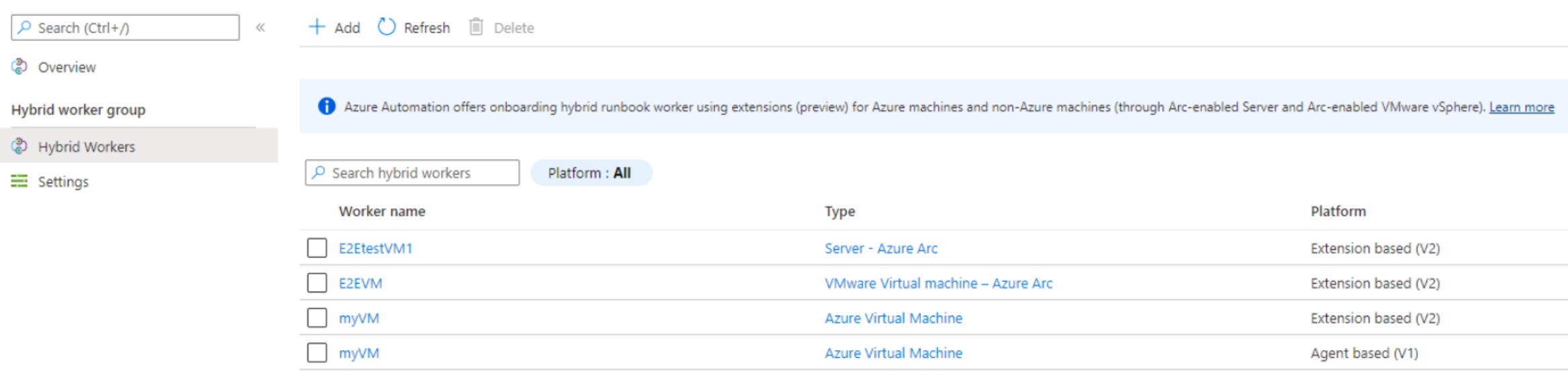
Deploy an extension-based Windows or Linux User Hybrid Runbook Worker in Azure Automation
The extension-based onboarding is only for User Hybrid Runbook Workers. This article describes how to: deploy a user Hybrid Runbook Worker on a Windows or Linux machine, remove the worker, and remove a Hybrid Runbook Worker group.
For System Hybrid Runbook Worker onboarding, see Deploy an agent-based Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker in Automation or Deploy an agent-based Linux Hybrid Runbook Worker in Automation.
You can use the user Hybrid Runbook Worker feature of Azure Automation to run runbooks directly on an Azure or non-Azure machine, including Azure Arc-enabled servers, Arc-enabled VMware vSphere, and Arc-enabled SCVMM. From the machine or server that's hosting the role, you can run runbooks directly against it and against resources in the environment to manage those local resources. Azure Automation stores and manages runbooks and then delivers them to one or more chosen machines. After you successfully deploy a runbook worker, review Run runbooks on a Hybrid Runbook Worker to learn how to configure your runbooks to automate processes in your on-premises datacenter or other cloud environment.
Note
A hybrid worker can co-exist with both platforms: Agent based (V1) and Extension based (V2). If you install Extension based (V2) on a hybrid worker already running Agent based (V1), then you would see two entries of the Hybrid Runbook Worker in the group. One with Platform Extension based (V2) and the other Agent based (V1). Learn more.
Prerequisites
Machine minimum requirements
- Two cores
- 4 GB of RAM
- Non-Azure machines must have the Azure Connected Machine agent installed. To install the
AzureConnectedMachineAgent, see Connect hybrid machines to Azure from the Azure portal for Arc-enabled servers. See Install Arc agent for Arc-enabled VMware VMs to enable guest management for Arc-enabled VMware vSphere VMs and install Arc agent for Arc-enabled SCVMM to enable guest management for Arc-enabled SCVMM VMs. - The system-assigned managed identity must be enabled on the Azure virtual machine, Arc-enabled server, Arc-enabled VMware vSphere VM or Arc-enabled SCVMM VM. If the system-assigned managed identity isn't enabled, it will be enabled as part of the adding process.
