes with view instances for Apache Hive and Apache TEZ, among others. To grant access to one or more Hive view instances, go to the Ambari management page.
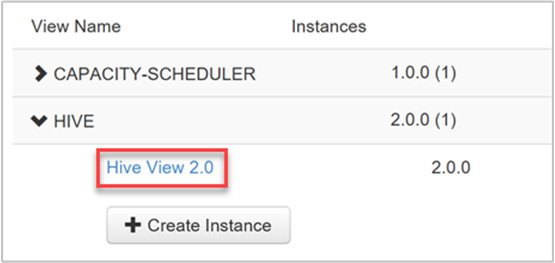
From the management page, select the Views link under the Views menu heading on the left.
On the Views page, expand the HIVE row. There is one default Hive view that is created when the Hive service is added to the cluster. You can also create more Hive view instances as needed. Select a Hive view:
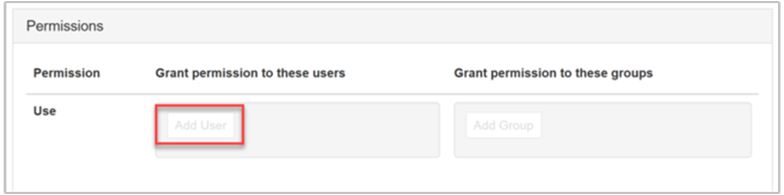
Scroll toward the bottom of the View page. Under the Permissions section, you have two options for granting domain users their permissions to the view:
Grant permission to these users
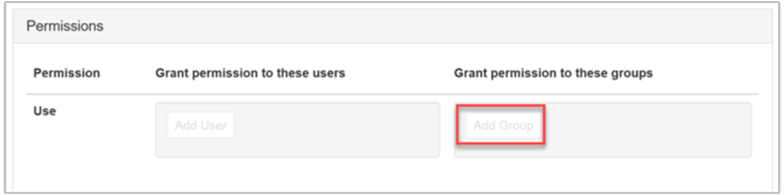
Grant permission to these groups
To add a user, select the Add User button.
Start typing the user name and you will see a dropdown list of previously defined names.
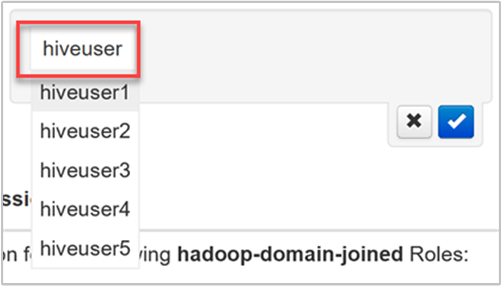
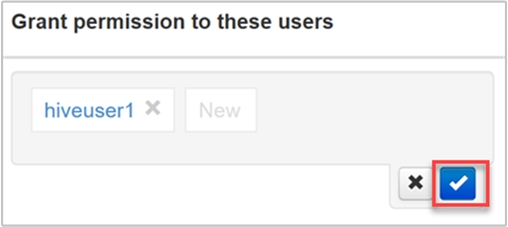
Select, or finish typing, the user name. To add this user name as a new user, select the New button.
To save your changes, select the blue checkbox.
To add a group, select the Add Group button.
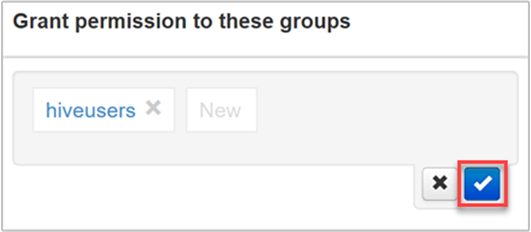
Start typing the group name. The process of selecting an existing group name, or adding a new group, is the same as for adding users.
To save your changes, select the blue checkbox.
Adding users directly to a view is useful when you want to assign permissions to a user to use that view, but do not want them to be a member of a group that has additional permissions. To reduce the amount of administrative overhead, it may be simpler to assign permissions to groups.
Grant permissions to Apache TEZ views
The Apache TEZ view instances allow the users to monitor and debug all Tez jobs, submitted by Apache Hive queries and Apache Pig scripts. There is one default Tez view instance that is created when the cluster is provisioned.
To assign users and groups to a Tez view instance, expand the TEZ row on the Views page, as described previously.
To add users or groups, repeat steps 3 - 5 in the previous section.
Assign users to roles
There are five security roles for users and groups, listed in order of decreasing access permissions:
- Cluster Administrator
- Cluster Operator
- Service Administrator
- Service Operator
- Cluster User
To manage roles, go to the Ambari management page, then select the Roles link within the Clusters menu group on the left.
