Deploy disaster recovery with VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM)
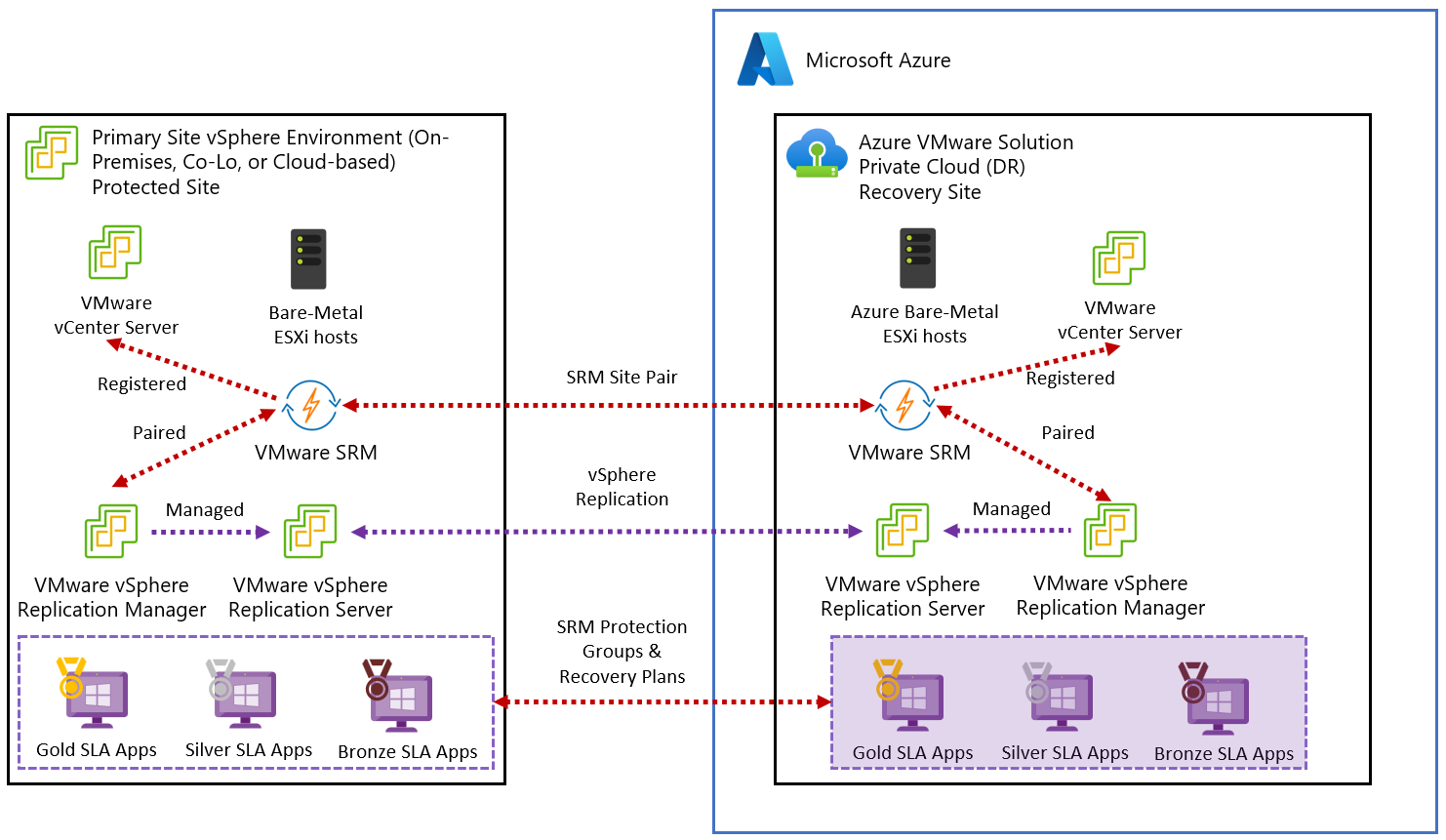
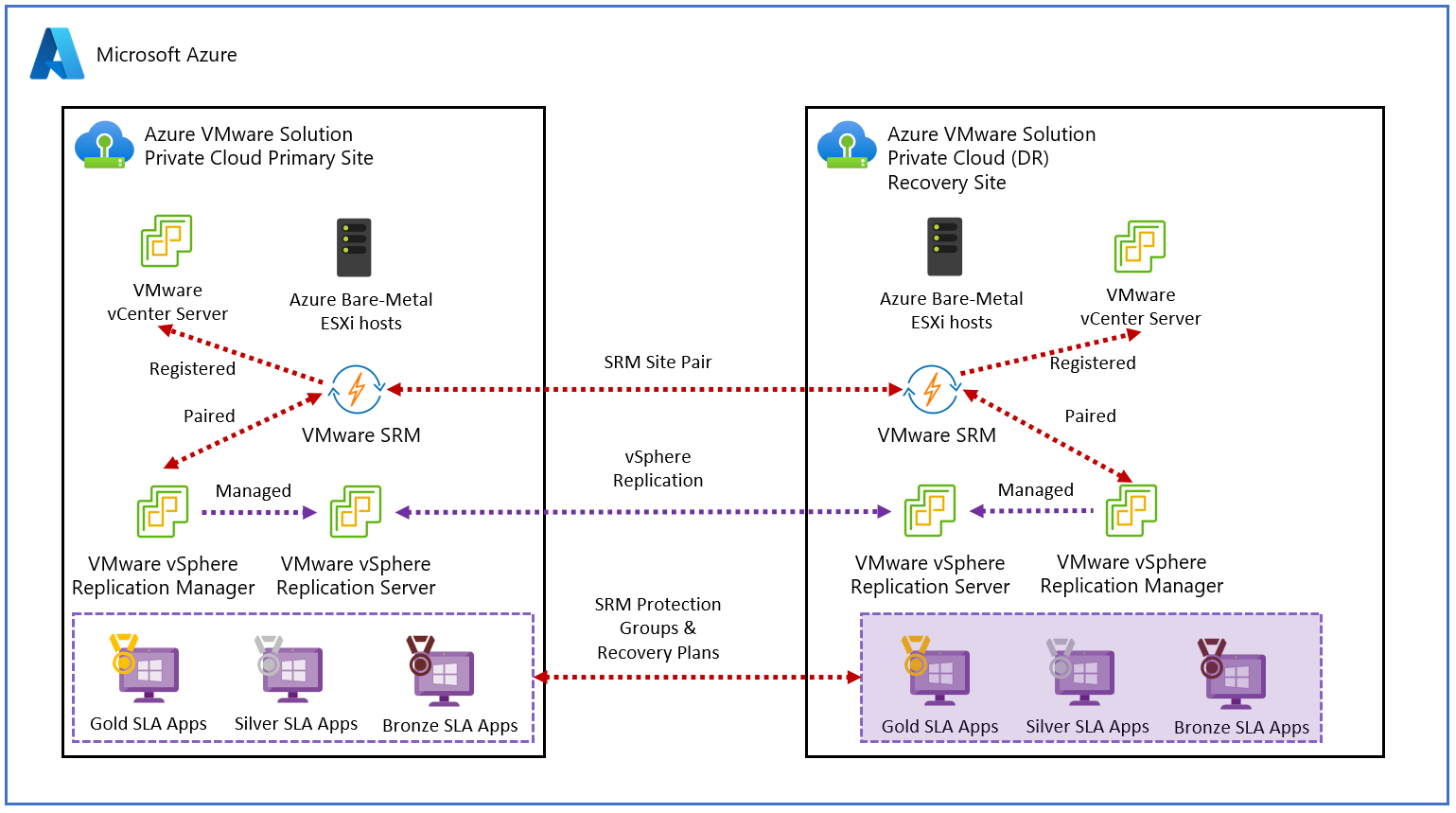
This article explains how to implement disaster recovery for on-premises VMware vSphere virtual machines (VMs) or Azure VMware Solution-based VMs. The solution in this article uses VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) and vSphere Replication with Azure VMware Solution. Instances of VMware SRM and replication servers are deployed at both the protected and the recovery sites.
VMware SRM is a disaster recovery solution designed to minimize downtime of the virtual machines in an Azure VMware Solution environment if there was a disaster. VMware SRM automates and orchestrates failover and failback, ensuring minimal downtime in a disaster. Also, built-in nondisruptive testing ensures your recovery time objectives are met. Overall, VMware SRM simplifies management through automation and ensures fast and highly predictable recovery times.
VMware vSphere Replication is VMware's hypervisor-based replication technology for VMware vSphere VMs. It protects VMs from partial or complete site failures. In addition, it simplifies DR protection through storage-independent, VM-centric replication. VMware vSphere Replication is configured on a per-VM basis, allowing more control over which VMs are replicated.
Note
The current version of VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) in Azure VMware Solution is 8.7.0.3.
Supported scenarios
VMware SRM helps you plan, test, and run the recovery of VMs between a protected VMware vCenter Server site and a recovery VMware vCenter Server site. You can use VMware SRM with Azure VMware Solution with the following two DR scenarios:
- On-premises VMware vSphere to Azure VMware Solution private cloud disaster recovery
