How to ingest data by using Azure Stream Analytics in Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL
APPLIES TO:
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL (powered by the Citus database
extension to PostgreSQL)
Azure Stream Analytics is a real-time analytics and event-processing engine that is designed to process high volumes of fast streaming data from devices, sensors, and web sites. It's also available on the Azure IoT Edge runtime, enabling data processing on IoT devices.
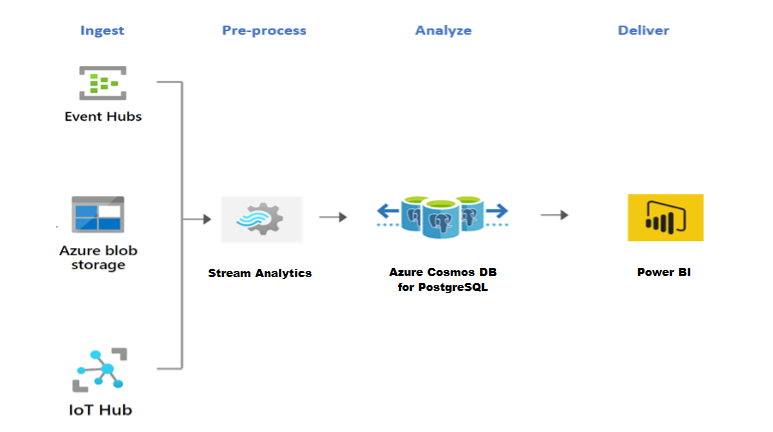
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL shines at real-time workloads such as IoT. For these workloads, Stream Analytics can act as a no-code, performant and scalable alternative to pre-process and stream data from Azure Event Hubs, Azure IoT Hub, and Azure Blob Storage into Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL.
Steps to set up Stream Analytics
Note
This article uses Azure IoT Hub as an example datasource, but the technique is applicable to any other source supported by Stream Analytics. Also, the following demonstration data comes from the Azure IoT Device Telemetry Simulator. This article doesn't cover setting up the simulator.
In the Azure portal, expand the portal menu at upper left and select Create a resource.
Select Analytics > Stream Analytics job from the results list.
Fill out the New Stream Analytics job page with the following information:
- Subscription - Select the Azure subscription that you want to use for this job.
- Resource group - Select the same resource group as your IoT hub.
- Name - Enter a name to identify your Stream Analytics job.
- Region - Select the Azure region to host your Stream Analytics job. Use the geographic location that's closest to your users for better performance and to reduce the data transfer cost.
- Hosting environment - Select Cloud to deploy to the Azure cloud, or Edge to deploy to an IoT Edge device.
- Streaming units - Select the number of streaming units for the computing resources you need to execute the job.
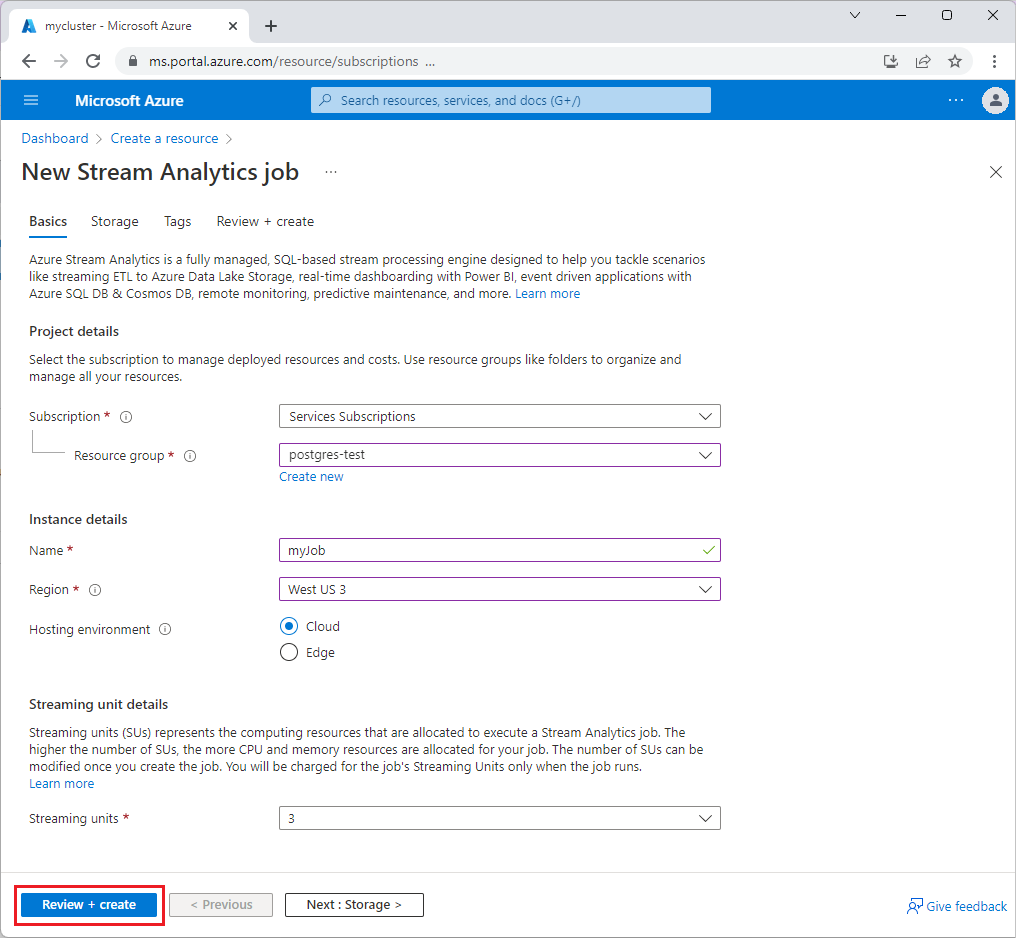
Select Review + create, and then select Create. You should see a Deployment in progress notification at upper right.
Configure job input.
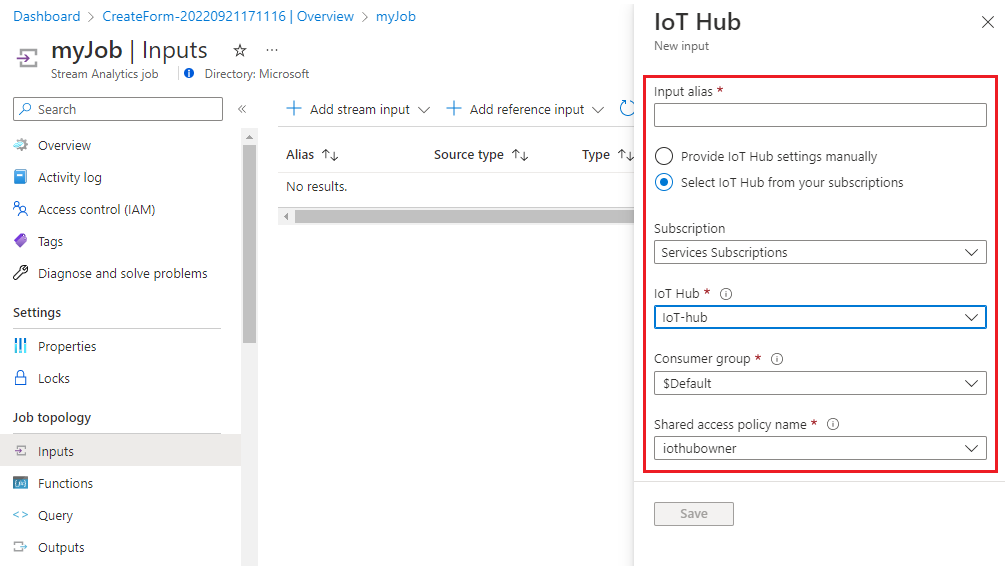
Once the resource deployment is complete, navigate to your Stream Analytics job. Select Inputs > Add stream input > IoT Hub.
Fill out the IoT Hub page with the following values:
- Input alias - Enter a name to identify the job input.
- Subscription - Select the Azure subscription that has your IoT Hub account.
- IoT Hub – Select the name of your IoT hub.
Select Save.
