Microsoft Defender External Attack Surface Management overview
Microsoft Defender External Attack Surface Management (Defender EASM) continuously discovers and maps your digital attack surface to give you an external view of your online infrastructure.
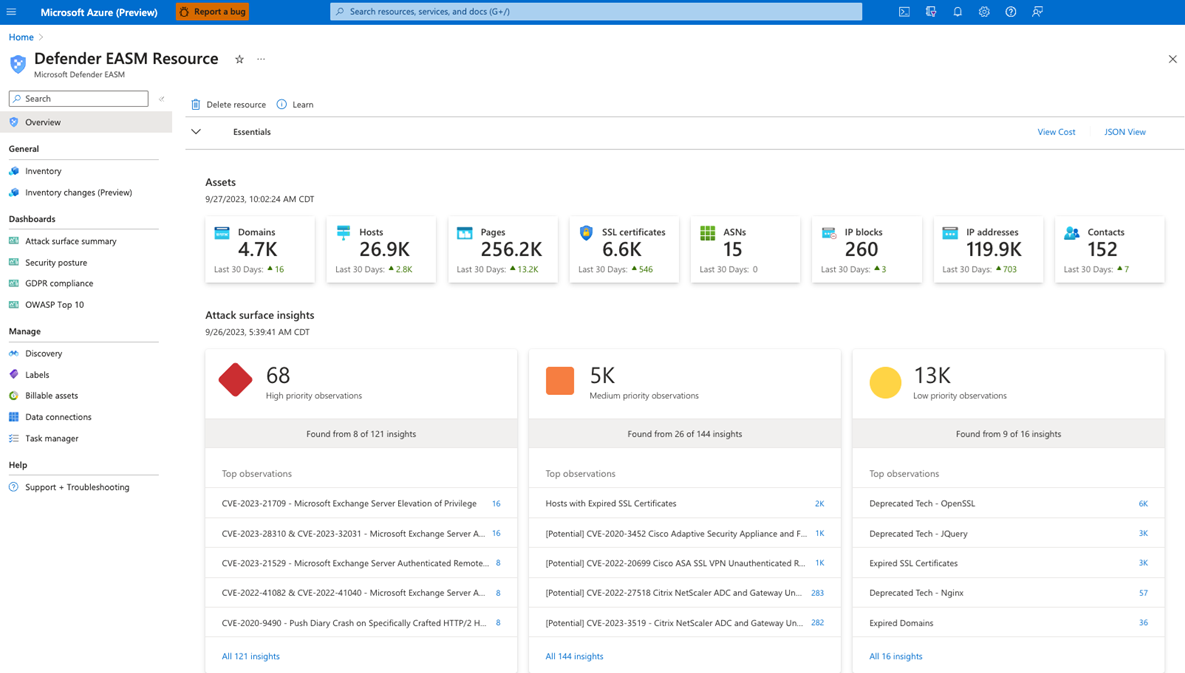
Defender EASM gives your security and IT teams essential visibility to help them identify unknowns, prioritize risk, eliminate threats, and extend control of vulnerabilities and exposure beyond the firewall. Attack surface insights are generated by using vulnerability and infrastructure data to showcase key areas of concern for your organization.