- Primary Azure VMware Solution to Secondary Azure VMware Solution private cloud disaster recovery
The diagram shows the deployment of the on-premises VMware vSphere to Azure VMware Solution private cloud disaster recovery scenario.
The diagram shows the deployment of the primary Azure VMware Solution to secondary Azure VMware Solution scenario.
You can use VMware SRM to implement different types of recovery, such as:
Planned migration commences when both primary and secondary Azure VMware Solution sites are running and fully functional. It's an orderly migration of virtual machines from the protected site to the recovery site where no data loss is expected when migrating workloads in an orderly fashion.
Disaster recovery using SRM can be invoked when the protected Azure VMware Solution site goes offline unexpectedly. VMware Site Recovery Manager orchestrates the recovery process with the replication mechanisms to minimize data loss and system downtime.
In Azure VMware Solution, only individual VMs can be protected on a host by using VMware SRM in combination with VMware vSphere Replication.
Bidirectional Protection uses a single set of paired VMware SRM sites to protect VMs in both directions. Each site can simultaneously be a protected site and a recovery site, but for a different set of VMs.
Important
Azure VMware Solution doesn't support:
- Array-based replication and storage policy protection groups
- VMware vVOLs Protection Groups
- VMware SRM IP customization using SRM command-line tools
- One-to-Many and Many-to-One topologies
- Custom VMware SRM plug-in identifier or extension ID
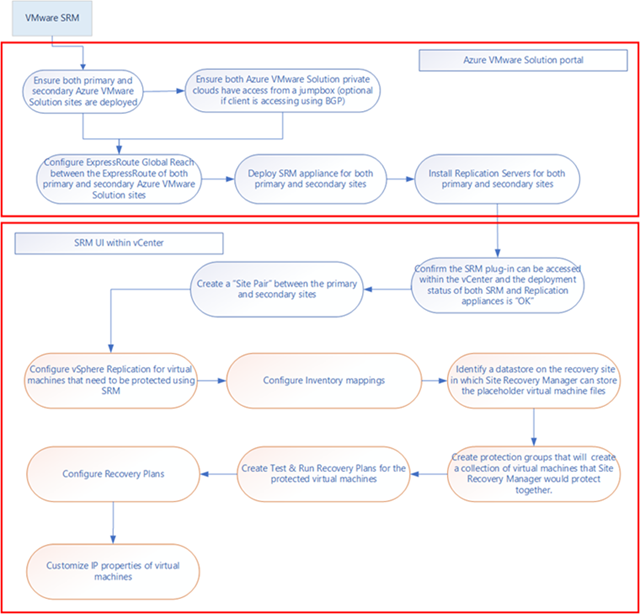
Deployment workflow
The workflow diagram shows the Primary Azure VMware Solution to secondary workflow. In addition, it shows steps to take within the Azure portal and the VMware vSphere environments of Azure VMware Solution to achieve the end-to-end protection of VMs.