Once the input stream is added, you can also verify or download the dataset flowing in. The following code shows the data for an example event:
{ "deviceId": "sim000001", "time": "2022-04-25T13:49:11.6892185Z", "counter": 1, "EventProcessedUtcTime": "2022-04-25T13:49:41.4791613Z", "PartitionId": 3, "EventEnqueuedUtcTime": "2022-04-25T13:49:12.1820000Z", "IoTHub": { "MessageId": null, "CorrelationId": "aaaa0000-bb11-2222-33cc-444444dddddd", "ConnectionDeviceId": "sim000001", "ConnectionDeviceGenerationId": "637842405470327268", "EnqueuedTime": "2022-04-25T13:49:11.7060000Z" } }
Configure job output.
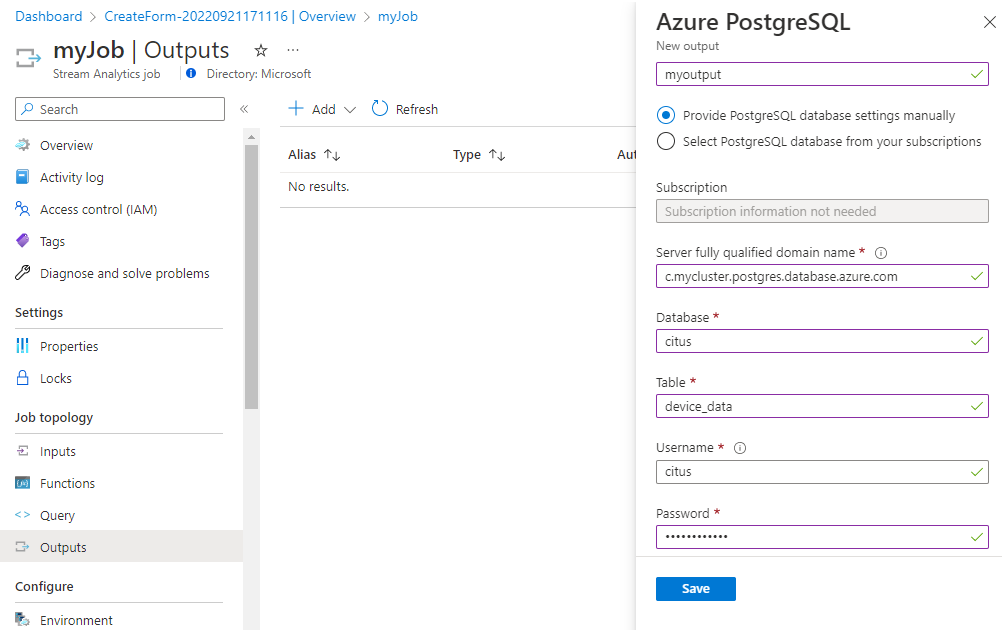
On the Stream Analytics job page, select Outputs > Add > PostgreSQL database (preview).
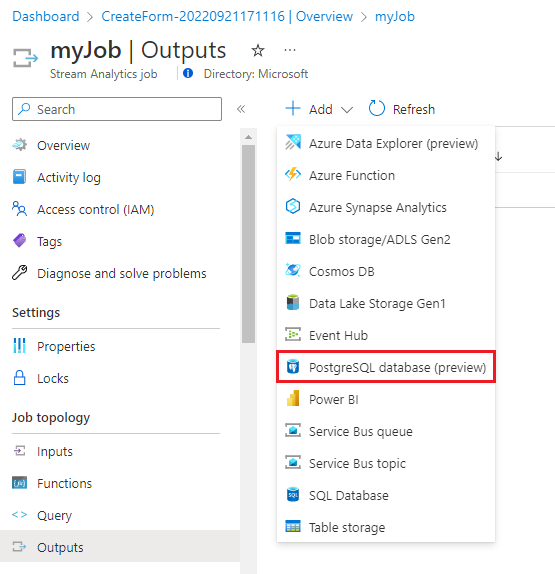
Fill out the Azure PostgreSQL page with the following values:
- Output alias - Enter a name to identify the job's output.
- Select Provide PostgreSQL database settings manually and enter the Server fully qualified domain name, Database, Table, Username, and Password. From the example dataset, use the table device_data.
Select Save.
Define the transformation query.