Discovery and inventory
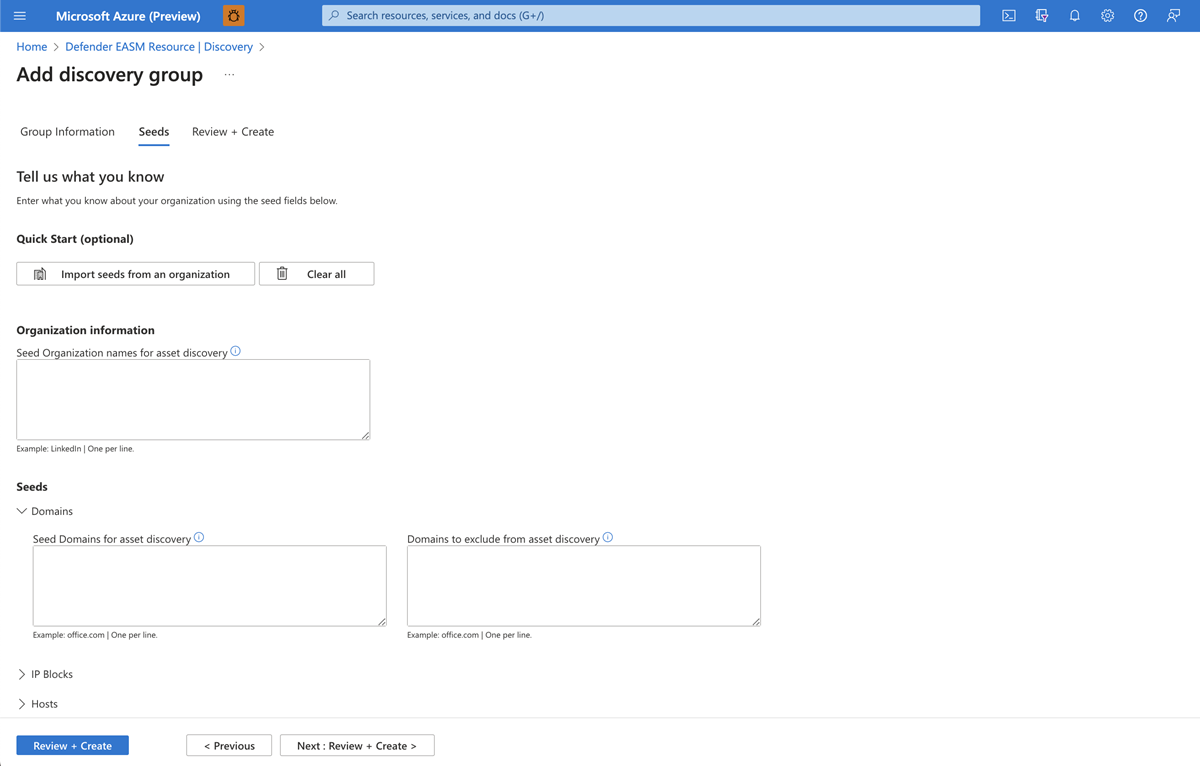
Microsoft proprietary discovery technology recursively searches for infrastructure through observed connections to known legitimate assets. It makes inferences about that infrastructure's relationship to the organization to uncover previously unknown and unmonitored properties. These known legitimate assets are called discovery seeds. Defender EASM first discovers strong connections to these selected entities, and then recurses to unveil more connections and ultimately compile your attack surface.
Defender EASM discovery includes the following kinds of assets:
- Domains
- IP address blocks
- Hosts
- Email contacts
- Autonomous system numbers (ASNs)
- Whois organizations
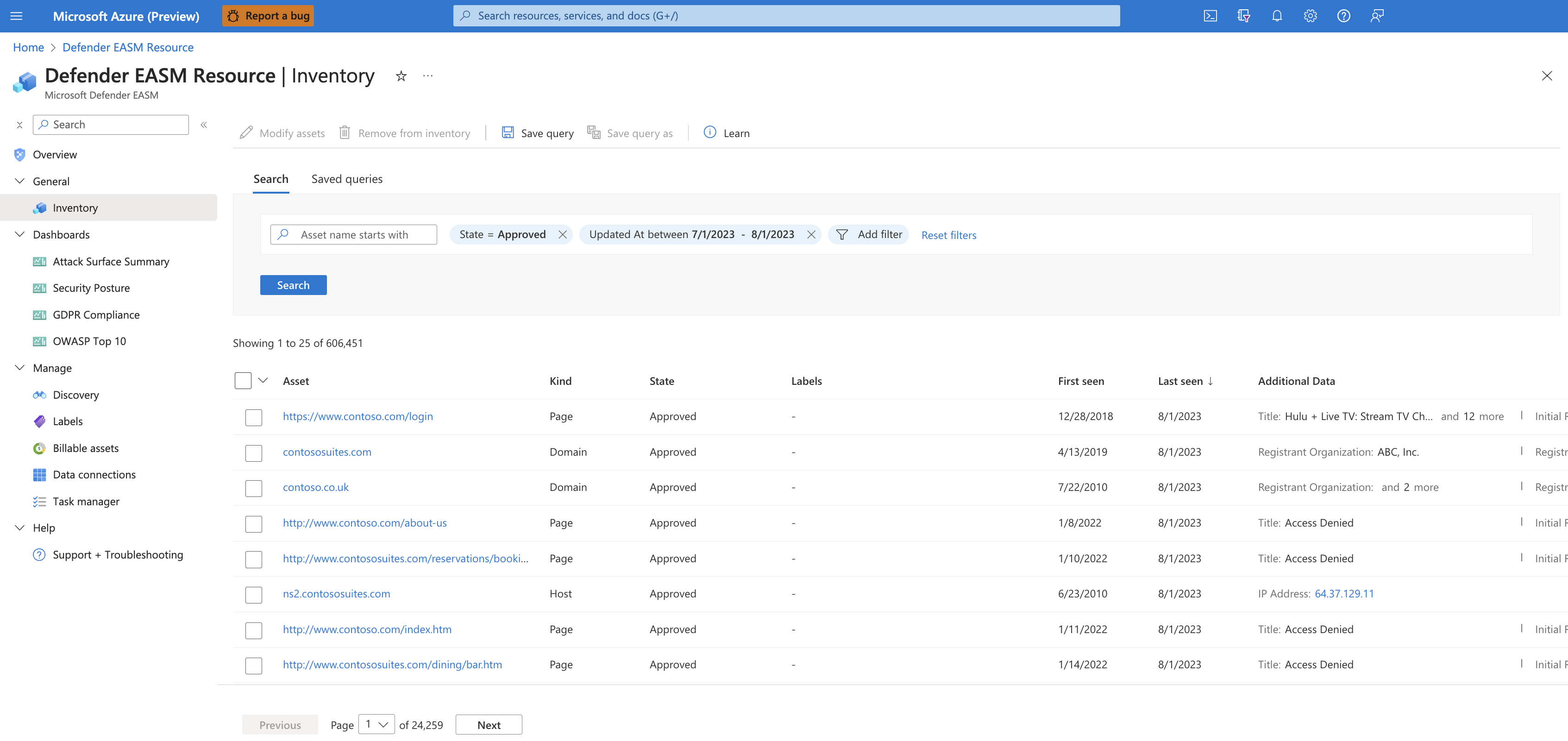
Discovered assets are indexed and classified in your Defender EASM inventory to give you a dynamic record of the entire web infrastructure under your management. Assets are categorized as recent (currently active) or historic. They can include web applications, third-party dependencies, and other asset connections.
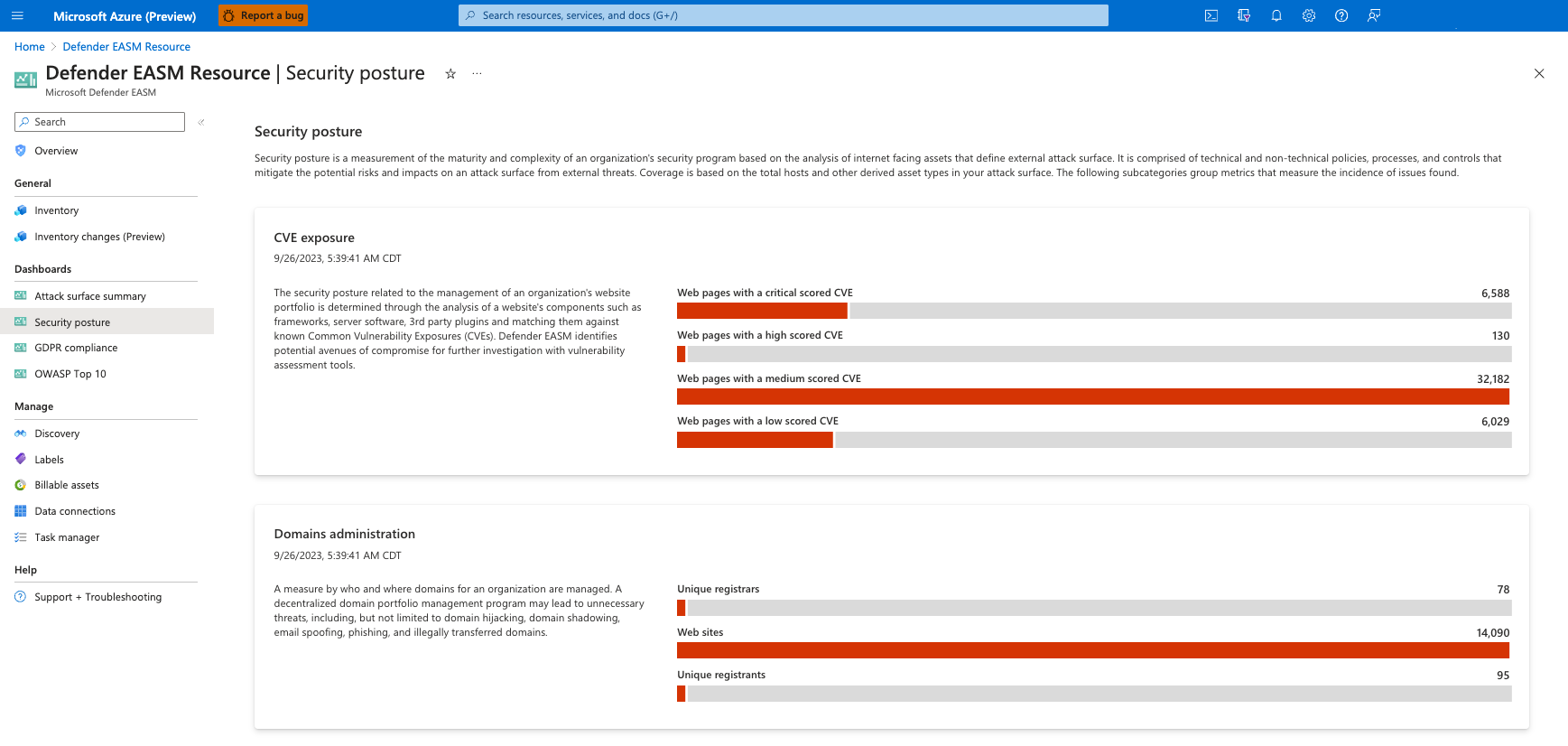
Dashboards