Prerequisites
Ensure you provide the remote user the VMware VRM administrator and VMware SRM administrator roles in the remote vCenter Server.
Scenario: On-premises to Azure VMware Solution
Azure VMware Solution private cloud deployed as a secondary region.
DNS resolution to on-premises VMware SRM and virtual cloud appliances.
Note
For private clouds created on or after July 1, 2021, you can configure private DNS resolution. For private clouds created before July 1, 2021, that need a private DNS resolution, open a support request to request Private DNS configuration.
ExpressRoute connectivity between on-premises VMware vSphere and Azure VMware Solution - 2 Gbps.
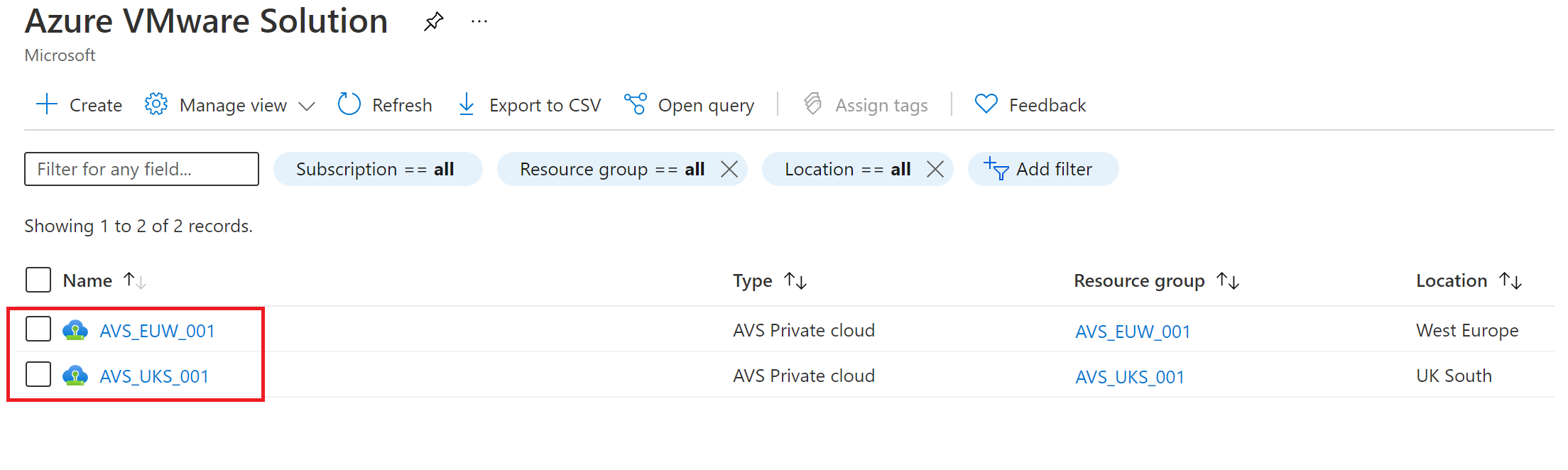
Scenario: Primary Azure VMware Solution to secondary
Azure VMware Solution private cloud must be deployed in the primary and secondary region.
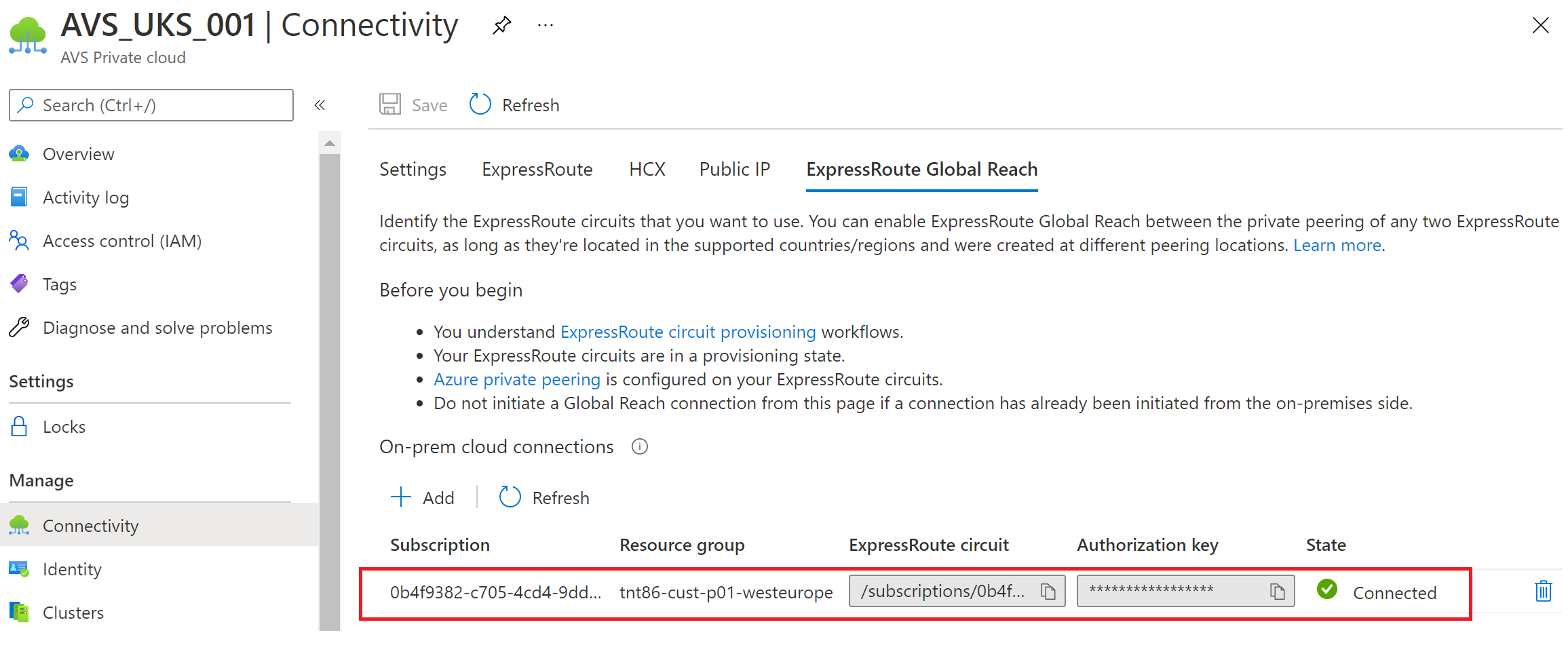
Connectivity, like ExpressRoute Global Reach, between the source and target Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
Install SRM in Azure VMware Solution
In your on-premises data center, install VMware SRM and vSphere Replication.
