Report across scaled-out cloud databases (preview)
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
You can create reports from multiple databases from a single connection point using an elastic query. The databases must be horizontally partitioned (also known as "sharded").
If you have an existing database, see Migrating existing databases to scaled-out databases.
To understand the SQL objects needed to query, see Query across horizontally partitioned databases.
Prerequisites
Download and run the Getting started with Elastic Database tools sample.
Create a shard map manager using the sample app
Here you will create a shard map manager along with several shards, followed by insertion of data into the shards. If you happen to already have shards setup with sharded data in them, you can skip the following steps and move to the next section.
Build and run the Getting started with Elastic Database tools sample application by following the steps in the article section Download and run the sample app. Once you finish all the steps, you will see the following command prompt:
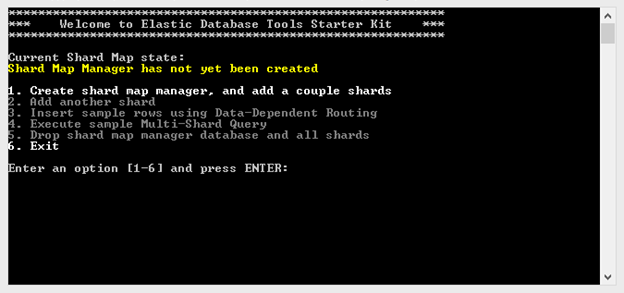
In the command window, type "1" and press Enter. This creates the shard map manager, and adds two shards to the server. Then type "3" and press Enter; repeat the action four times. This inserts sample data rows in your shards.
The Azure portal should show three new databases in your server:
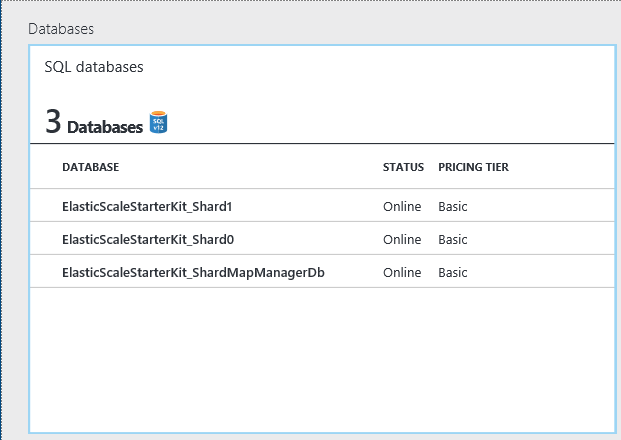
At this point, cross-database queries are supported through the Elastic Database client libraries. For example, use option 4 in the command window. The results from a multi-shard query are always a UNION ALL of the results from all shards.
In the next section, we create a sample database endpoint that supports richer querying of the data across shards.
Create an elastic query database
Open the Azure portal and log in.
Create a new database in Azure SQL Database in the same server as your shard setup. Name the database "ElasticDBQuery."
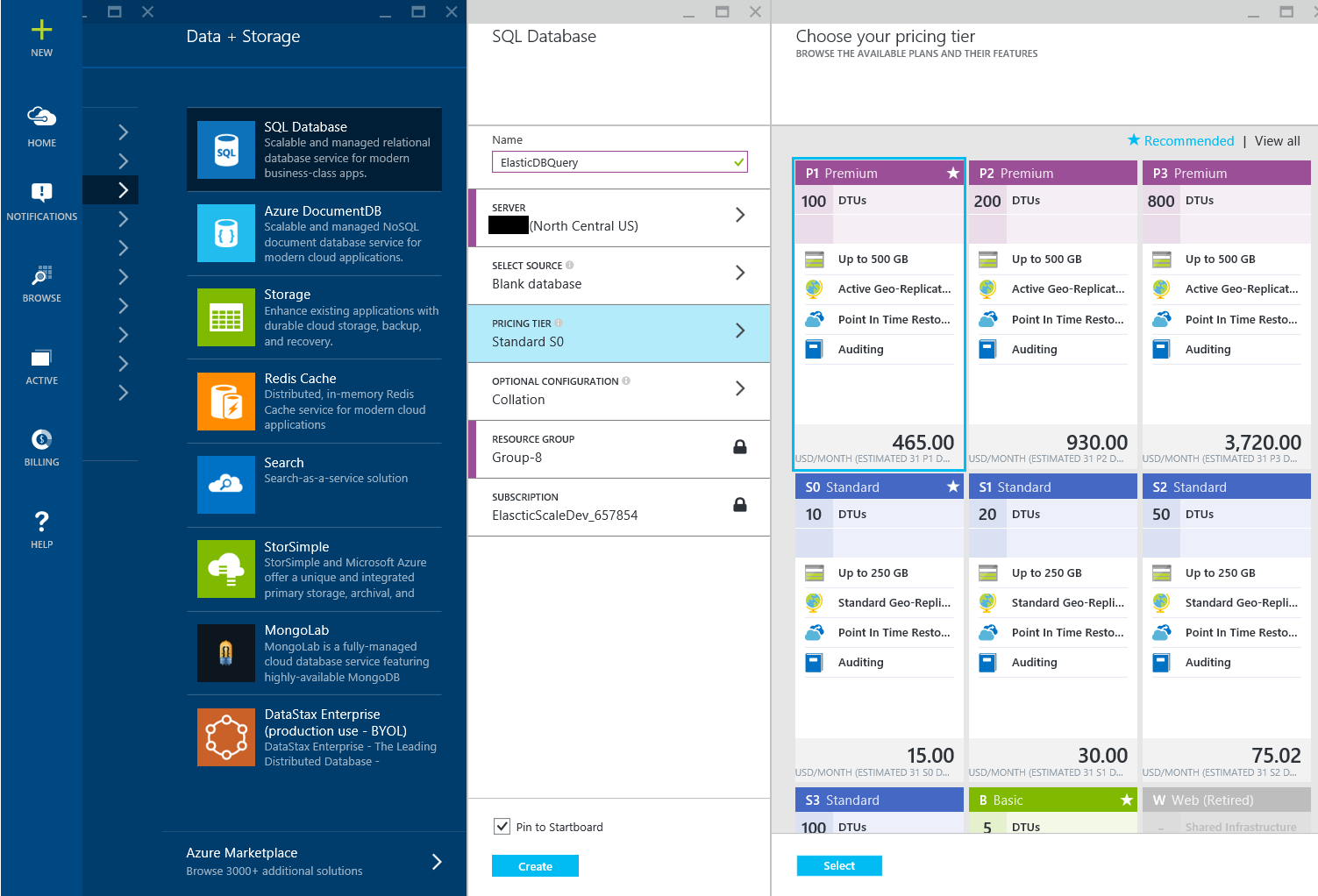
Note
you can use an existing database. If you can do so, it must not be one of the shards that you would like to execute your queries on. This database will be used for creating the metadata objects for an elastic database query.
Create database objects
Database-scoped master key and credentials
These are used to connect to the shard map manager and the shards:
Open SQL Server Management Studio or SQL Server Data Tools in Visual Studio.
Connect to ElasticDBQuery database and execute the following T-SQL commands:
CREATE MASTER KEY ENCRYPTION BY PASSWORD = '<master_key_password>'; CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL ElasticDBQueryCred WITH IDENTITY = '<username>', SECRET = '<password>';"username" and "password" should be the same as login information used in step 3 of section Download and run the sample app in the Getting started with Elastic Database tools article.
External data sources
To create an external data source, execute the following command on the ElasticDBQuery database:
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE MyElasticDBQueryDataSrc WITH
(TYPE = SHARD_MAP_MANAGER,