To see the list of permissions given to each role, click on the blue question mark next to the Roles table header on the Roles page.
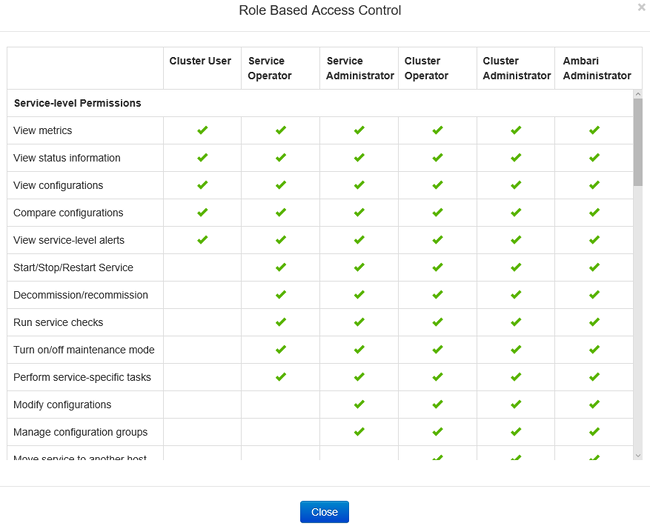
On this page, there are two different views you can use to manage roles for users and groups: Block and List.
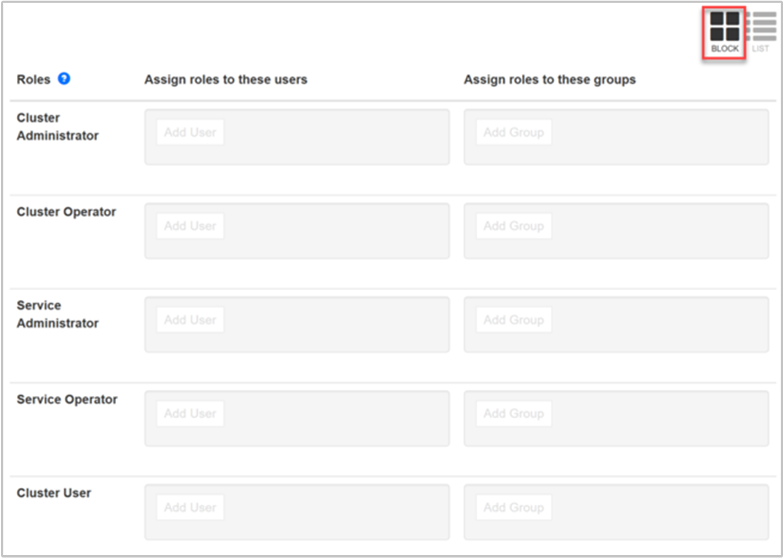
Block view
The Block view displays each role in its own row, and provides the Assign roles to these users and *Assign roles to these groups options as described previously.
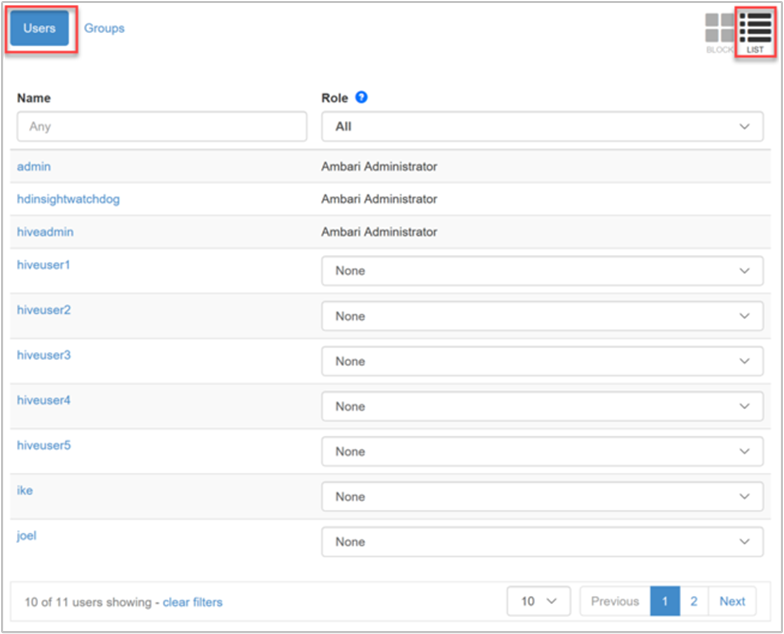
List view
The List view provides quick editing capabilities in two categories: Users and Groups.