Note
Use the Two-site Topology with one vCenter Server instance per PSC deployment model. Also, make sure that the required vSphere Replication Network ports are opened.
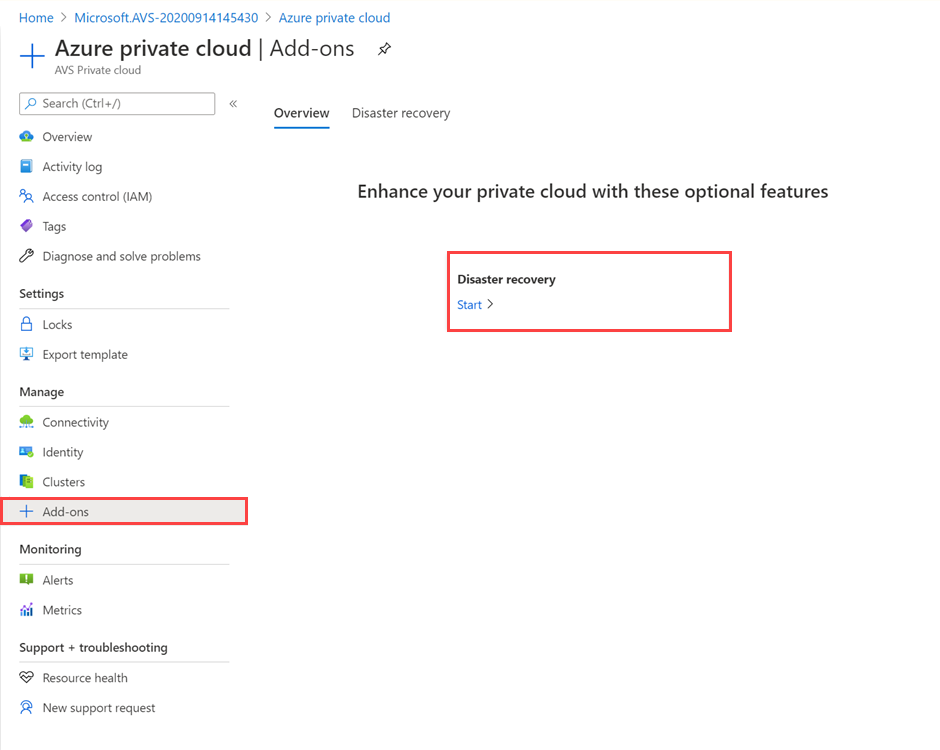
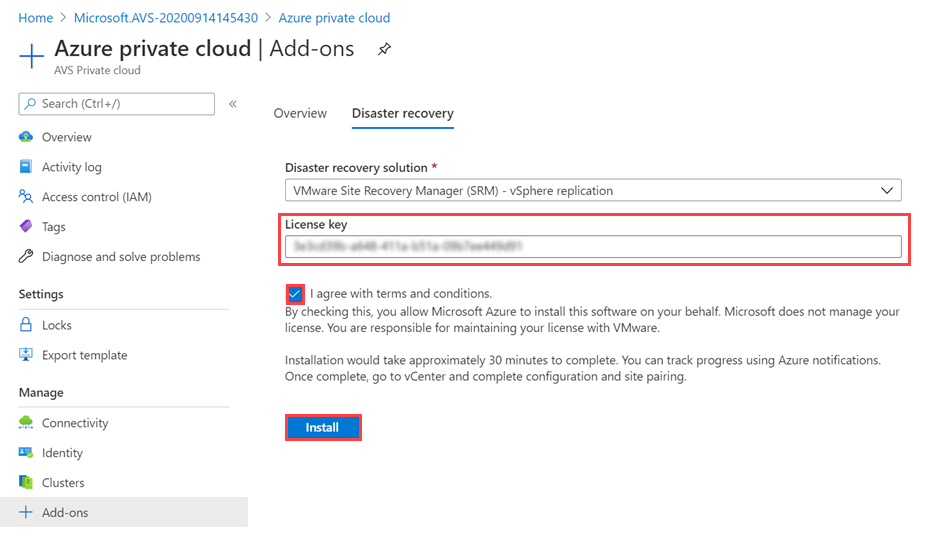
In your Azure VMware Solution private cloud, under Manage, select Add-ons > Disaster recovery.