Supported operating systems
| Windows (x64) | Linux (x64) |
|---|---|
| ● Windows Server 2022 (including Server Core) ● Windows Server 2019 (including Server Core) ● Windows Server 2016, version 1709, and 1803 (excluding Server Core) ● Windows Server 2012, 2012 R2 (excluding Server Core) ● Windows 10 Enterprise (including multi-session) and Pro |
● Debian GNU/Linux 8, 9, 10, and 11 ● Ubuntu 18.04 LTS, 20.04 LTS, and 22.04 LTS ● SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15.2, and 15.3 ● Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server 7, 8, and 9 ● SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) 15 ● Rocky Linux 9 ● Oracle Linux 7 and 8 Hybrid Worker extension would follow support timelines of the OS vendor. |
Other Requirements
| Windows (x64) | Linux (x64) |
|---|---|
| Windows PowerShell 5.1 (download WMF 5.1). PowerShell Core isn't supported. | Linux Hardening must not be enabled. |
| .NET Framework 4.6.2 or later. |
Package requirements for Linux
| Required package | Description | Minimum version |
|---|---|---|
| Glibc | GNU C Library | 2.5-12 |
| Openssl | OpenSSL Libraries | 1.0 (TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2 are supported) |
| Curl | cURL web client | 7.15.5 |
| Python-ctypes | Foreign function library for Python | Python 2.x or Python 3.x are required |
| PAM | Pluggable Authentication Modules |
| Optional package | Description | Minimum version |
|---|---|---|
| PowerShell Core | To run PowerShell runbooks, PowerShell Core needs to be installed. For instructions, see Installing PowerShell Core on Linux | 6.0.0 |
Note
Hybrid Runbook Worker is currently not supported for Virtual Machine Scale Sets (VMSS).
We strongly recommend that you never configure Hybrid Worker extension on a Virtual machine hosting domain controller. Security best practices don't advise such a setup due to the high-risk nature of exposing domain controllers to potential attack vectors via Azure Automation jobs. Domain controllers should be highly secured and isolated from non-essential services to prevent unauthorized access and maintain the integrity of the Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) environment.
Permissions for Hybrid worker credentials
If extension-based Hybrid Worker is using custom Hybrid Worker credentials, then ensure that following folder permissions are assigned to the custom user to avoid jobs from getting suspended.
| Resource Type | Folder permissions |
|---|---|
| Azure VM | C:\Packages\Plugins\Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker.HybridWorkerForWindows (read and execute) |
| Arc-enabled Server | C:\ProgramData\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\Tokens (read) C:\Packages\Plugins\Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker.HybridWorkerForWindows (read and execute). |
Note
When a system has UAC/LUA in place, permissions must be granted directly and not through any group membership. Learn more.
Network requirements
Proxy server use
If you use a proxy server for communication between Azure Automation and machines running the extension-base Hybrid Runbook Worker, ensure that the appropriate resources are accessible. The timeout for requests from the Hybrid Runbook Worker and Automation services is 30 seconds. After three attempts, a request fails.
Note
For Azure VMs and Arc-enabled Servers, you can set up the proxy settings using PowerShell cmdlets or API. This is currently not supported for Arc-enabled VMware vSphere VMs.
To install the extension using cmdlets:
Get the automation account details using the below API call.
GET https://westcentralus.management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/{automationAccountName}?api-version=2021-06-22The API call will provide the value with the key:
AutomationHybridServiceUrl. Use the URL in the next step to enable extension on the VM.Install the Hybrid Worker Extension on the VM by running the following PowerShell cmdlet (Required module: Az.Compute). Use the
properties.automationHybridServiceUrlprovided by the above API call
Proxy server settings
$settings = @{
"AutomationAccountURL" = "<registrationurl>";
"ProxySettings" = @{
"ProxyServer" = "<ipaddress>:<port>";
"UserName"="test";
}
};
$protectedsettings = @{
"ProxyPassword" = "password";
};
Azure VMs
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName <VMResourceGroupName> -Location <VMLocation> -VMName <VMName> -Name "HybridWorkerExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker" -ExtensionType HybridWorkerForWindows -TypeHandlerVersion 1.1 -Settings $settings -ProtectedSettings $protectedsettings -EnableAutomaticUpgrade $true/$false
Azure Arc-enabled VMs
New-AzConnectedMachineExtension -ResourceGroupName <VMResourceGroupName> -Location <VMLocation> -MachineName <VMName> -Name "HybridWorkerExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker" -ExtensionType HybridWorkerForWindows -TypeHandlerVersion 1.1 -Setting $settings -ProtectedSetting $protectedsettings -NoWait -EnableAutomaticUpgrade
Firewall use
If you use a firewall to restrict access to the Internet, you must configure the firewall to permit access. The following port and URLs are required for the Hybrid Runbook Worker, and for Automation State Configuration to communicate with Azure Automation.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Port | 443 for outbound internet access |
| Global URL | *.azure-automation.net |
| Global URL of US Gov Virginia | *.azure-automation.us |
CPU quota limit
There is a CPU quota limit of 25% while configuring extension-based Linux Hybrid Runbook worker. There is no such limit for Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker.
