Restore SAP ASE databases on Azure VMs (preview)
This article describes how to restore SAP ASE databases that are running on Azure virtual machines (VMs). You can use the restored data to create copies for development and test scenarios or to return to a previous state.
Note
The master database can't be restored using original or alternate locations directly because the SAP ASE instance must be started in single-user/single-server mode. Instead, you should use the restore as files method to recover and apply the dump files.
Recover the SAP ASE (Sybase) database (preview)
To recover the SAP ASE (Sybase) database, follow these steps:
Start the database in single-user mode using the following command:
startserver -f RUN_Instance -mRestore the master database dump using the restore as files method.
Apply the restore using the dump file.
Restart the database in multi-user mode with the command:
startserver -f RUN_Instance
Note
If the target database doesn't already exist, ensure the default device is set if you want to create the target database with a different name for the restore. When the default device is set, both the data and log devices will point to the same location. If the default device is not set in the target database location, the database creation will fail.
If you don't want to use the default settings for the target database, the database should be created before the restore. Otherwise, it will be created in the default device path if already set.
Restore to a point in time or to a recovery point
Azure Backup restores SAP ASE user databases that are running on Azure VMs. It can:
Restore them to a specific date or time (to the second) by using log backups. Azure Backup automatically determines the appropriate full backups, differential backups, and chain of log backups that are required to restore based on the selected time.
Use a specific full or differential backup to restore the database to a specific recovery point.
Restore a user database
Ensure that you have the following permissions to restore a database:
Backup Operator: Provides permissions in the vault where you're doing the restore.
Contributor (write): Provides access to the source Virtual Machine (VM) backed-up.
Contributor (write): Provides access to the target VM.
If you're restoring to the same VM, this VM is the source VM.
If you're restoring to an alternate location, this VM is the new target VM.
To restore a user database, follow these steps:
Go to the Recovery Services vault, select Backup items > SAP ASE (Sybase) in Azure VM (preview) under the Backup Management Type.
On the Backup Items blade, select View Details for the database to perform operations such as Backup or Restore.
On the database specific blade, select Restore.
Choose the recovery type: Alternate Location, Original Location, or Restore as File.
Restore the SAP ASE database to an alternate location
To restore the SAP ASE database to an alternate location, follow these steps:
Go to the Recovery Services vault.
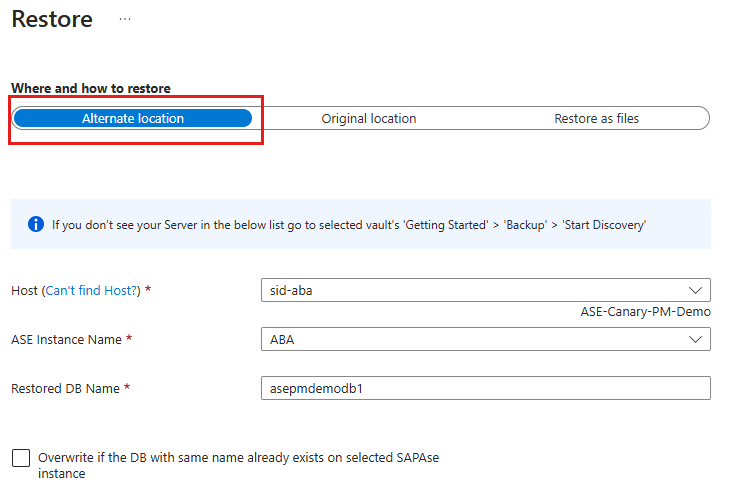
On the Restore blade, under Where and how to restore, select Alternate location.
Select the SAP ASE hostname and instance name to which you want to restore the database.
In the Restored DB Name box, enter the name of the target database.
If applicable, select the Overwrite if the DB with the same name already exists on selected ASE instance checkbox.
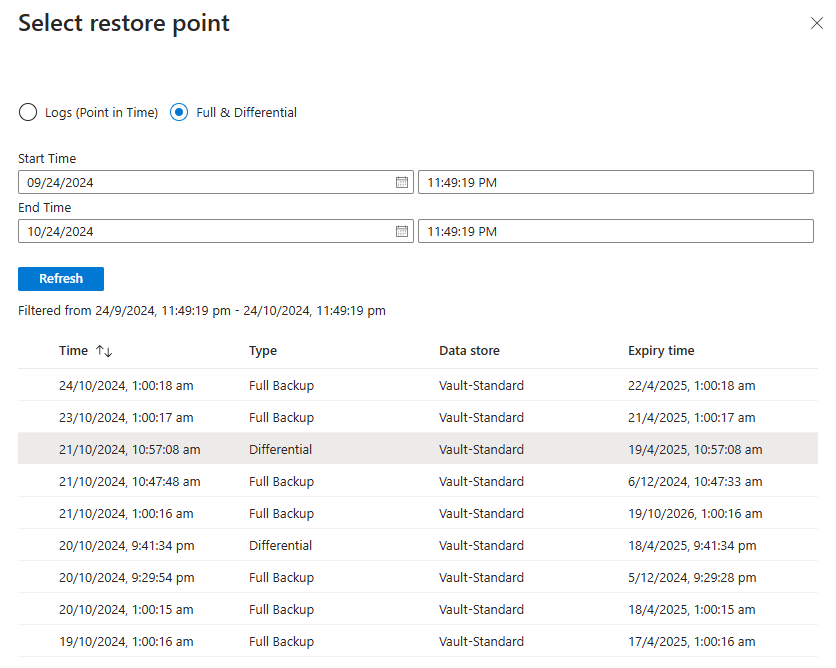
On the Select restore point blade, select Logs (Point in Time) to restore to a specific point in time. Or select Full & Differential to restore to a specific recovery point.