The default CloudAdmin user in the Azure VMware Solution private cloud doesn't have sufficient privileges to install VMware SRM or vSphere Replication. The installation process involves multiple steps outlined in the Prerequisites section. Instead, you can install VMware SRM with vSphere Replication as an add-on service from your Azure VMware Solution private cloud.
Note
The current version of VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) in Azure VMware Solution is 8.7.0.3.
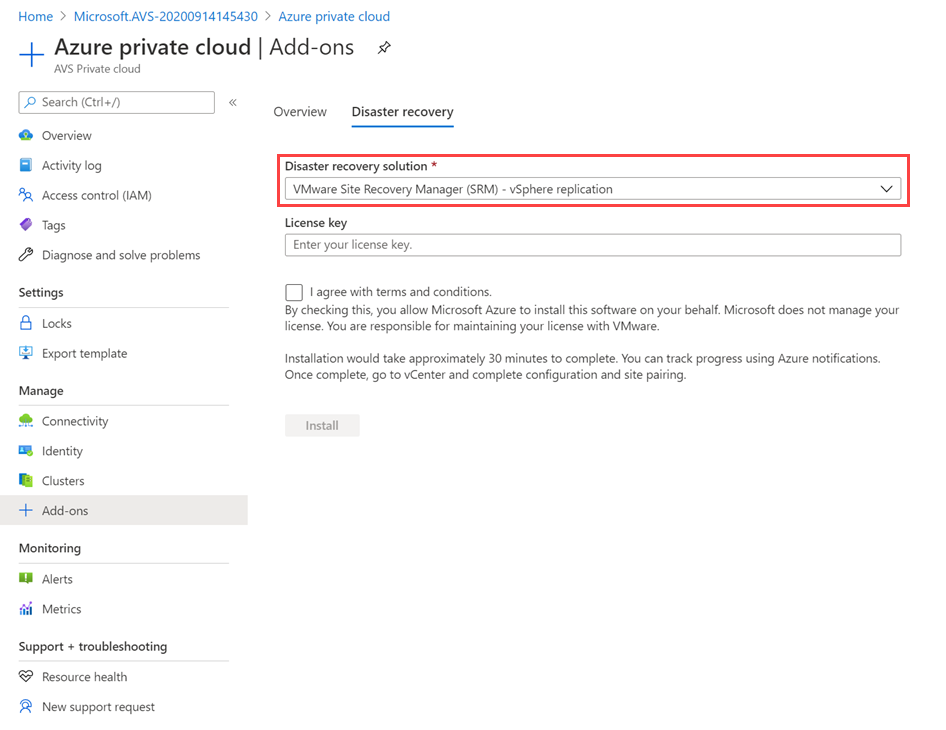
From the Disaster Recovery Solution drop-down, select VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) – vSphere Replication.
Provide the License key, select agree with terms and conditions, and then select Install.
Note
If you don't provide the license key, SRM is installed in an Evaluation mode. The license is used only to enable VMware SRM.
Install the vSphere Replication appliance
After the VMware SRM appliance installs successfully, you'll need to install the vSphere Replication appliances. Each replication server accommodates up to 200 protected VMs. Scale in or scale out as per your needs.
From the Replication using drop-down, on the Disaster recovery tab, select vSphere Replication.
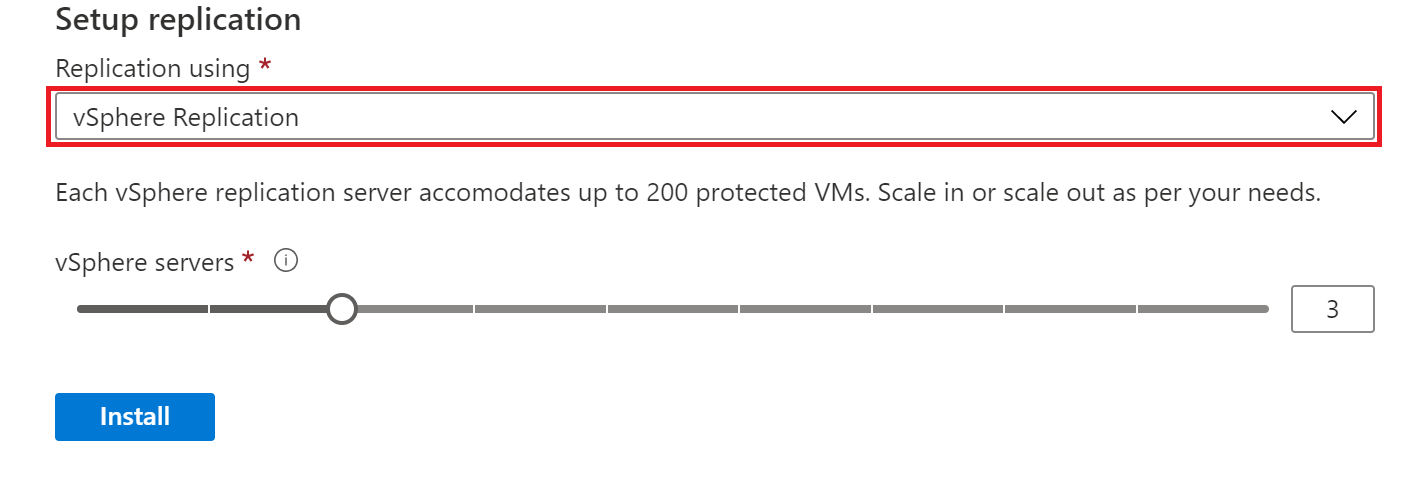
Move the vSphere server slider to indicate the number of replication servers you want based on the number of VMs to be protected. Then select Install.

