Deploy Geospatial Consumption Zone
The OSDU Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) is a service that enables enhanced management and utilization of geospatial data. The GCZ streamlines the handling of location-based information. It abstracts away technical complexities, allowing software applications to access geospatial data without needing to deal with intricate details. By providing ready-to-use map services, the GCZ facilitates seamless integration with OSDU-enabled applications.
This guide shows you how to deploy the Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) service integrated with Azure Data Manager for Energy (ADME).
Create an App Registration in Microsoft Entra ID
To deploy the GCZ, you need to create an App Registration in Microsoft Entra ID. The App Registration is used to authenticate the GCZ APIs with Azure Data Manager for Energy to be able to generate the cache of the geospatial data.
See Create an App Registration in Microsoft Entra ID for instructions on how to create an App Registration.
Grant the App Registration permission to read the relevant data in Azure Data Manager for Energy. See How to add members to an OSDU group for further instructions.
Setup
There are two main deployment options for the GCZ service:
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): Deploy the GCZ service on an AKS cluster. This deployment option is recommended for production environments. It requires more effort to set up, configure, and maintain.
- Windows: Deploy the GCZ service on a Windows. This deployment option recommended for development and testing environments.
Deploy Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Learn how to deploy Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
Prerequisites
- Azure Subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account.
- Azure Kubernetes Cluster (AKS) with virtual network integration. See Create an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster and Azure Container Networking Interface (CNI) networking for further instructions.
- Azure Cloud Shell or Azure CLI, kubectl, and Git CLI.
Deploy Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) HELM Chart
Clone the GCZ repository to your local environment:
git clone https://community.opengroup.org/osdu/platform/consumption/geospatial.gitChange directory to the
geospatialfolder:cd geospatial/devops/azure/charts/geospatialDefine variables for the deployment:
# Define the variables for Azure Data Manager for Energy AZURE_DNS_NAME="<instanceName>.energy.azure.com" # Example: demo.energy.azure.com DATA_PARTITION_ID="<dataPartitionId>" # Data partition ID. Example: opendes AZURE_TENANT_ID="<tenantId>" # Entra ID tenant ID. Example: aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee AZURE_CLIENT_ID="<clientId>" # App Registration client ID. Example: 00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444 AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET="<clientSecret>" # App Registration client secret. Example: Aa1Bb~2Cc3.-Dd4Ee5Ff6Gg7Hh8Ii9_Jj0Kk1Ll2 SCOPE="<scope>" # Scope of the App Registration. Example: 00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444/.default CALLBACK_URL="http://localhost:8080" # Redirect URI of the ADME App Registration (from scope) ie: http://localhost:8080 PRIVATE_NETWORK="true" # Set to false if you want to expose the service publicly using a LoadBalancer. You can still expose the service using an Ingress Controller or Azure API Management at a later stage. # Define the variables for AKS AKS_NAME="<aksName>" # Name of the AKS cluster. Example: gcz-aks-cluster. RESOURCE_GROUP="<resourceGroupName>" # Name of the resource group. Example: gcz-rg. NAMESPACE="ignite" # Name of the AKS namespace you want to deploy to. We recommend to leave it default. GCZ_IGNITE_SERVICE="ignite-service" # Name of the ignite service. We recommend to leave it default. GCZ_IGNITE_NAMESPACE=$NAMESPACE CHART=osdu-gcz-service CHART_VERSION=1.27.0 VERSION=0.27.0Create the HELM chart:
cat > osdu_gcz_custom_values.yaml << EOF # This file contains the essential configs for the gcz on azure helm chart ################################################################################ # Specify the values for each service. # global: ignite: namespace: $NAMESPACE name: ignite image: name: gridgain/community tag: 8.8.43 configuration: gcz_ignite_namespace: "$GCZ_IGNITE_NAMESPACE" gcz_ignite_service: "$GCZ_IGNITE_SERVICE" provider: namespace: $NAMESPACE entitlementsGroupsURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/entitlements/v2/groups" image: repository: community.opengroup.org:5555 name: osdu/platform/consumption/geospatial/geospatial-provider-master tag: latest service: type: LoadBalancer configuration: privateNetwork: "$PRIVATE_NETWORK" transformer: namespace: $NAMESPACE image: repository: community.opengroup.org:5555 name: osdu/platform/consumption/geospatial/geospatial-transformer-master tag: latest service: type: LoadBalancer configuration: privateNetwork: "$PRIVATE_NETWORK" datapartitionid: $DATA_PARTITION_ID clientId: $AZURE_CLIENT_ID tenantId: $AZURE_TENANT_ID callbackURL: $CALLBACK_URL scope: $SCOPE searchQueryURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/search/v2/query" searchCursorURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/search/v2/query_with_cursor" schemaURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/schema-service/v1/schema" entitlementsURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/entitlements/v2" fileRetrievalURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/dataset/v1/retrievalInstructions" crsconvertorURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/crs/converter/v3/convertTrajectory" storageURL: "https://$AZURE_DNS_NAME/api/storage/v2/records" clientSecret: $(echo "$AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET" | base64) gcz_ignite_namespace: "$GCZ_IGNITE_NAMESPACE" gcz_ignite_service: "$GCZ_IGNITE_SERVICE" EOFChange service type to
LoadBalancerfor theproviderandtransformerservices configuration files.cat > ../provider/templates/service.yaml << EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: gcz-provider namespace: {{ $.Values.global.provider.namespace }} annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal: "{{ $.Values.global.provider.configuration.privateNetwork }}" spec: selector: app: provider ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8083 type: {{ $.Values.global.provider.service.type }} EOF cat > ../transformer/templates/service.yaml << EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: gcz-transformer namespace: {{ $.Values.global.transformer.namespace }} annotations: service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal: "{{ $.Values.global.transformer.configuration.privateNetwork }}" spec: selector: app: transformer ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 type: {{ $.Values.global.transformer.service.type }} EOFReview the transformer configuration file
application.ymlto ensure the correct schemas are included.nano ../transformer/application.ymlReview the provider configuration file
koop-config.json.nano ../provider/koop-config.jsonAuthenticate to the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster:
az aks get-credentials --resource-group $RESOURCE_GROUP --name $AKS_NAME --adminCreate AKS Namespace:
kubectl create namespace $NAMESPACEDeploy HELM dependencies:
helm dependency buildDeploy the GCZ HELM chart:
helm upgrade -i $CHART . -n $NAMESPACE -f osdu_gcz_custom_values.yaml --set-file global.provider.configLoaderJs="../../../../gcz-provider/gcz-provider-core/config/configLoader.js"Verify the deployment:
kubectl get pods -n $NAMESPACENow you should see the pods for the
ignite,provider, andtransformerservices.Next get note the External IPs for the
providerandtransformerservices.kubectl get service -n $NAMESPACEThese IPs are used to connect to the GCZ API endpoints.
Important
If you wish to update the configuration files (e.g., application.yml or koop-config.json), you must update the AKS configuration (configmap) and then delete the existing pods for the provider and transformer services. The pods will be recreated with the new configuration. If you change the configuration using the GCZ APIs, the changes will not persist after a pod restart.
Deploy Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) on a Windows Virtual Machine
Learn how to deploy Geospatial Consumption Zone (GCZ) on Windows. This deployment option is recommended for development and testing environments, as it's easier to set up and configure, and requires less maintenance.
Prerequisites
- An Azure Data Manager for Energy instance. If you don't have an Azure Data Manager for Energy instance, see Create an Azure Data Manager for Energy instance.
- A Windows Virtual Machine. If you don't have a Windows Virtual Machine, see Create a Windows Virtual Machine in Azure. It's also possible to use your local machine.
- Java JDK 17 installed on the Windows Virtual Machine. If you don't have Java installed, see Install Java on Windows.
- Node 18.19.1 (LTS) installed on the Windows Virtual Machine. If you don't have Node installed, see Install Node.js and npm on Windows.