Create hybrid worker group
To create a hybrid worker group in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Go to your Automation account.
Under Process Automation, select Hybrid worker groups.
Select + Create hybrid worker group.
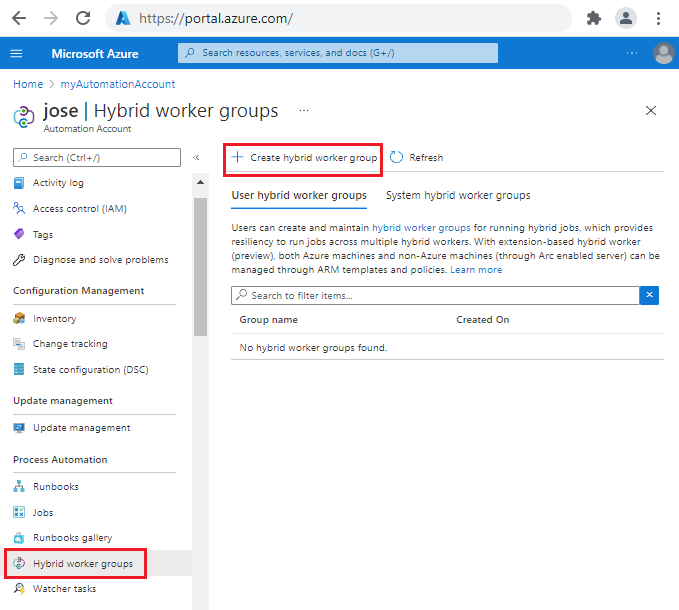
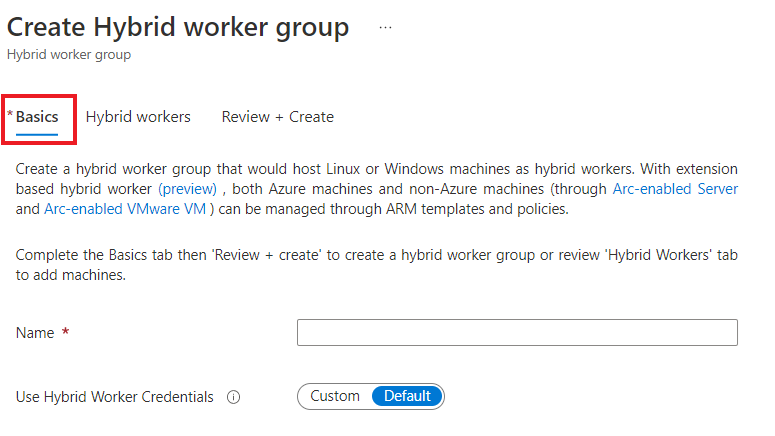
From the Basics tab, in the Name text box, enter a name for your Hybrid worker group.
For the Use Hybrid Worker Credentials option:
- If you select Default, the hybrid extension will be installed using the local system account.
- If you select Custom, then from the drop-down list, select the credential asset.
Select Next to advance to the Hybrid workers tab. You can select Azure virtual machines, Azure Arc-enabled servers, Azure Arc-enabled VMware vSphere and Arc-enabled SCVMM to be added to this Hybrid worker group. If you don't select any machines, an empty Hybrid worker group will be created. You can still add machines later.
Select Add machines to go to the Add machines as hybrid worker page. You'll only see machines that aren't part of any other hybrid worker group.
Select the checkbox next to the machine(s) you want to add to the hybrid worker group. If you don't see your non-Azure machine listed, ensure Azure Arc Connected Machine agent is installed on the machine.
Select Add.
Select Next to advance to the Review + Create tab.
Select Create.
The hybrid worker extension installs on the machine and the hybrid worker gets registered to the hybrid worker group. Adding a hybrid worker to the group happens immediately, while installation of the extension might take a few minutes. Select Refresh to see the new group. Select the group name to view the hybrid worker details.
Note
A selected machine won't be added to a hybrid worker group if it is already part of another hybrid worker group.