Defender EASM uses dashboards to help you quickly understand your online infrastructure and any key risks to your organization. The dashboards are designed to provide insight on specific areas of risk, including vulnerabilities, compliance, and security hygiene. These insights help you quickly address the components of your attack surface that pose the greatest risk to your organization.
Asset management
You can filter your inventory to surface the insights that are most important to you and your organization. Filtering gives you flexibility and customization to help you access a specific subset of assets. Filtering also puts Defender EASM data to work for your specific use case, whether you're searching for assets that connect to deprecating infrastructure or identifying new cloud resources.
User permissions
A user in your organization who is assigned the Owner or Contributor role can create, delete, and edit Defender EASM resources and the inventory assets in a resource. The Owner and Contributor roles have permissions to use all of the platform's capabilities and features.
A user who is assigned the Reader role can view Defender EASM data, but they can't create, delete, or edit a resource or inventory asset.
Data residency, availability, and privacy
Microsoft Defender EASM contains both global data and customer-specific data. The underlying internet data is global data that originates with Microsoft. Labels that customers apply are considered customer data. Your customer data is stored in the region you select.
For security purposes, Microsoft collects a user's IP address when the user signs in. The IP address is stored for up to 30 days, but it can be stored longer if it's needed to investigate potential fraudulent or malicious use of the product.
If an Azure region is down, only the Defender EASM customers in that region are affected. Services and data in other Azure regions continue to be active.
If an organization is no longer a customer of Microsoft, the Microsoft compliance framework requires all the customer's data to be deleted within 180 days. This policy includes customer data that's stored in offline locations, such as database backups. After a resource is deleted, it can't be restored by our teams. Customer data is retained in our data stores for another 75 days, but the actual resource can't be restored. After the 75-day period, customer data is permanently deleted.