- Python 3.11.4 or newer installed on the Windows Virtual Machine. If you don't have Python installed, see Install Python on Windows.
- Ensure you add
pipduring the installation process. If you forget to addpip, you can install it manually.
- Ensure you add
Deploy GCZ on Windows
Connect to your Windows Virtual Machine.
Download the following files from the OSDU GitLab repository:
Open PowerShell as an administrator and navigate to the folder where you downloaded the files.
Run the following commands to extract the files:
Expand-Archive -Path .\GCZ_PROVIDER.zip -DestinationPath C:\gcz\ Expand-Archive -Path .\GCZ_TRANSFORMER.zip -DestinationPath C:\gcz\ Expand-Archive -Path .\GCZ_PYTHON_DEPENDENCIES.zip -DestinationPath C:\gcz\Configure the environment variables:
$ADME_HOSTNAME = "<adme-hostname>" # ADME Hostname, e.g. "https://contoso.energy.azure.com" $GCZ_DATA_PARTITION_ID = "<data-partition-id>" # ADME Data Partition ID, e.g. "opendes" $GCZ_QUERY_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/search/v2/query" # ADME Query Endpoint $GCZ_QUERY_CURSOR_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/search/v2/query_with_cursor" # ADME Query with Cursor Endpoint $GCZ_SCHEMA_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/schema-service/v1/schema" # ADME Schema Endpoint $GCZ_ENTITLEMENT_SERVICE_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/entitlements/v2" # ADME Entitlement Service Endpoint $GCZ_FILE_RETRIEVAL_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/dataset/v1/retrievalInstructions" # ADME File Retrieval Endpoint $GCZ_CONVERT_TRAJECTORY_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/crs/converter/v3/convertTrajectory" # ADME Convert Trajectory Endpoint $GCZ_STORAGE_URL = "$ADME_HOSTNAME/api/storage/v2/records/" # ADME Storage EndpointFor more environment variables, see the OSDU GitLab documentation.
Validate the configuration files for the GCZ Provider and Transformer by opening the configuration files in a text editor and updating the values if needed.
- Provider:
C:\gcz\gcz-provider\gcz-provider-core\config\koop-config.json - Transformer:
C:\gcz\gcz-transformer-core\config\application.yml
Important
If you make changes to the schemas in the configuration files, you have to make sure that those schemas are represented in both of the configuration files.
- Provider:
(optional) Install Python Dependencies (only required for Well Log Interpolation).
pip install -r C:\gcz\gcz-transformer-core\src\main\resources\script\requirements.txt --no-index --find-links python-dependenciesStart the GCZ Transformer.
C:\gcz\transformer\transformer.bat localBuild the GCZ Provider.
cd C:\gcz\gcz-provider\gcz-provider-core npm install npm start
By default the Provider is listening on http://localhost:8083 and the Transformer is listening on http://localhost:8080.
Publish GCZ APIs publicly (optional)
If you want to expose the GCZ APIs publicly, you can use Azure API Management (APIM). Azure API Management allows us to securely expose the GCZ service to the internet, as the GCZ service doesn't yet have authentication and authorization built in. Through APIM we can add policies to secure, monitor, and manage the APIs.
Prerequisites
- An Azure API Management instance. If you don't have an Azure API Management instance, see Create an Azure API Management instance.
- The GCZ APIs are deployed and running.
Important
The Azure API Management instance will need to be injected into a virtual network that is routable to the AKS cluster to be able to communicate with the GCZ API's.
Add the GCZ APIs to Azure API Management
Download the GCZ OpenAPI specifications
Download the two OpenAPI specification to your local computer.
Open each OpenAPI specification file in a text editor and replace the
serverssection with the corresponding IPs of the AKS GCZ Services' Load Balancer.servers: - url: "http://<GCZ-Service-LoadBalancer-IP>/ignite-provider"
Add the GCZ APIs to Azure API Management
Navigate to your Azure API Management service in the Azure portal.