Add a machine to a hybrid worker group
You can also add machines to an existing hybrid worker group.
Under Process Automation, select Hybrid worker groups and then your existing hybrid worker group to go to the Hybrid Worker Group page.
Under Hybrid worker group, select Hybrid Workers.
Select + Add to go to the Add machines as hybrid worker page. You'll only see machines that aren't part of any other hybrid worker group.
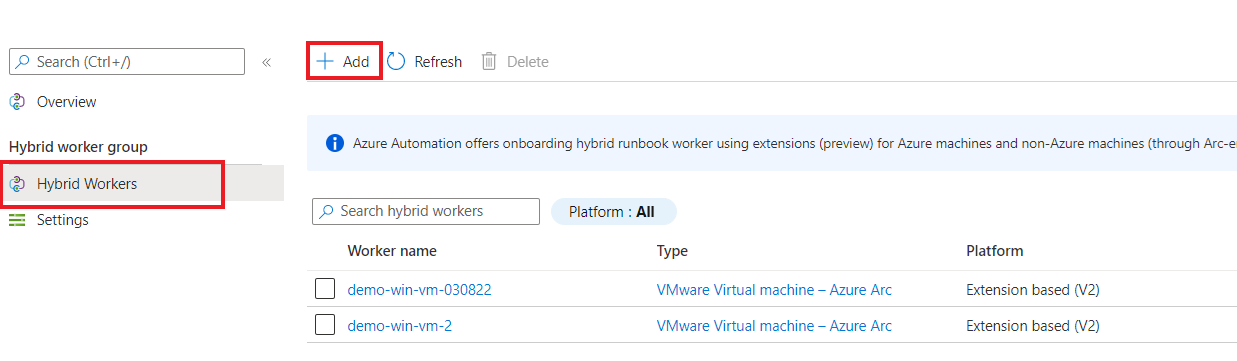
Select the checkbox next to the machine(s) you want to add to the hybrid worker group.
If you don't see your non-Azure machine listed, ensure Azure Arc Connected Machine agent is installed on the machine. To install the
AzureConnectedMachineAgentsee Connect hybrid machines to Azure from the Azure portal for Arc-enabled servers. See Install Arc agent for Arc-enabled VMs to enable guest management for Arc-enabled VMware vSphere and Install Arc agent for Arc-enabled SCVMM to enable guest management for Arc-enabled SCVMM VMs.Select Add to add the machine to the group.
After adding, you can see the machine type as Azure virtual machine, Machine – Azure Arc , Machine – Azure Arc (VMware) or Machine – Azure Arc SCVMM. The Platform field shows the worker as Agent based (V1) or Extension based (V2).
Migrate an existing Agent based to Extension based Hybrid Workers
To utilize the benefits of extension based Hybrid Workers, you must migrate all existing agent based User Hybrid Workers to extension based Workers. A hybrid worker machine can co-exist on both Agent based (V1) and Extension based (V2) platforms. The extension based installation doesn't affect the installation or management of an agent based Worker.
To install Hybrid worker extension on an existing agent based hybrid worker, ensure the prerequisites are fulfilled before following these steps:
- Under Process Automation, select Hybrid worker groups, and then select your existing hybrid worker group to go to the Hybrid worker group page.
- Under Hybrid worker group, select Hybrid Workers > + Add to go to the Add machines as hybrid worker page.
- Select the checkbox next to the existing Agent based (V1) Hybrid worker.
- Select Add to append the machine to the group.
The Platform column shows the same Hybrid worker as both Agent based (V1) and Extension based (V2). After you're confident of the extension based Hybrid Worker experience and use, you can remove the agent based Worker.
For at-scale migration of multiple Agent based Hybrid Workers, you can also use other channels such as - Bicep, ARM templates, PowerShell cmdlets, REST API, and Azure CLI.
