Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes identity and access overview
You can authenticate, authorize, and control access to your Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters. This topic provides an overview of the options for doing so with your Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
This image shows the ways that these different options can be used:
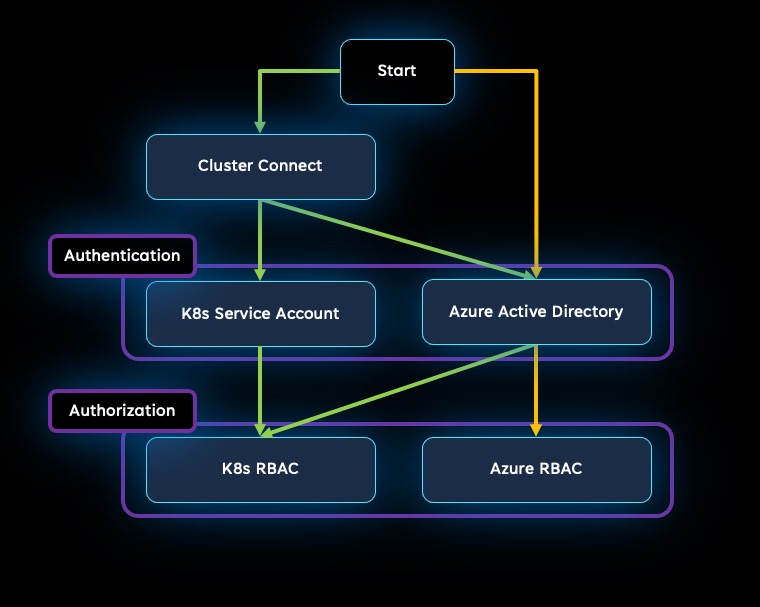
You can also use both cluster connect and Azure RBAC together if that is most appropriate for your needs.
Connectivity options
When planning how users will authenticate and access Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters, the first decision is whether or not you want to use the cluster connect feature.
Cluster connect
The Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster connect feature provides connectivity to the apiserver of the cluster. This connectivity doesn't require any inbound port to be enabled on the firewall. A reverse proxy agent running on the cluster can securely start a session with the Azure Arc service in an outbound manner.
With cluster connect, your Arc-enabled clusters can be accessed either within Azure or from the internet. This feature can help enable interactive debugging and troubleshooting scenarios. Cluster connect may also require less interaction for updates when permissions are needed for new users. All of the authorization and authentication options described in this article work with cluster connect.
Cluster connect is required if you want to use custom locations or viewing Kubernetes resources from Azure portal.
For more information, see Use cluster connect to securely connect to Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
Microsoft Entra ID and Azure RBAC without cluster connect
If you don't want to use cluster connect, you can authenticate and authorize users so they can access the connected cluster by using Microsoft Entra ID and Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC). Using Azure RBAC on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes lets you control the access that's granted to users in your tenant, managing access directly from Azure using familiar Azure identity and access features. You can also configure roles at the subscription or resource group scope, letting them roll out to all connected clusters within that scope.
Azure RBAC supports conditional access, allowing you to enable just-in-time cluster access or limit access to approved clients or devices.
Azure RBAC also supports a direct mode of communication, using Microsoft Entra identities to access connected clusters directly from within the datacenter, rather than requiring all connections to go through Azure.
Azure RBAC on Arc-enabled Kubernetes is currently in public preview. For more information, see Use Azure RBAC on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
Authentication options
Authentication is the process of verifying a user's identity. There are two options for authenticating to an Arc-enabled Kubernetes cluster: cluster connect and Azure RBAC.
Microsoft Entra authentication
The Azure RBAC on Arc-enabled Kubernetes feature lets you use Microsoft Entra ID to allow users in your Azure tenant to access your connected Kubernetes clusters.
You can also use Microsoft Entra authentication with cluster connect. For more information, see Microsoft Entra authentication option.
Service token authentication
With cluster connect, you can choose to authenticate via service accounts.
For more information, see Service account token authentication option.
Authorization options
Authorization grants an authenticated user the permission to perform specified actions. With Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes, there are two authorization options, both of which use role-based access control (RBAC):
- Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) uses Microsoft Entra ID and Azure Resource Manager to provide fine-grained access management to Azure resources. This allows the benefits of Azure role assignments, such as activity logs tracking all changes made, to be used with your Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
- Kubernetes role-based access control (Kubernetes RBAC) lets you dynamically configure policies through the Kubernetes API so that users, groups, and service accounts only have access to specific cluster resources.
While Kubernetes RBAC works only on Kubernetes resources within your cluster, Azure RBAC works on resources across your Azure subscription.
Azure RBAC authorization
Azure role-based access control (RBAC) is an authorization system built on Azure Resource Manager and Microsoft Entra ID that provides fine-grained access management of Azure resources. With Azure RBAC, role definitions outline the permissions to be applied. You assign these roles to users or groups via a role assignment for a particular scope. The scope can be across the entire subscription or limited to a resource group or to an individual resource such as a Kubernetes cluster.
If you're using Microsoft Entra authentication without cluster connect, then Azure RBAC authorization is your only option for authorization.
If you're using cluster connect with Microsoft Entra authentication, you have the option to use Azure RBAC for connectivity to the apiserver of the cluster. For more information, see Microsoft Entra authentication option.
Kubernetes RBAC authorization
Kubernetes RBAC provides granular filtering of user actions. With Kubernetes RBAC, you assign users or groups permission to create and modify resources or view logs from running application workloads. You can create roles to define permissions, and then assign those roles to users with role bindings. Permissions may be scoped to a single namespace or across the entire cluster.
If you're using cluster connect with the service account token authentication option, you must use Kubernetes RBAC to provide connectivity to the apiserver of the cluster. This connectivity doesn't require any inbound port to be enabled on the firewall. A reverse proxy agent running on the cluster can securely start a session with the Azure Arc service in an outbound manner.
If you're using cluster connect with Microsoft Entra authentication, you also have the option to use Kubernetes RBAC instead of Azure RBAC.
Next steps
- Learn more about Azure Microsoft Entra ID and Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC).
- Learn about cluster connect access to Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes clusters.
- Learn about Azure RBAC on Azure Arc-enabled Kubernetes
- Learn about access and identity options for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters.