Tutorial: Sign and make requests with Postman
In this tutorial, we'll be setting up and using Postman to make a request against Azure Communication Services using HTTP. By the end of this tutorial, you'll have successfully sent an SMS message using Communication Services and Postman. You'll then be able to use Postman to explore other APIs within Azure Communication Services.
In this tutorial we'll be:
- Downloading Postman
- Setting up Postman to sign HTTP Requests
- Making a request against the Communication Services SMS API to send a message.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. For details, see Create an account for free. The free account gives you $200 in Azure credits to try out any combination of services.
- An active Communication Services resource and connection string. Learn how to create a Communication Services resource.
- An Azure Communication Services Telephone number that can send SMS messages, see our Get a phone number to get one.
Downloading and installing Postman
Postman, is a desktop application that is capable of making API requests against any HTTP API. It is commonly used for testing and exploring APIs. We'll be downloading the latest Desktop version from Postman's website. Postman has versions for Windows, Mac, and Linux so download the version appropriate for your operating system. Once downloaded open the application. You will be presented with a start screen, which asks you to sign in or to create a Postman account. Creating an account is optional and can be skipped by clicking the "Skip and go to app" link. Creating an account will save your API request settings to Postman, which can then allow you to pick up your requests on other computers.
Once you've created an account or skipped creating one, you should now see Postman's main window.
Creating and configuring a Postman collection
Postman, can organize requests in many ways. For the purposes of this tutorial. We'll be creating a Postman Collection. To do this, select the collections button on the left-hand side of the application:
Once selected, click "Create new Collection", to start the collection creation process. A new tab will open in the center area of Postman. Name the collection whatever you'd like. Here the collection is named "Azure Communication Services":
Once your collection is created and named, you are ready to configure it.
Adding collection variables
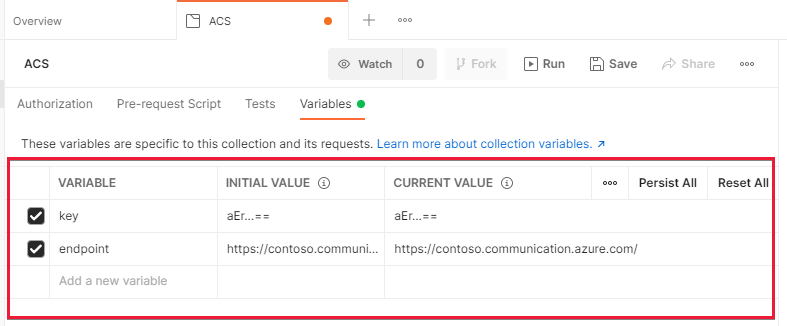
To handle authentication and to make requests easier, we'll be specifying two collection variables within the newly created Communication Services collection. These variables are available to all requests within your Communication Services collection. To get started in creating variables, visit the Collection's Variable's Tab.