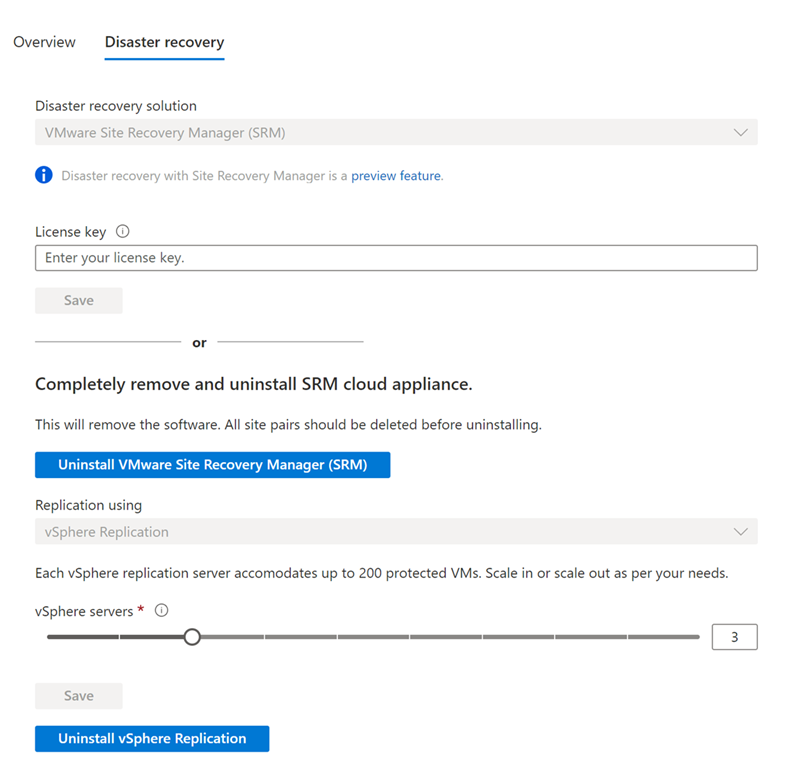
Once installed, verify that both VMware SRM and the vSphere Replication appliances are installed.
Tip
The Uninstall button indicates that both VMware SRM and the vSphere Replication appliances are currently installed.
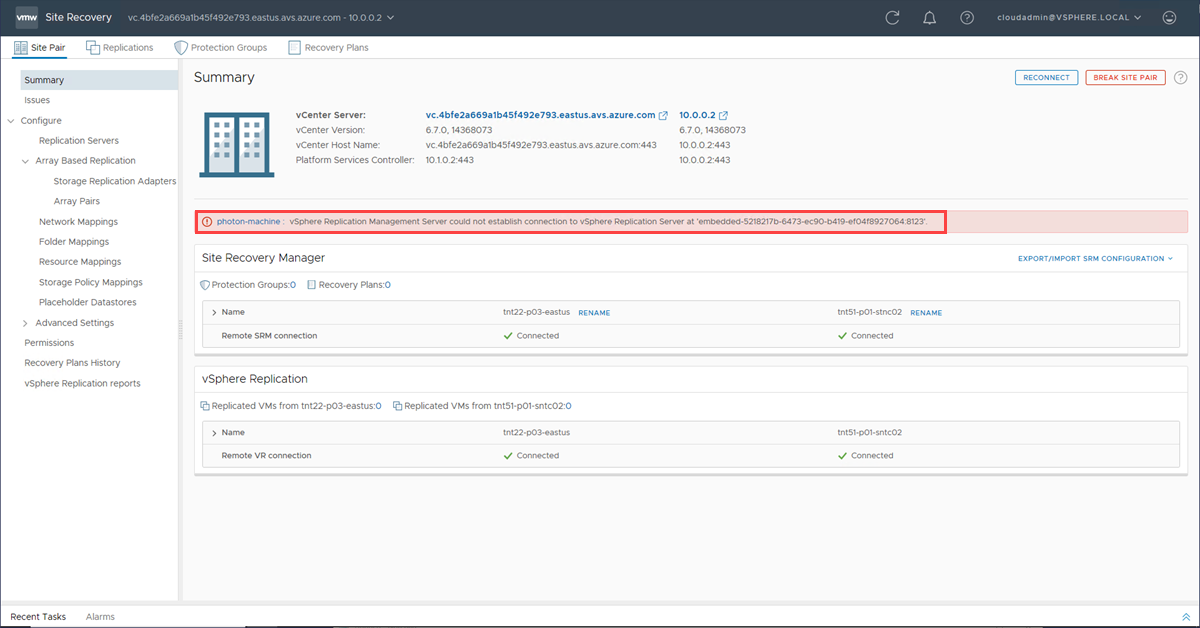
Configure site pairing in vCenter Server
After installing VMware SRM and vSphere Replication, you need to complete the configuration and site pairing in vCenter Server.
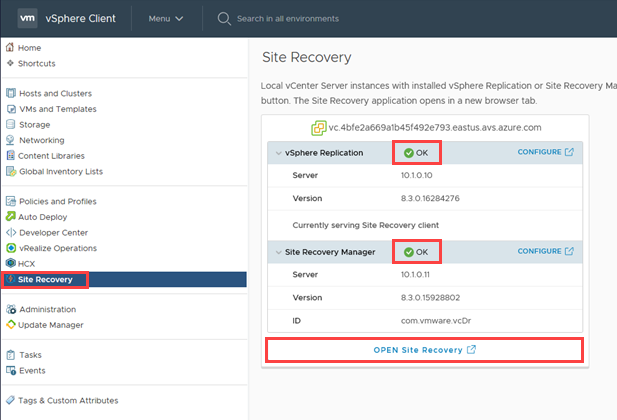
Sign in to the vSphere Client as cloudadmin@vsphere.local.