LOCATION = '<server_name>.database.windows.net',
DATABASE_NAME = 'ElasticScaleStarterKit_ShardMapManagerDb',
CREDENTIAL = ElasticDBQueryCred,
SHARD_MAP_NAME = 'CustomerIDShardMap'
) ;
"CustomerIDShardMap" is the name of the shard map, if you created the shard map and shard map manager using the elastic database tools sample. However, if you used your custom setup for this sample, then it should be the shard map name you chose in your application.
External tables
Create an external table that matches the Customers table on the shards by executing the following command on ElasticDBQuery database:
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE [dbo].[Customers]
( [CustomerId] [int] NOT NULL,
[Name] [nvarchar](256) NOT NULL,
[RegionId] [int] NOT NULL)
WITH
( DATA_SOURCE = MyElasticDBQueryDataSrc,
DISTRIBUTION = SHARDED([CustomerId])
) ;
Execute a sample elastic database T-SQL query
Once you have defined your external data source and your external tables you can now use full T-SQL over your external tables.
Execute this query on the ElasticDBQuery database:
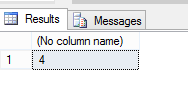
select count(CustomerId) from [dbo].[Customers]
You will notice that the query aggregates results from all the shards and gives the following output:
Import elastic database query results to Excel
You can import the results from of a query to an Excel file.
Launch Excel 2013.
Navigate to the Data ribbon.
Click From Other Sources and click From SQL Server.
In the Data Connection Wizard type the server name and login credentials. Then click Next.
In the dialog box Select the database that contains the data you want, select the ElasticDBQuery database.
Select the Customers table in the list view and click Next. Then click Finish.
In the Import Data form, under Select how you want to view this data in your workbook, select Table and click OK.
All the rows from Customers table, stored in different shards populate the Excel sheet.
You can now use Excel's powerful data visualization functions. You can use the connection string with your server name, database name and credentials to connect your BI and data integration tools to the elastic query database. Make sure that SQL Server is supported as a data source for your tool. You can refer to the elastic query database and external tables just like any other SQL Server database and SQL Server tables that you would connect to with your tool.
Cost
There is no additional charge for using the Elastic Database Query feature.
For pricing information see SQL Database Pricing Details.
Next steps
- For an overview of elastic query, see Elastic query overview.
- For a vertical partitioning tutorial, see Getting started with cross-database query (vertical partitioning).
- For syntax and sample queries for vertically partitioned data, see Querying vertically partitioned data)
- For syntax and sample queries for horizontally partitioned data, see Querying horizontally partitioned data)
- See sp_execute _remote for a stored procedure that executes a Transact-SQL statement on a single remote Azure SQL Database or set of databases serving as shards in a horizontal partitioning scheme.