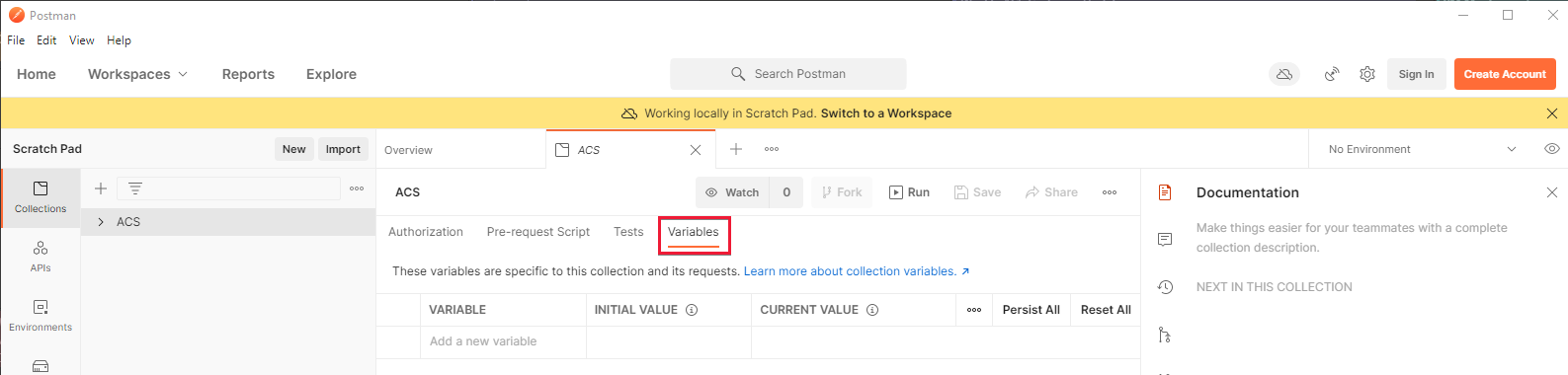
Once on the collection tab, create two variables:
- key - This variable should be one of your keys from your Azure Communication Services' key page within the Azure portal. For example,
oW...A==. - endpoint - This variable should be your Azure Communication Services' endpoint from the key page. Ensure you remove the trailing slash. For example,
https://contoso.communication.azure.com.
Enter these values into the "Initial Value" column of the variables screen. Once entered, press the "Persist All" button just above the table on the right. When configured correctly your Postman screen should look something like this:
You can learn more about variables by reading Postman's documentation on them.
Creating a pre-request script
The next step is to create a pre-request Script within Postman. A pre-request script, is a script that runs before each request in Postman and can modify or alter request parameters on your behalf. We'll be using this to sign our HTTP requests so that they can be authorized by Azure Communication Services. For more information about the Signing requirements, you can read our guide on authentication.
We'll be creating this script within the Collection such that it runs on any request within the collection. To do this, within the collection tab click the "Pre-request Script" Sub-Tab.
On this Sub-Tab, you can create a pre-request script by entering it into the text area below. It may be easier to write this, within a full code editor such as Visual Studio Code before pasting it in when complete. We'll be going through each part of the script in this tutorial. Feel free to skip to the end if you'd like to just copy it into Postman and get started. Let's start writing the script.
Writing the pre-request script
The first thing we'll be doing is creating a Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) string and adding this to the "Date" HTTP Header. We also store this string in a variable to use it later when signing:
// Set the Date header to our Date as a UTC String.
const dateStr = new Date().toUTCString();
pm.request.headers.upsert({key:'Date', value: dateStr});
Next, we'll hash the request body using SHA 256 and place it in the x-ms-content-sha256 header. Postman includes some standard libraries for hashing and signing globally, so we don't need to install them or require them:
// Hash the request body using SHA256 and encode it as Base64
const hashedBodyStr = CryptoJS.SHA256(pm.request.body.raw).toString(CryptoJS.enc.Base64)
// And add that to the header x-ms-content-sha256
pm.request.headers.upsert({
key:'x-ms-content-sha256',
value: hashedBodyStr
});
Now, we'll use our previously specified endpoint variable to discern the value for the HTTP Host header. We need to do this as the Host header is not set until after this script is processed:
// Get our previously specified endpoint variable
const endpoint = pm.variables.get('endpoint')
// Remove the https, prefix to create a suitable "Host" value
const hostStr = endpoint.replace('https://','');
With this information created, we can now create the string, which we'll be signing for the HTTP Request, this is composed of several previously created values:
// This gets the part of our URL that is after the endpoint, for example in https://contoso.communication.azure.com/sms, it will get '/sms'
const url = pm.request.url.toString().replace('{{endpoint}}','');
// Construct our string which we'll sign, using various previously created values.
const stringToSign = pm.request.method + '\n' + url + '\n' + dateStr + ';' + hostStr + ';' + hashedBodyStr;
Lastly, we need to sign this string using our Communication Services key and then add that to our request in the Authorization header:
// Decode our access key from previously created variables, into bytes from base64.
const key = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.parse(pm.variables.get('key'));
// Sign our previously calculated string with HMAC 256 and our key. Convert it to Base64.