Navigate to Site Recovery, check the status of both vSphere Replication and VMware SRM, and then select OPEN Site Recovery to launch the client.
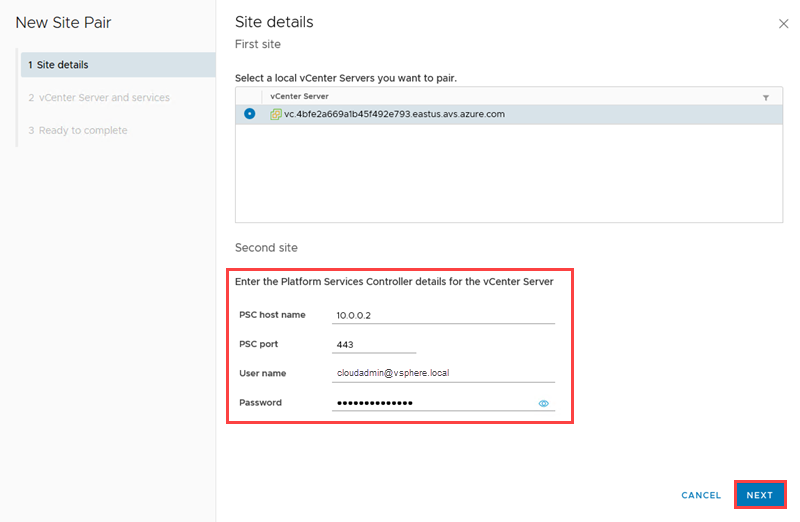
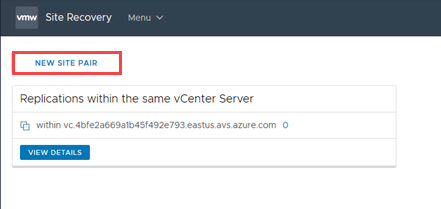
Select NEW SITE PAIR in the Site Recovery (SR) client in the new tab that opens.
Enter the remote site details, and then select NEXT.
Note
An Azure VMware Solution private cloud operates with an embedded Platform Services Controller (PSC), so only one local vCenter Server can be selected. If the remote vCenter Server is using an embedded Platform Service Controller (PSC), use the vCenter Server's FQDN (or its IP address) and port to specify the PSC.
The remote user must have sufficient permissions to perform the pairings. An easy way to ensure this is to give that user the VRM administrator and SRM administrator roles in the remote vCenter Server. For a remote Azure VMware Solution private cloud, cloudadmin is configured with those roles.
Select CONNECT to accept the certificate for the remote vCenter Server.
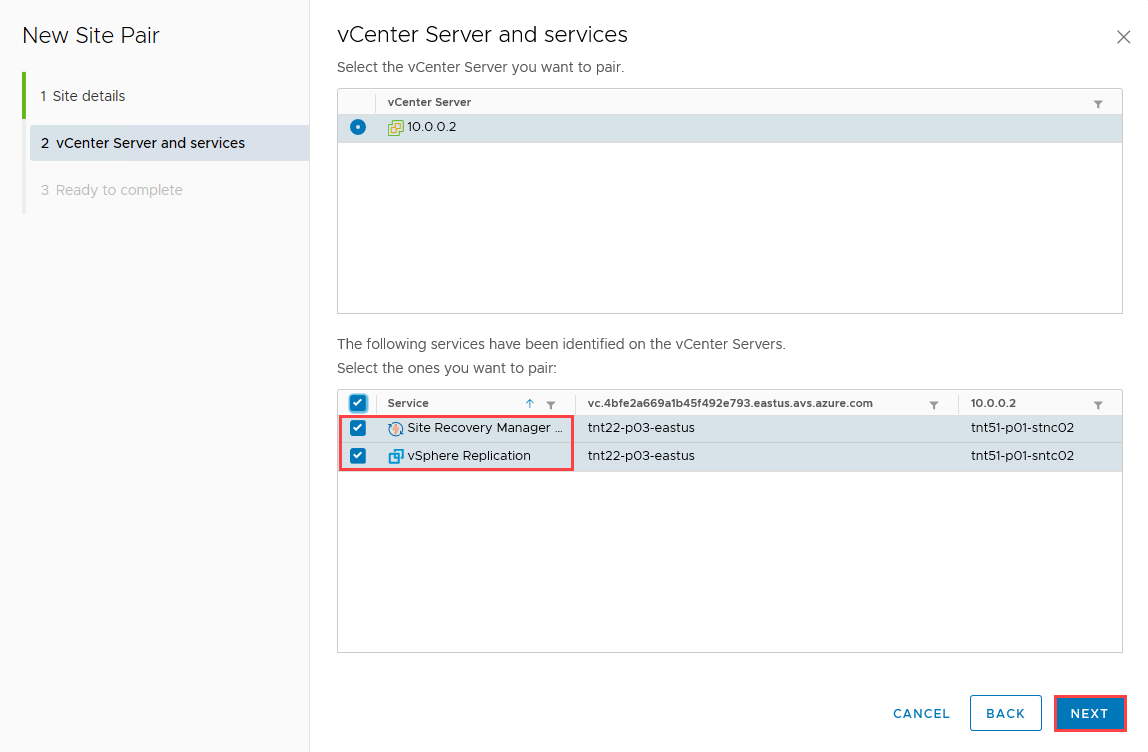
At this point, the client should discover the VMware VRM and VMware SRM appliances on both sides as services to pair.
Select the appliances to pair and then select NEXT.
Select CONNECT to accept the certificates for the remote VMware SRM and the remote vCenter Server (again).
Select CONNECT to accept the certificates for the local VMware SRM and the local vCenter Server.