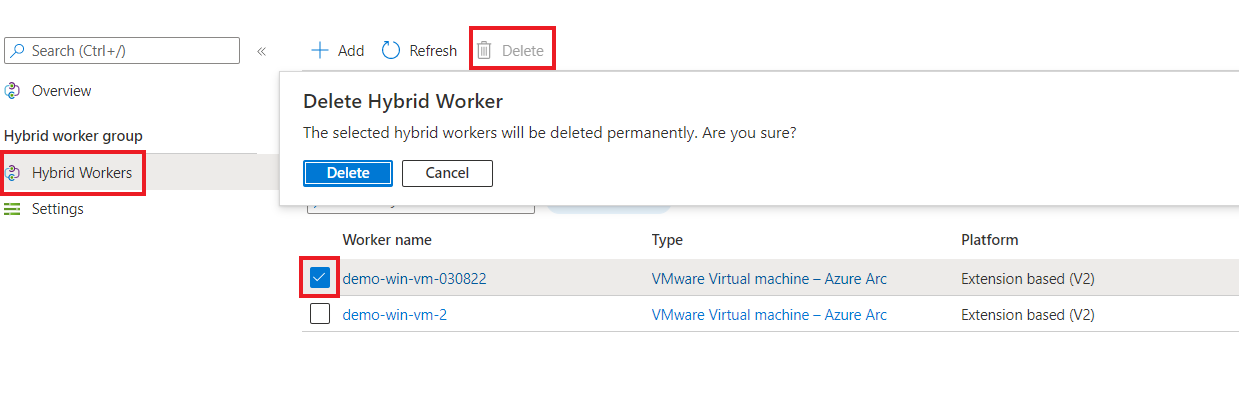
Delete a Hybrid Runbook Worker
You can delete the Hybrid Runbook Worker from the portal.
Under Process Automation, select Hybrid worker groups and then your hybrid worker group to go to the Hybrid Worker Group page.
Under Hybrid worker group, select Hybrid Workers.
Select the checkbox next to the machine(s) you want to delete from the hybrid worker group.
Select Delete.
You'll be presented with a warning in a dialog box Delete Hybrid worker that the selected hybrid worker would be deleted permanently. Select Delete. This operation will delete the extension for the Extension based (V2) worker or remove the Agent based (V1) entry from the portal. However, it leaves the stale hybrid worker on the VM. To manually uninstall the agent, see Uninstall agent.
Note
- A hybrid worker can co-exist with both platforms: Agent based (V1) and Extension based (V2). If you install Extension based (V2) on a hybrid worker already running Agent based (V1), then you would see two entries of the Hybrid Runbook Worker in the group. One with Platform Extension based (V2) and the other Agent based (V1).
- After you disable the Private Link in your Automation account, it might take up to 60 minutes to remove the Hybrid Runbook worker.
- Hybrid Runbook Worker proxy settings can be deleted from HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Azure\HybridWorker\Parameters, "Http Connection Proxy Url".
- A hybrid worker can co-exist with both platforms: Agent based (V1) and Extension based (V2). If you install Extension based (V2) on a hybrid worker already running Agent based (V1), then you would see two entries of the Hybrid Runbook Worker in the group. One with Platform Extension based (V2) and the other Agent based (V1).
Delete a Hybrid Runbook Worker group
You can delete an empty Hybrid Runbook Worker group from the portal.
Under Process Automation, select Hybrid worker groups and then your hybrid worker group to go to the Hybrid Worker Group page.
Select Delete.
A warning message appears to remove any machines that are defined as hybrid workers in the hybrid worker group. If there's already a worker added to the group, you'll first have to delete the worker from the group.
Select Yes.
The hybrid worker group will be deleted.
Automatic upgrade of extension
Hybrid Worker extension supports Automatic upgrade of minor versions by default. We recommend that you enable Automatic upgrades to take advantage of any security or feature updates without manual overhead. However, to prevent the extension from automatically upgrading (for example, if there is a strict change windows and can only be updated at specific time), you can opt out of this feature by setting the enableAutomaticUpgradeproperty in ARM, Bicep template, PowerShell cmdlets to false. Set the same property to true whenever you want to re-enable the Automatic upgrade.
$extensionType = "HybridWorkerForLinux/HybridWorkerForWindows"
$extensionName = "HybridWorkerExtension"
$publisher = "Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker"
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName <RGName> -Location <Location> -VMName <vmName> -Name $extensionName -Publisher $publisher -ExtensionType $extensionType -TypeHandlerVersion 1.1 -Settings $settings -EnableAutomaticUpgrade $true/$false
Major version upgrades must be managed manually. Run the below cmdlets with the latest TypeHandlerVersion.
Note
If you had installed the Hybrid Worker extension during the public preview, ensure to upgrade it to the latest major version.