const signature = CryptoJS.HmacSHA256(stringToSign, key).toString(CryptoJS.enc.Base64);
// Add our final signature in Base64 to the authorization header of the request.
pm.request.headers.upsert({
key:'Authorization',
value: "HMAC-SHA256 SignedHeaders=date;host;x-ms-content-sha256&Signature=" + signature
});
The final pre-request script
The final pre-request script should look something like this:
// Set the Date header to our Date as a UTC String.
const dateStr = new Date().toUTCString();
pm.request.headers.upsert({key:'Date', value: dateStr});
// Hash the request body using SHA256 and encode it as Base64
const hashedBodyStr = CryptoJS.SHA256(pm.request.body.raw).toString(CryptoJS.enc.Base64)
// And add that to the header x-ms-content-sha256
pm.request.headers.upsert({
key:'x-ms-content-sha256',
value: hashedBodyStr
});
// Get our previously specified endpoint variable
const endpoint = pm.variables.get('endpoint')
// Remove the https, prefix to create a suitable "Host" value
const hostStr = endpoint.replace('https://','');
// This gets the part of our URL that is after the endpoint, for example in https://contoso.communication.azure.com/sms, it will get '/sms'
const url = pm.request.url.toString().replace('{{endpoint}}','');
// Construct our string which we'll sign, using various previously created values.
const stringToSign = pm.request.method + '\n' + url + '\n' + dateStr + ';' + hostStr + ';' + hashedBodyStr;
// Decode our access key from previously created variables, into bytes from base64.
const key = CryptoJS.enc.Base64.parse(pm.variables.get('key'));
// Sign our previously calculated string with HMAC 256 and our key. Convert it to Base64.
const signature = CryptoJS.HmacSHA256(stringToSign, key).toString(CryptoJS.enc.Base64);
// Add our final signature in Base64 to the authorization header of the request.
pm.request.headers.upsert({
key:'Authorization',
value: "HMAC-SHA256 SignedHeaders=date;host;x-ms-content-sha256&Signature=" + signature
});
Enter or paste this final script, into the text area within the Pre-request Script Tab:
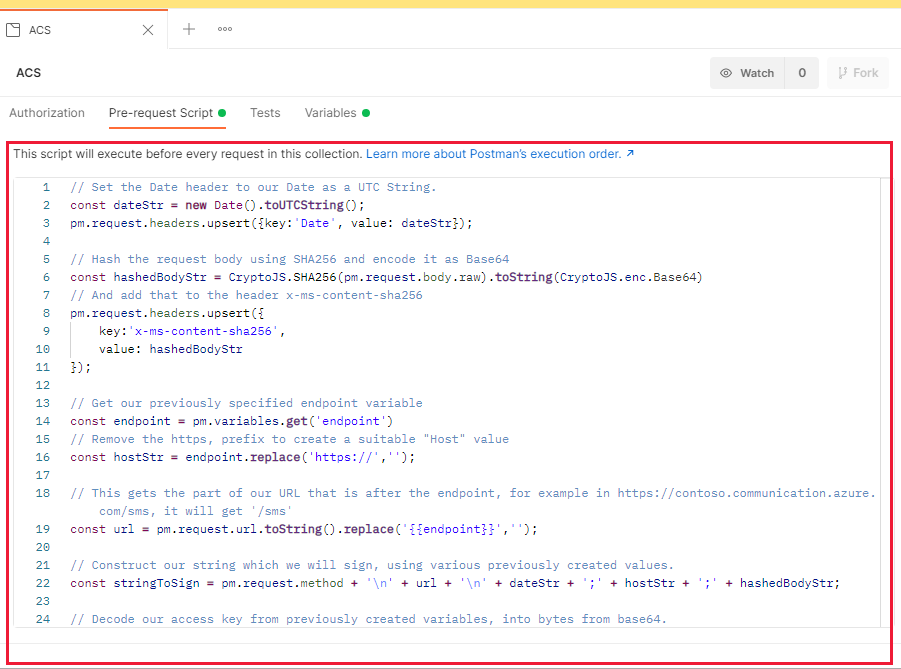
Once entered, press CTRL + S or press the save button this will save the script to the collection.
