Collect Syslog events from virtual machine client with Azure Monitor
Syslog is an event logging protocol that's common to Linux. You can use the Syslog daemon that's built into Linux devices and appliances to collect local events of the types you specify. Applications send messages that are either stored on the local machine or delivered to a Syslog collector. Collect Syslog events from virtual machines using a data collection rule (DCR) with a Linux Syslog data source.
Tip
To collect data from devices that don't allow local installation of Azure Monitor agent, configure a dedicated Linux-based log forwarder as described in Forward Syslog data to a Log Analytics workspace with Microsoft Sentinel by using Azure Monitor Agent.
Details for the creation of the DCR are provided in Collect data from VM client with Azure Monitor. This article provides additional details for the Linux Syslog data source type.
Note
To work with the DCR definition directly or to deploy with other methods such as ARM templates, see Data collection rule (DCR) samples in Azure Monitor.
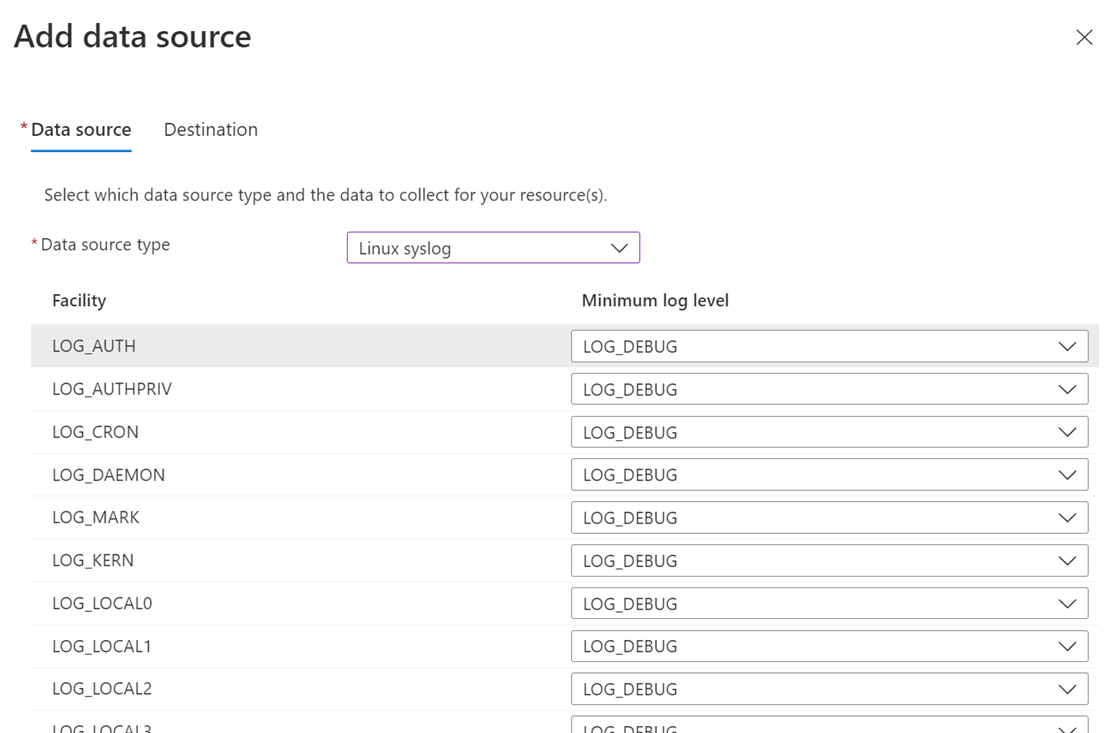
Configure Syslog data source
Create the DCR using the process in Collect data from virtual machine client with Azure Monitor. On the Collect and deliver tab of the DCR, select Linux Syslog from the Data source type dropdown.
Select a Minimum log level for each facility or NONE to collect no events for that facility. You can configure multiple facilities at once by selecting their checkbox and then selecting a log level in Set minimum log level for selected facilities.
All logs with the selected severity level and higher are collected for the facility. The supported severity levels and their relative severity are as follows:
- Debug
- Info
- Notice
- Warning
- Error
- Critical
- Alert
- Emergency
Add destinations
Syslog data can only be sent to a Log Analytics workspace where it's stored in the Syslog table. Add a destination of type Azure Monitor Logs and select a Log Analytics workspace.
Verify data collection
To verify that data is being collected, check for records in the Syslog table. From the virtual machine or from the Log Analytics workspace in the Azure portal, select Logs and then click the Tables button. Under the Virtual machines category, click Run next to Syslog.
Configure Syslog on the Linux agent
When Azure Monitor Agent is installed on a Linux machine, it installs a default Syslog configuration file that defines the facility and severity of the messages that are collected if Syslog is enabled in a DCR. The configuration file is different depending on the Syslog daemon that the client has installed.
Note
Azure Monitor Linux Agent versions 1.15.2 and higher support syslog RFC formats including Cisco Meraki, Cisco ASA, Cisco FTD, Sophos XG, Juniper Networks, Corelight Zeek, CipherTrust, NXLog, McAfee, and Common Event Format (CEF).
Rsyslog
On many Linux distributions, the rsyslogd daemon is responsible for consuming, storing, and routing log messages sent by using the Linux Syslog API. Azure Monitor Agent uses the TCP forward output module (omfwd) in rsyslog to forward log messages.
The Azure Monitor Agent installation includes default config files located in /etc/opt/microsoft/azuremonitoragent/syslog/rsyslogconf/. When Syslog is added to a DCR, this configuration is installed under the etc/rsyslog.d system directory and rsyslog is automatically restarted for the changes to take effect.