Azure VMs
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName <VMResourceGroupName> -Location <VMLocation> -VMName <VMName> -Name "HybridWorkerExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker" -ExtensionType HybridWorkerForWindows -TypeHandlerVersion 1.1 -Settings $settings -EnableAutomaticUpgrade $true/$false
Azure Arc-enabled VMs
New-AzConnectedMachineExtension -ResourceGroupName <VMResourceGroupName> -Location <VMLocation> -MachineName <VMName> -Name "HybridWorkerExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker" -ExtensionType HybridWorkerForWindows -TypeHandlerVersion 1.1 -Setting $settings -NoWait -EnableAutomaticUpgrade
Manage Hybrid Worker extension using Bicep & ARM templates, REST API, Azure CLI, and PowerShell
You can use the Bicep template to create a new Hybrid Worker group, create a new Azure Windows VM and add it to an existing Hybrid Worker Group. Learn more about Bicep.
Follow the steps mentioned below as an example:
- Create a Hybrid Worker Group.
- Create either an Azure VM or Arc-enabled server. Alternatively, you can also use an existing Azure VM or Arc-enabled server.
- Connect the Azure VM or Arc-enabled server to the above created Hybrid Worker Group.
- Generate a new GUID and pass it as the name of the Hybrid Worker.
- Enable System-assigned managed identity on the VM.
- Install Hybrid Worker Extension on the VM.
- To confirm if the extension has been successfully installed on the VM, in Azure portal, go to the VM > Extensions tab and check the status of the Hybrid Worker extension installed on the VM.
param automationAccount string
param automationAccountLocation string
param workerGroupName string
@description('Name of the virtual machine.')
param virtualMachineName string
@description('Username for the Virtual Machine.')
param adminUsername string
@description('Password for the Virtual Machine.')
@minLength(12)
@secure()
param adminPassword string
@description('Location for the VM.')
param vmLocation string = 'North Central US'
@description('Size of the virtual machine.')
param vmSize string = 'Standard_DS1_v2'
@description('The Windows version for the VM. This will pick a fully patched image of this given Windows version.')
@allowed([
'2008-R2-SP1'
'2012-Datacenter'
'2012-R2-Datacenter'
'2016-Nano-Server'
'2016-Datacenter-with-Containers'
'2016-Datacenter'
'2019-Datacenter'
'2019-Datacenter-Core'
'2019-Datacenter-Core-smalldisk'
'2019-Datacenter-Core-with-Containers'
'2019-Datacenter-Core-with-Containers-smalldisk'
'2019-Datacenter-smalldisk'
'2019-Datacenter-with-Containers'
'2019-Datacenter-with-Containers-smalldisk'
])
param osVersion string = '2019-Datacenter'
@description('DNS name for the public IP')
param dnsNameForPublicIP string
var nicName_var = 'myVMNict'
var addressPrefix = '10.0.0.0/16'
var subnetName = 'Subnet'
var subnetPrefix = '10.0.0.0/24'
var subnetRef = resourceId('Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/subnets', virtualNetworkName_var, subnetName)
var vmName_var = virtualMachineName
var virtualNetworkName_var = 'MyVNETt'
var publicIPAddressName_var = 'myPublicIPt'
var networkSecurityGroupName_var = 'default-NSGt'
var UniqueStringBasedOnTimeStamp = uniqueString(resourceGroup().id)
resource publicIPAddressName 'Microsoft.Network/publicIPAddresses@2020-08-01' = {
name: publicIPAddressName_var
location: vmLocation
properties: {
publicIPAllocationMethod: 'Dynamic'
dnsSettings: {
domainNameLabel: dnsNameForPublicIP
}
}
}
resource networkSecurityGroupName 'Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups@2020-08-01' = {
name: networkSecurityGroupName_var
location: vmLocation
properties: {
securityRules: [
{
name: 'default-allow-3389'
properties: {
priority: 1000
access: 'Allow'
direction: 'Inbound'
destinationPortRange: '3389'
protocol: 'Tcp'
sourceAddressPrefix: '*'
sourcePortRange: '*'
destinationAddressPrefix: '*'
}
}
]
}
}
resource virtualNetworkName 'Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks@2020-08-01' = {
name: virtualNetworkName_var
location: vmLocation
properties: {
addressSpace: {
addressPrefixes: [
addressPrefix
]
}
subnets: [
{
name: subnetName
properties: {
addressPrefix: subnetPrefix
networkSecurityGroup: {
id: networkSecurityGroupName.id
}
}
}
]
}
}
resource nicName 'Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces@2020-08-01' = {
name: nicName_var
location: vmLocation
properties: {
ipConfigurations: [
{
name: 'ipconfig1'
properties: {
privateIPAllocationMethod: 'Dynamic'
publicIPAddress: {
id: publicIPAddressName.id
}
subnet: {
id: subnetRef
}
}
}
]
}
dependsOn: [
virtualNetworkName
]
}
resource vmName 'Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines@2020-12-01' = {