In the left-hand navigation pane, select APIs.
Select + Add API.
Select OpenAPI.
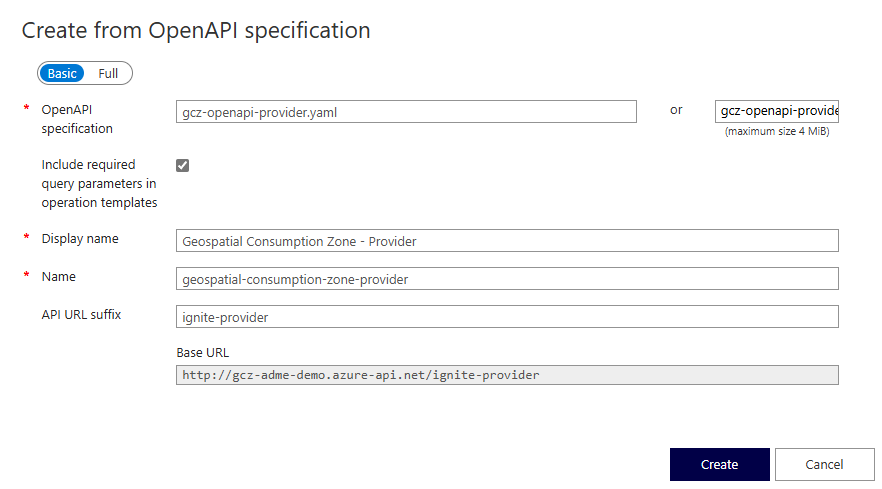
Select Select a file and upload the
gcz-openapi-provider.yamlfile.In the API URL suffix field, enter
ignite-provider.Select Create.
Repeat the steps for the
gcz-openapi-transformer.yamlfile, but usegcz/transformer/adminas the API URL suffix.
Configure policies
Next we need to configure the policies to validate the JSON Web Tokens (JWT).
You need the following information:
- Your Microsoft Entra ID tenant ID.
- The Azure Data Manager for Energy client ID (or token-issuing client ID if separate).
Note
If you have multiple App Registrations issuing tokens, you can add multiple <application-id> elements to the <client-application-ids> element.
In the newly created
Geospatial Consumption Zone - ProviderAPI, make sure All operations is selected.Under Inbound processing, select ... and then Code editor.
Paste the following policy definition in the editor:
<policies> <!-- Throttle, authorize, validate, cache, or transform the requests --> <inbound> <base /> <validate-azure-ad-token tenant-id="%tenant-id%" failed-validation-httpcode="401"> <client-application-ids> <application-id>%client-id%</application-id> </client-application-ids> </inbound> <!-- Control if and how the requests are forwarded to services --> <backend> <base /> </backend> <!-- Customize the responses --> <outbound> <base /> </outbound> <!-- Handle exceptions and customize error responses --> <on-error> <base /> </on-error> </policies>Replace
%tenant-id%with your Microsoft Entra ID tenant ID, and%client-id%with the Azure Data Manager for Energy client ID.Select Save.
Repeat the steps for the
Geospatial Consumption Zone - TransformerAPI.
Testing the GCZ service
Download the API client collection from the OSDU GitLab and import it into your API client of choice (i.e. Bruno, Postman).
Add the following environment variables to your API client:
PROVIDER_URL- The URL to the GCZ Provider API.AMBASSADOR_URL- The URL to the GCZ Transformer API.access_token- A valid ADME access token.
To verify that the GCZ is working as expected, run the API calls in the collection.
Next steps
After you have a successful deployment of GCZ, you can:
- Visualize your GCZ data using the GCZ WebApps from the OSDU GitLab.
Important
The GCZ WebApps are currently in development and does not support authentication. We recommend deploying the WebApps in a private network and exposing them using Azure Application Gateway or Azure Front Door to enable authentication and authorization.
You can also ingest data into your Azure Data Manager for Energy instance:
References
- For information about Geospatial Consumption Zone, see OSDU GitLab.