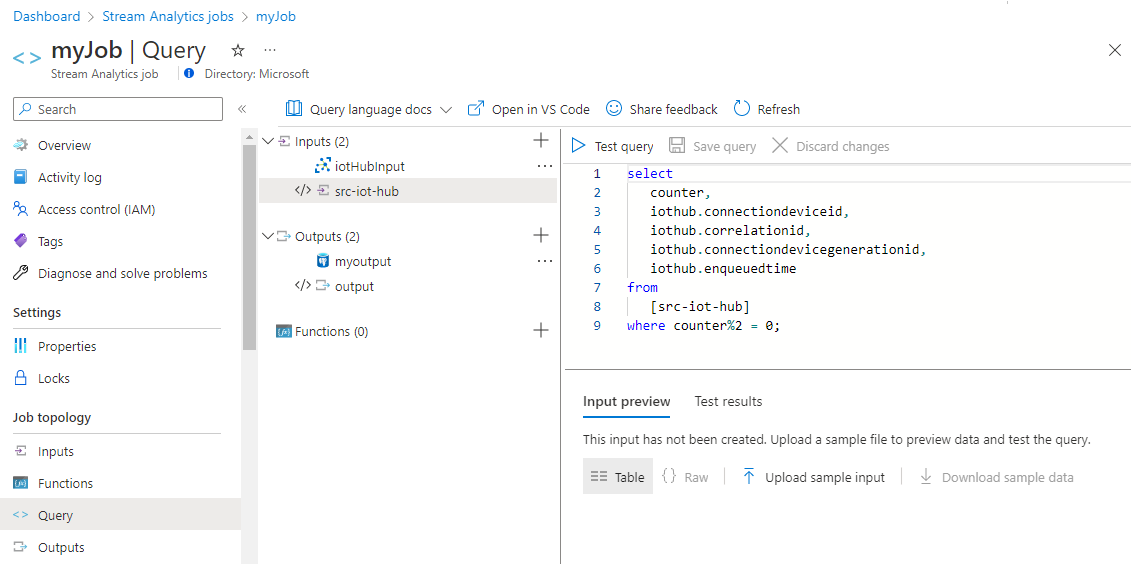
On the Stream Analytics job page, select Query from the left menu.
For this tutorial, you ingest only the alternate events from IoT Hub into Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL, to reduce the overall data size. Copy and paste the following query into the query pane:
select counter, iothub.connectiondeviceid, iothub.correlationid, iothub.connectiondevicegenerationid, iothub.enqueuedtime from [src-iot-hub] where counter%2 = 0;Select Save query.
Note
You use the query to not only sample the data, but also to extract the desired attributes from the data stream. The custom query option with Stream Analytics is helpful in pre-processing/transforming the data before it gets ingested into the database.
Start the Stream Analytics job and verify output.
Return to the job overview page and select Start.
On the Start job page, select Now for the Job output start time, and then select Start.
The job takes some time to start the first time, but once triggered it continues to run as the data arrives. After a few minutes, you can query the cluster to verify that the data loaded.
citus=> SELECT * FROM public.device_data LIMIT 10; counter | connectiondeviceid | correlationid | connectiondevicegenerationid | enqueuedtime ---------+--------------------+--------------------------------------+------------------------------+------------------------------ 2 | sim000001 | 7745c600-5663-44bc-a70b-3e249f6fc302 | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:03.4600000Z 4 | sim000001 | 389abfde-5bec-445c-a387-18c0ed7af227 | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:05.4600000Z 6 | sim000001 | 3932ce3a-4616-470d-967f-903c45f71d0f | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:07.4600000Z 8 | sim000001 | 4bd8ecb0-7ee1-4238-b034-4e03cb50f11a | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:09.4600000Z 10 | sim000001 | 26cebc68-934e-4e26-80db-e07ade3775c0 | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:11.4600000Z 12 | sim000001 | 067af85c-a01c-4da0-b208-e4d31a24a9db | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:13.4600000Z 14 | sim000001 | 740e5002-4bb9-4547-8796-9d130f73532d | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:15.4600000Z 16 | sim000001 | 343ed04f-0cc0-4189-b04a-68e300637f0e | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:17.4610000Z 18 | sim000001 | 54157941-2405-407d-9da6-f142fc8825bb | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:19.4610000Z 20 | sim000001 | 219488e5-c48a-4f04-93f6-12c11ed00a30 | 637842405470327268 | 2022-05-25T18:24:21.4610000Z (10 rows)
Note
The Test Connection feature currently isn't supported for Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL and might throw an error, even when the connection works fine.
Next steps
Learn how to create a real-time dashboard with Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL.