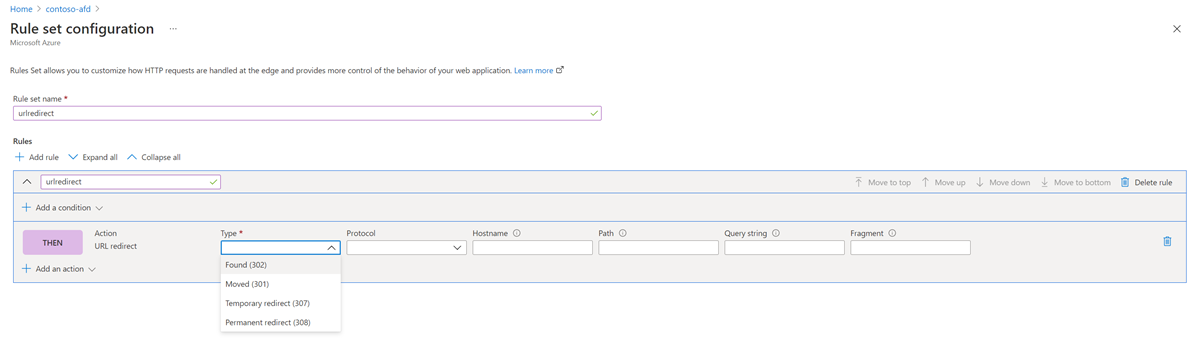
URL redirect
Azure Front Door can redirect traffic at each of the following levels: protocol, hostname, path, query string. These functionalities can be configured for individual microservices since the redirection is path-based. This setup can simplify application configuration by optimizing resource usage, and supports new redirection scenarios including global and path-based redirection.
Important
Azure Front Door (classic) will be retired on March 31, 2027. To avoid any service disruption, it is important that you migrate your Azure Front Door (classic) profiles to Azure Front Door Standard or Premium tier by March 2027. For more information, see Azure Front Door (classic) retirement.
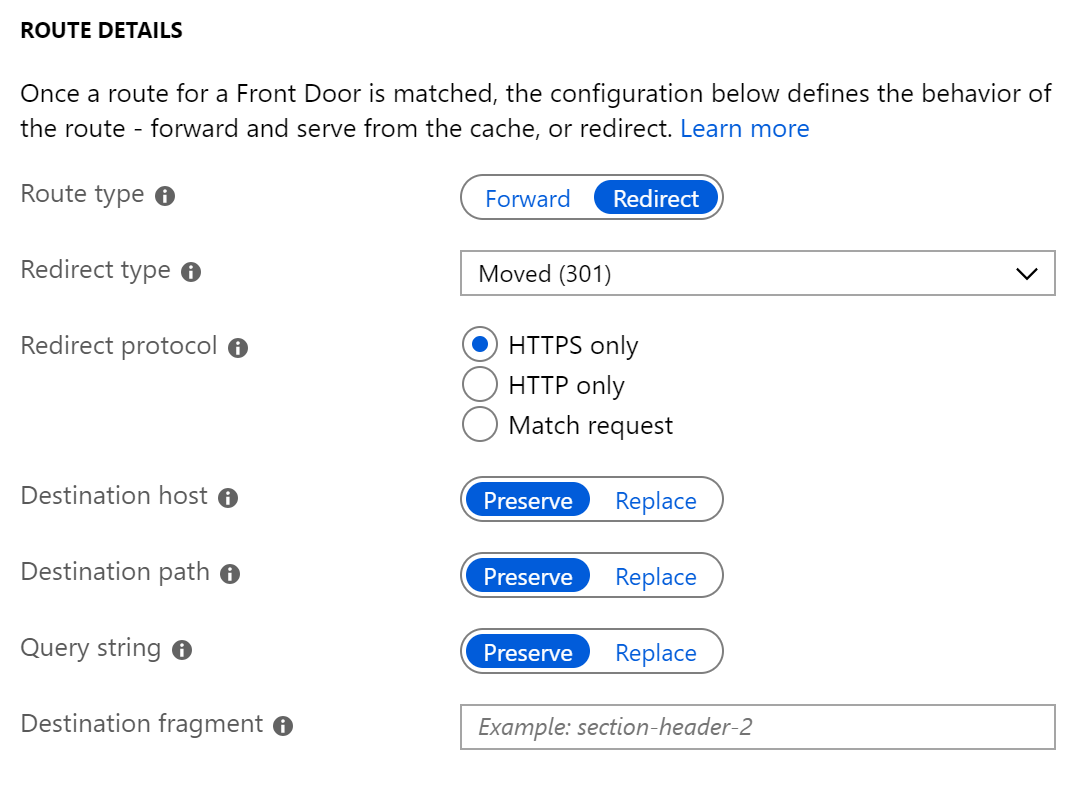
Redirection types
A redirect type sets the response status code for the clients to understand the purpose of the redirect. The following types of redirection are supported:
- 301 (Moved permanently): Indicates that the target resource has been assigned a new permanent URI. Any future references to this resource use one of the enclosed URIs. Use 301 status code for HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
- 302 (Found): Indicates that the target resource is temporarily under a different URI. Since the redirection can change on occasion, the client should continue to use the effective request URI for future requests.
- 307 (Temporary redirect): Indicates that the target resource is temporarily under a different URI. The user agent MUST NOT change the request method if it does an automatic redirection to that URI. Since the redirection can change over time, the client ought to continue using the original effective request URI for future requests.
- 308 (Permanent redirect): Indicates that the target resource has been assigned a new permanent URI. Any future references to this resource should use one of the enclosed URIs.
Redirection protocol
You can set the protocol that is used for redirection. The most common use cases of the redirect feature are to set HTTP to HTTPS redirection.
- HTTPS only: Set the protocol to HTTPS only, if you're looking to redirect the traffic from HTTP to HTTPS. Azure Front Door recommends that you should always set the redirection to HTTPS only.
- HTTP only: Redirects the incoming request to HTTP. Use this value only if you want to keep your traffic HTTP that is, nonencrypted.
- Match request: This option keeps the protocol used by the incoming request. So, an HTTP request remains HTTP and an HTTPS request remains HTTPS post redirection.
Destination host
As part of configuring a redirect routing, you can also change the hostname or domain for the redirect request. You can set this field to change the hostname in the URL for the redirection or otherwise preserve the hostname from the incoming request. So, using this field you can redirect all requests sent on https://www.contoso.com/* to https://www.fabrikam.com/*.
Destination path
For cases where you want to replace the path segment of a URL as part of redirection, you can set this field with the new path value. Otherwise, you can choose to preserve the path value as part of redirect. So, using this field, you can redirect all requests sent to https://www.contoso.com/\* to https://www.contoso.com/redirected-site.
Query string parameters
The set of query strings to be used in the redirect URL. The value of this field will overwrite the incoming query strings, leaving this field empty will preserve the incoming query string. Query string must be in <key>=<value> format, separated by &.
Destination fragment
The destination fragment is the portion of URL after '#', which is used by the browser to land on a specific section of a web page. You can set this field to add a fragment to the redirect URL.
Next steps
- Learn how to create a Front Door.
- Learn more about Azure Front Door Rule Set.
- Learn how Front Door works.