The Users category of the List view displays a list of all users, allowing you to select a role for each user in the dropdown list.
The Groups category of the List view displays all groups, and the role assigned to each group. In our example, the list of groups is synchronized from the Microsoft Entra groups specified in the Access user group property of the cluster's Domain settings. See Create a HDInsight cluster with ESP enabled.
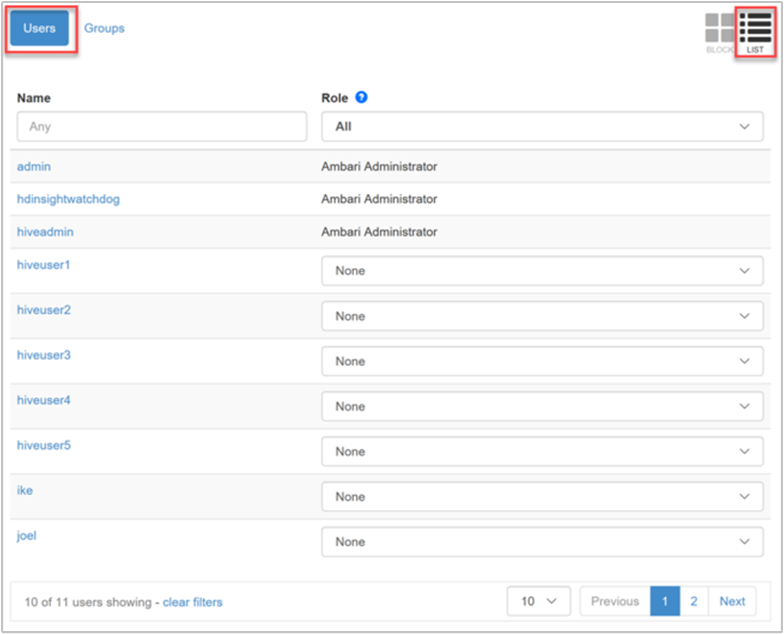
In the image above, the hive users group is assigned the Cluster User role. This is a read-only role that allows the users of that group to view but not change service configurations and cluster metrics.
Log in to Ambari as a view-only user
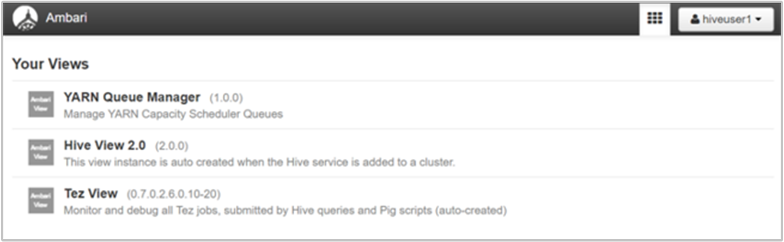
We have assigned our Microsoft Entra domain user "hiveuser1" permissions to Hive and Tez views. When we launch the Ambari Web UI and enter this user's domain credentials (Microsoft Entra user name in e-mail format, and password), the user is redirected to the Ambari Views page. From here, the user can select any accessible view. The user cannot visit any other part of the site, including the dashboard, services, hosts, alerts, or admin pages.
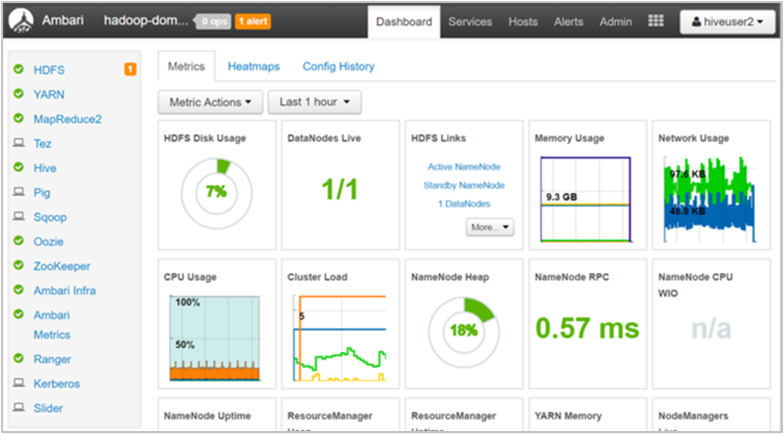
Log in to Ambari as a cluster user
We have assigned our Microsoft Entra domain user "hiveuser2" to the Cluster User role. This role is able to access the dashboard and all of the menu items. A cluster user has fewer permitted options than an administrator. For example, hiveuser2 can view configurations for each of the services, but cannot edit them.