Note
On rsyslog-based systems, Azure Monitor Linux Agent adds forwarding rules to the default ruleset defined in the rsyslog configuration. If multiple rulesets are used, inputs bound to non-default ruleset(s) are not forwarded to Azure Monitor Agent. For more information about multiple rulesets in rsyslog, see the official documentation.
Following is the default configuration which collects Syslog messages sent from the local agent for all facilities with all log levels.
$ cat /etc/rsyslog.d/10-azuremonitoragent-omfwd.conf
# Azure Monitor Agent configuration: forward logs to azuremonitoragent
template(name="AMA_RSYSLOG_TraditionalForwardFormat" type="string" string="<%PRI%>%TIMESTAMP% %HOSTNAME% %syslogtag%%msg:::sp-if-no-1st-sp%%msg%")
# queue.workerThreads sets the maximum worker threads, it will scale back to 0 if there is no activity
# Forwarding all events through TCP port
*.* action(type="omfwd"
template="AMA_RSYSLOG_TraditionalForwardFormat"
queue.type="LinkedList"
queue.filename="omfwd-azuremonitoragent"
queue.maxFileSize="32m"
queue.maxDiskSpace="1g"
action.resumeRetryCount="-1"
action.resumeInterval="5"
action.reportSuspension="on"
action.reportSuspensionContinuation="on"
queue.size="25000"
queue.workerThreads="100"
queue.dequeueBatchSize="2048"
queue.saveonshutdown="on"
target="127.0.0.1" Port="28330" Protocol="tcp")
The following configuration is used when you use SELinux and decide to use Unix sockets.
$ cat /etc/rsyslog.d/10-azuremonitoragent.conf
# Azure Monitor Agent configuration: forward logs to azuremonitoragent
$OMUxSockSocket /run/azuremonitoragent/default_syslog.socket
template(name="AMA_RSYSLOG_TraditionalForwardFormat" type="string" string="<%PRI%>%TIMESTAMP% %HOSTNAME% %syslogtag%%msg:::sp-if-no-1st-sp%%msg%")
$OMUxSockDefaultTemplate AMA_RSYSLOG_TraditionalForwardFormat
# Forwarding all events through Unix Domain Socket
*.* :omuxsock:
$ cat /etc/rsyslog.d/05-azuremonitoragent-loadomuxsock.conf
# Azure Monitor Agent configuration: load rsyslog forwarding module.
$ModLoad omuxsock
On some legacy systems, you may see rsyslog log formatting issues when a traditional forwarding format is used to send Syslog events to Azure Monitor Agent. For these systems, Azure Monitor Agent automatically places a legacy forwarder template instead:
template(name="AMA_RSYSLOG_TraditionalForwardFormat" type="string" string="%TIMESTAMP% %HOSTNAME% %syslogtag%%msg:::sp-if-no-1st-sp%%msg%\n")
Syslog-ng
The Azure Monitor Agent installation includes default config files located in /etc/opt/microsoft/azuremonitoragent/syslog/syslog-ngconf/azuremonitoragent-tcp.conf. When Syslog is added to a DCR, this configuration is installed under the /etc/syslog-ng/conf.d/azuremonitoragent-tcp.conf system directory and syslog-ng is automatically restarted for the changes to take effect.
The default contents are shown in the following example. This example collects Syslog messages sent from the local agent for all facilities and all severities.
$ cat /etc/syslog-ng/conf.d/azuremonitoragent-tcp.conf
# Azure MDSD configuration: syslog forwarding config for mdsd agent
options {};
# during install time, we detect if s_src exist, if it does then we
# replace it by appropriate source name like in redhat 's_sys'
# Forwrding using tcp
destination d_azure_mdsd {
network("127.0.0.1"
port(28330)
log-fifo-size(25000));
};
log {
source(s_src); # will be automatically parsed from /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf
destination(d_azure_mdsd);
flags(flow-control);
};
The following configuration is used when you use SELinux and decide to use Unix sockets.
$ cat /etc/syslog-ng/conf.d/azuremonitoragent.conf
# Azure MDSD configuration: syslog forwarding config for mdsd agent options {};
# during install time, we detect if s_src exist, if it does then we
# replace it by appropriate source name like in redhat 's_sys'
# Forwrding using unix domain socket
destination d_azure_mdsd {
unix-dgram("/run/azuremonitoragent/default_syslog.socket"
flags(no_multi_line) );
};
log {
source(s_src); # will be automatically parsed from /etc/syslog-ng/syslog-ng.conf
destination(d_azure_mdsd);
};
Note
Azure Monitor supports collection of messages sent by rsyslog or syslog-ng, where rsyslog is the default daemon. The default Syslog daemon on version 5 of Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Oracle Linux version (sysklog) isn't supported for Syslog event collection. To collect Syslog data from this version of these distributions, the rsyslog daemon should be installed and configured to replace sysklog.
If you edit the Syslog configuration, you must restart the Syslog daemon for the changes to take effect.
Supported facilities
The following facilities are supported with the Syslog collector:
| Pri index | Pri Name |
|---|---|
| 0 | None |
| 1 | Kern |
| 2 | user |
| 3 | |
| 4 | daemon |
| 4 | auth |
| 5 | syslog |
| 6 | lpr |
| 7 | news |
| 8 | uucp |
| 9 | ftp |
| 10 | ntp |
| 11 | audit |
| 12 | alert |
| 13 | mark |
| 14 | local0 |
| 15 | local1 |
| 16 | local2 |
| 17 | local3 |
| 18 | local4 |
| 19 | local5 |
| 20 | local6 |
| 21 | local7 |
Next steps
- Learn more about Azure Monitor Agent.
- Learn more about data collection rules.