name: vmName_var
location: vmLocation
identity: {
type: 'SystemAssigned'
}
properties: {
hardwareProfile: {
vmSize: vmSize
}
osProfile: {
computerName: vmName_var
adminUsername: adminUsername
adminPassword: adminPassword
}
storageProfile: {
imageReference: {
publisher: 'MicrosoftWindowsServer'
offer: 'WindowsServer'
sku: osVersion
version: 'latest'
}
osDisk: {
createOption: 'FromImage'
}
}
networkProfile: {
networkInterfaces: [
{
id: nicName.id
}
]
}
}
}
resource automationAccount_resource 'Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts@2021-06-22' = {
name: automationAccount
location: automationAccountLocation
properties: {
sku: {
name: 'Basic'
}
}
}
resource automationAccount_workerGroupName 'Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups@2022-02-22' = {
parent: automationAccount_resource
name: workerGroupName
dependsOn: [
vmName
]
}
resource automationAccount_workerGroupName_testhw_UniqueStringBasedOnTimeStamp 'Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers@2021-06-22' = {
parent: automationAccount_workerGroupName
name: guid('testhw', UniqueStringBasedOnTimeStamp)
properties: {
vmResourceId: resourceId('Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines', virtualMachineName)
}
dependsOn: [
vmName
]
}
resource virtualMachineName_HybridWorkerExtension 'Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions@2022-03-01' = {
name: '${virtualMachineName}/HybridWorkerExtension'
location: vmLocation
properties: {
publisher: 'Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker'
type: 'HybridWorkerForWindows'
typeHandlerVersion: '1.1'
autoUpgradeMinorVersion: true
enableAutomaticUpgrade: true
settings: {
AutomationAccountURL: automationAccount_resource.properties.automationHybridServiceUrl
}
}
dependsOn: [
vmName
]
}
output output1 string = automationAccount_resource.properties.automationHybridServiceUrl
Manage Role permissions for Hybrid Worker Groups and Hybrid Workers
You can create custom Azure Automation roles and grant following permissions to Hybrid Worker Groups and Hybrid Workers. To learn more about how to create Azure Automation custom roles, see Azure custom roles.
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/read | Reads a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/write | Creates a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/delete | Deletes a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers/read | Reads a Hybrid Runbook Worker. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers/write | Creates a Hybrid Runbook Worker. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers/move/action | Moves Hybrid Runbook Worker from one Worker Group to another. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/hybridRunbookWorkers/delete | Deletes a Hybrid Runbook Worker. |
Check version of Hybrid Worker
To check the version of the extension-based Hybrid Runbook Worker:
| OS types | Paths | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | C:\Packages\Plugins\Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker.HybridWorkerForWindows\ |
The path has version folder that has the version information. |
| Linux | /var/lib/waagent/Microsoft.Azure.Automation.HybridWorker.HybridWorkerForLinux-<version> |
The folder name ends with version information. |
Monitor performance of Hybrid Workers using VM insights
Using VM insights, you can monitor the performance of Azure VMs and Arc-enabled Servers deployed as Hybrid Runbook workers. Among multiple elements that are considered during performances, the VM insights monitors the key operating system performance indicators related to processor, memory, network adapter, and disk utilization.
- For Azure VMs, see How to chart performance with VM insights.
- For Arc-enabled servers, see Tutorial: Monitor a hybrid machine with VM insights.
Next steps
To learn how to configure your runbooks to automate processes in your on-premises datacenter or other cloud environments, see Run runbooks on a Hybrid Runbook Worker.
To learn how to troubleshoot your Hybrid Runbook Workers, see Troubleshoot Hybrid Runbook Worker issues.
To learn about Azure VM extensions, see Azure VM extensions and features for Windows and Azure VM extensions and features for Linux.
To learn about VM extensions for Arc-enabled servers, see VM extension management with Azure Arc-enabled servers.
To learn about Azure management services for Arc-enabled VMware VMs, see Install Arc agents at scale for your VMware VMs.
To learn about Azure management services for Arc-enabled SCVMM VMs, see Install Arc agents at scale for Arc-enabled SCVMM VMs.