Restore to Original Location
For an in-place restore, if the database is corrupted and you want to restore it to the original location (source), select Original location.
Restore as files
Note
Restore as files doesn't work on Common Internet File System (CIFS) shares, but it does work for Network File System (NFS).
To restore the backup data as files instead of a database, select Restore as Files. After the files are dumped to a specified path, you can take them to any SAP ASE machine where you want to restore them as a database. Because you can move the files to any machine, you can now restore the data across subscriptions and regions.
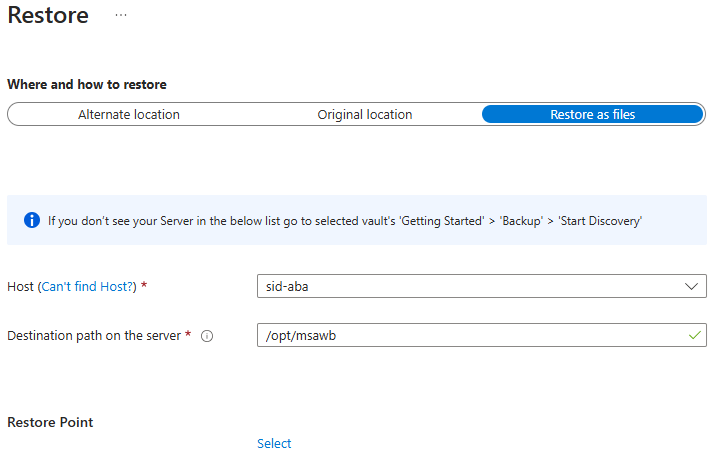
On the Restore blade, under Where and how to restore, select Restore as files.
Select the host or ASE server name to which you want to restore the backup files.
In the Destination path on the server box, enter the folder path on the server that you selected in the preceding step. This VM is the location where the service is dumped all the necessary backup files.
The files that are dumped are:
- Database backup files
- JSON metadata files (for each backup file involved)
Typically, a network share path, or the path of a mounted Azure file share specified as the destination path, enables easier access to these files by other machines in the same network or with the same Azure file share mounted on them.
Note
To restore the database backup files on an Azure file share mounted on the target registered VM, make sure that the root account has read/write permissions on the share.
All the backup files associated with the selected restore point are dumped into the destination path.
Depending on the type of restore point you've chosen (Point in time or Full & Differential), you'll see one or more folders created in the destination path. One of the folders, Data_<date and time of restore> contains the full backups, and the other folder, Log contains the log backups and other backups (such as differential).
Note
If you've selected Restore to a point in time, the log files, which were dumped to the target VM, might sometimes contain logs beyond the point in time that were chosen for restore. Azure Backup does this to ensure that log backups for all ASE services are available for consistent and successful restore to the chosen point in time.
Cross Region Restore
As one of the restore options, Cross Region Restore (CRR) allows you to restore SAP ASE databases that are hosted on Azure VMs in a secondary region, which is an Azure paired region. To begin using the feature, see Set Cross Region Restore.
View backup items in the secondary region
If CRR is enabled, you can view the backup items in the secondary region.
- Go to Recovery Services vault, and then select Backup items.
- Select Secondary Region to view the items in the secondary region.
Restore in the secondary region
The secondary region restore user experience is similar to the primary region restore user experience. When you configure the details on the Restore Configuration blade, you're prompted to provide only secondary region parameters. A vault should exist in the secondary region, and the SAP ASE server should be registered to the vault in the secondary region.
Note
After the restore is triggered and in the data transfer phase, the restore job can't be cancelled.
The role and access level that are required to perform a restore operation in cross-regions are the Backup Operator role in the subscription and Contributor (write) access on the source and target virtual machines. To view backup jobs, Backup reader is the minimum permission that's required in the subscription.
The recovery point objective (RPO) for the backup data to be available in secondary region is 12 hours. Therefore, when you turn on CRR, the RPO for the secondary region is 12 hours + log frequency duration (which can be set to a minimum of 15 minutes).
Learn about the minimum role requirements for cross-region restore.