Review the settings and then select FINISH.
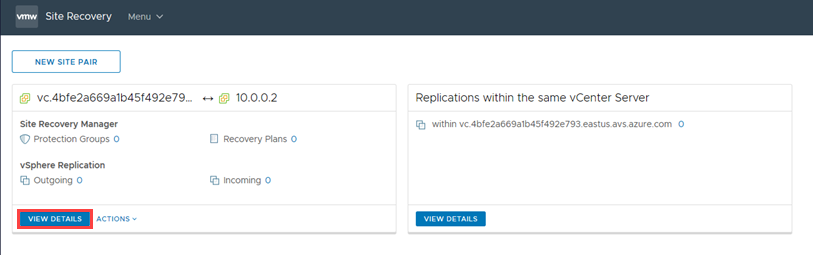
If successful, the client displays another panel for the pairing. However, if unsuccessful, an alarm is reported.
At the bottom, in the right corner, select the double-up arrow to expand the panel to show Recent Tasks and Alarms.
Note
The SR client sometimes takes a long time to refresh. If an operation seems to take too long or appears "stuck", select the refresh icon on the menu bar.
Select VIEW DETAILS to open the panel for remote site pairing, which opens a dialog to sign in to the remote vCenter Server.
Enter the username with sufficient permissions to do replication and site recovery and then select LOG IN.
For pairing, the sign in, which is often a different user, is a one-time action to establish pairing. The SR client requires this sign in every time the client is launched to work with the pairing.
Note
The user with sufficient permissions should have VRM administrator and SRM administrator roles given to them in the remote vCenter Server. The user should also have access to the remote vCenter Server inventory, like folders and datastores. For a remote Azure VMware Solution private cloud, the cloudadmin user has the appropriate permissions and access.
You see a warning message indicating that the embedded VRS in the local VRM isn't running. The warning is because Azure VMware Solution doesn't use the embedded VRS in an Azure VMware Solution private cloud, it uses VRS appliances instead.
VMware SRM protection, reprotection, and failback
After you created the site pairing, use the following VMware documentation for end-to-end protection of VMs from the Azure portal.
Ongoing management of your VMware SRM solution
Microsoft aims to simplify VMware SRM and vSphere Replication installation on an Azure VMware Solution private cloud. You're responsible for managing your license and the day-to-day operation of the disaster recovery solution.
Scale limitations
To learn about the limits for the VMware Site Recovery Manager Add-On with the Azure VMware Solution, check the Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
VMware SRM licenses
You can install VMware SRM using an evaluation license or a production license. The evaluation license is valid for 60 days. After the evaluation period, you'll be required to obtain a production license of VMware SRM.
You can't use pre-existing on-premises VMware SRM licenses for your Azure VMware Solution private cloud. Work with your sales teams and VMware to acquire a new term-based production license of VMware SRM.
Once a production license of VMware SRM is acquired, you can start using the Azure VMware Solution portal to update VMware SRM with the new production license.
Uninstall VMware SRM
If you no longer require VMware SRM, you must uninstall it in a clean manner. Before you uninstall VMware SRM, you must remove all VMware SRM configurations from both sites in the correct order. If you don't remove all configurations before uninstalling VMware SRM, some VMware SRM components, such as placeholder VMs, might remain in the Azure VMware Solution infrastructure.
In the vSphere Client, select Site Recovery > Open Site Recovery.
On the Site Recovery home tab, select a site pair and select View Details.
Select the Recovery Plans tab, right-click on a recovery plan and select Delete.
Note
You cannot delete recovery plans that are running.
Select the Protection Groups tab, select a protection group, and select the Virtual Machines tab.
Highlight all virtual machines, right-click, and select Remove Protection.
Removing protection from a VM deletes the placeholder VM from the recovery site. Repeat this operation for all protection groups.
In the Protection Groups tab, right-click a protection group and select Delete.
Note
You cannot delete a protection group that is included in a recovery plan. You cannot delete vSphere Replication protection groups that contain virtual machines on which protection is still configured.
Select Site Pair > Configure and remove all inventory mappings.
a. Select each of the Network Mappings, Folder Mappings, and Resource Mappings tabs.
b. In each tab, select a site, right-click a mapping, and select Delete.
For both sites, select Placeholder Datastores, right-click the placeholder datastore, and select Remove.
Select Site Pair > Summary, and select Break Site Pair.
Note
Breaking the site pairing removes all information related to registering Site Recovery Manager with Site Recovery Manager, vCenter Server, and the Platform Services Controller on the remote site.
In your private cloud, under Manage, select Add-ons > Disaster recovery, and then select Uninstall the replication appliances.
Once replication appliances are uninstalled, from the Disaster recovery tab, select Uninstall for the Site Recovery Manager.
Repeat these steps on the secondary Azure VMware Solution site.
Support
VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) is a Disaster Recovery solution from VMware.
Microsoft only supports install/uninstall of VMware SRM and vSphere Replication Manager and scale up/down of vSphere Replication appliances within Azure VMware Solution.
For all other issues, such as configuration and replication, contact VMware for support.
VMware and Microsoft support teams engage each other as needed to troubleshoot VMware SRM issues on Azure VMware Solution.
References
- VMware Site Recovery Manager Documentation
- Compatibility Matrices for VMware Site Recovery Manager 8.8
- VMware SRM 8.8 release notes
- VMware vSphere Replication Documentation
- Compatibility Matrices for vSphere Replication 8.8
- Operational Limits of Site Recovery Manager 8.8
- Operational Limits of vSphere Replication 8.8
- Calculate bandwidth for vSphere Replication
- SRM installation and configuration
- vSphere Replication administration
- Prerequisites and Best Practices for SRM installation
- Network ports for SRM
- Network ports for vSphere Replication