Azure Firewall Policy rule sets
Firewall Policy is a top-level resource that contains security and operational settings for Azure Firewall. It allows you to manage rule sets that Azure Firewall uses to filter traffic. Firewall Policy organizes, prioritizes, and processes rule sets based on a hierarchy with the following components: rule collection groups, rule collections, and rules.
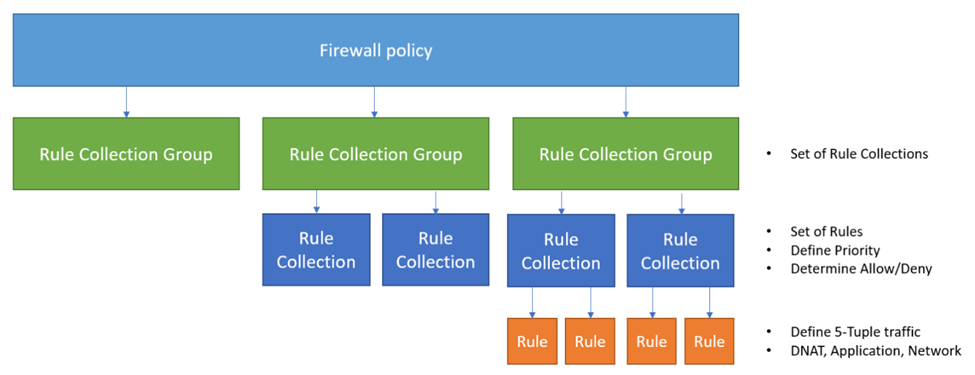
Rule collection groups
A rule collection group is used to group rule collections. It is the first unit processed by the firewall and follows a priority order based on values. There are three default rule collection groups with preset priority values, processed in the following order:
| Rule collection group name | Priority |
|---|---|
| Default DNAT (Destination Network Address Translation) rule collection group | 100 |
| Default Network rule collection group | 200 |
| Default Application rule collection group | 300 |
Although you cannot delete the default rule collection groups or modify their priority values, you can change the processing order by creating custom rule collection groups with your desired priority values. In this case, you would not use the default rule collection groups and instead use only the custom ones to define the processing logic.
Rule collection groups contain one or multiple rule collections, which can be of type DNAT, network, or application. For example, you can group rules belonging to the same workloads or a virtual network in a rule collection group.
For rule collection group size limits, see Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
Rule collections
A rule collection belongs to a rule collection group and contains one or more rules. It is the second unit processed by the firewall and follows a priority order based on values. Each rule collection must have a defined action (allow or deny) and a priority value. The action applies to all rules within the collection, and the priority value determines the order in which the rule collections are processed.
There are three types of rule collections:
- DNAT
- Network
- Application
The rule types must match their parent rule collection category. For example, a DNAT rule can only be part of a DNAT rule collection.
Rules
A rule belongs to a rule collection and specifies which traffic is allowed or denied in your network. It is the third unit processed by the firewall and does not follow a priority order based on values. The firewall processes rules in a top-down approach, evaluating all traffic against the defined rules to determine if it matches an allow or deny condition. If no rule allows the traffic, it is denied by default.
Our built-in infrastructure rule collection processes traffic for application rules before denying it by default.
Inbound vs. outbound
An inbound firewall rule protects your network from threats originating outside your network (traffic sourced from the Internet) attempting to infiltrate inwardly.
An outbound firewall rule protects against malicious traffic originating internally (traffic sourced from a private IP address within Azure) and traveling outwardly. This typically involves traffic from within Azure resources being redirected via the Firewall before reaching a destination.
Rule types
There are three types of rules:
- DNAT
- Network
- Application
DNAT rules
DNAT rules manage inbound traffic through one or more firewall public IP addresses. Use a DNAT rule to translate a public IP address into a private IP address. Azure Firewall public IP addresses can listen to inbound traffic from the Internet, filter it, and translate it to internal Azure resources.
Network rules
Network rules control inbound, outbound, and east-west traffic based on the network layer (L3) and transport layer (L4). Use a network rule to filter traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
Application rules
Application rules manage outbound and east-west traffic based on the application layer (L7). Use an application rule to filter traffic based on fully qualified domain names (FQDNs), URLs, and HTTP/HTTPS protocols.
Next steps
- To learn more about how Azure Firewall processes rules, see Configure Azure Firewall rules.