Creating a request in Postman
Now that everything is set up, we're ready to create a Communication Services request within Postman. To get started click the plus(+) icon next to the Communication Services Collection:

This will create a new tab for our request within Postman. With it created we need to configure it. We'll be making a request against the SMS Send API so be sure to refer to the documentation for this API for assistance. Let's configure Postman's request.
Start by setting, the request type to POST and entering {{endpoint}}/sms?api-version=2021-03-07 into the request URL field. This URL uses our previously created endpoint variable to automatically send it to your Communication Services resource.
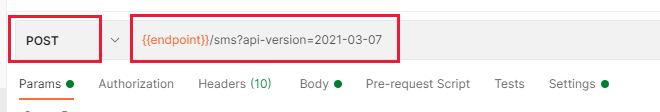
Now select the Body tab of the request and then change the radio button beneath to "raw". On the right, there is a dropdown that says "Text", change it to JSON:
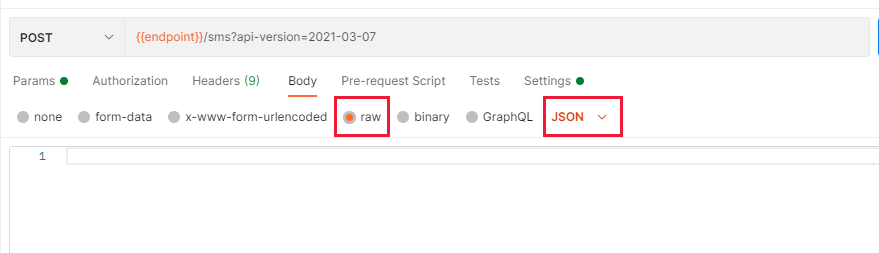
This will configure the request to send and receive information in a JSON format.
In the text area below you'll need to enter a request body, it should be in the following format:
{
"from":"<Your Azure Communication Services Telephone Number>",
"message":"<The message you'd like to send>",
"smsRecipients": [
{
"to":"<The number you'd like to send the message to>"
}
]
}
For the "from" value, you'll need to get a telephone number in the Azure Communication Services Portal as previously mentioned. Enter it without any spaces and prefixed by your country code. For example: +15555551234. Your "message" can be whatever you'd like to send but Hello from Azure Communication Services is a good example. The "to" value should be a phone you have access to that can receive SMS messages. Using your own mobile is a good idea.
Once entered, we need to save this request into the Communication Services Collection that we previously created. This will ensure that it picks up the variables and pre-request script that we previously created. To do, this click the "save" button in the top right of the request area.
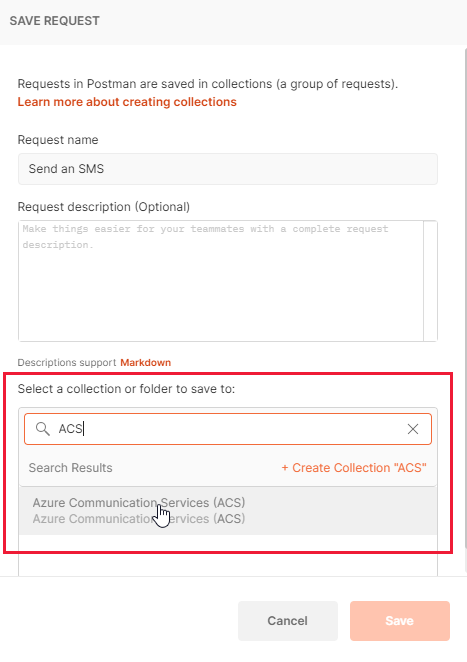
This will make a dialog window appear that asks you, what you'd like to call the request and where you'd like to save it. You can name it anything you'd like but ensure you select your Communication Services collection in the lower half of the dialog:
Sending a request
Now that everything is set up, you should be able to send the request and get an SMS message on your phone. To do this, ensure your created request is selected and then press the "Send" button on the right:
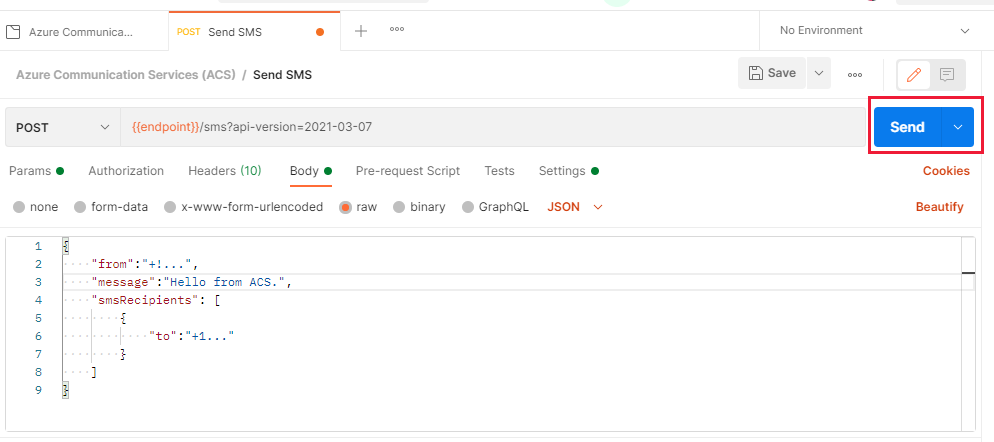
If everything went well, you should now see the response from Communication Services, which should be 202 Status code:
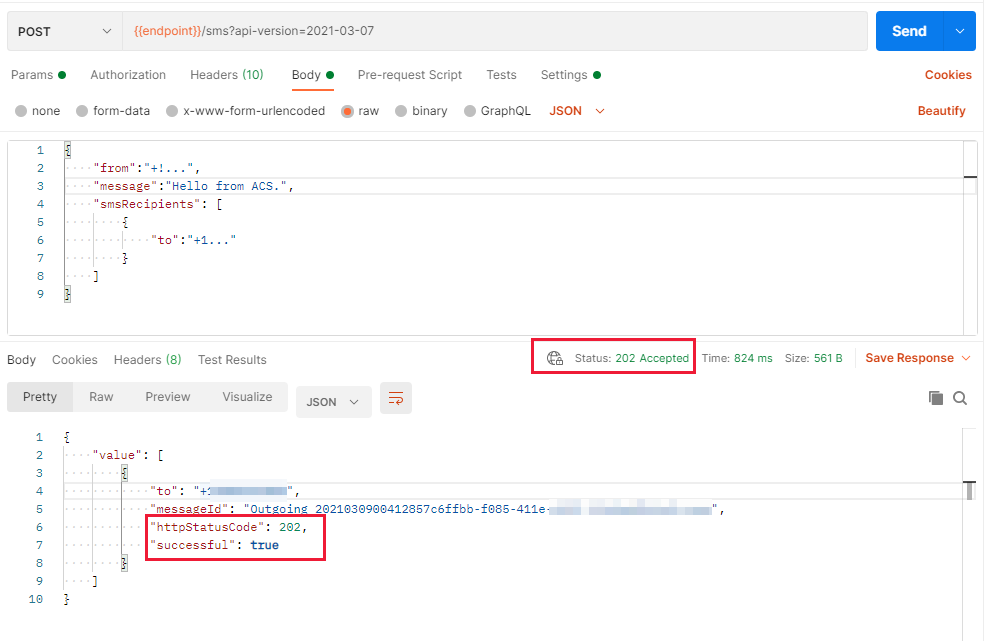
The Mobile phone, which owns the number you provided in the "to" value, should also have received an SMS message. You now have a functional Postman configuration that can talk to Azure Communication Services and send SMS messages.
Next steps
You might also want to: