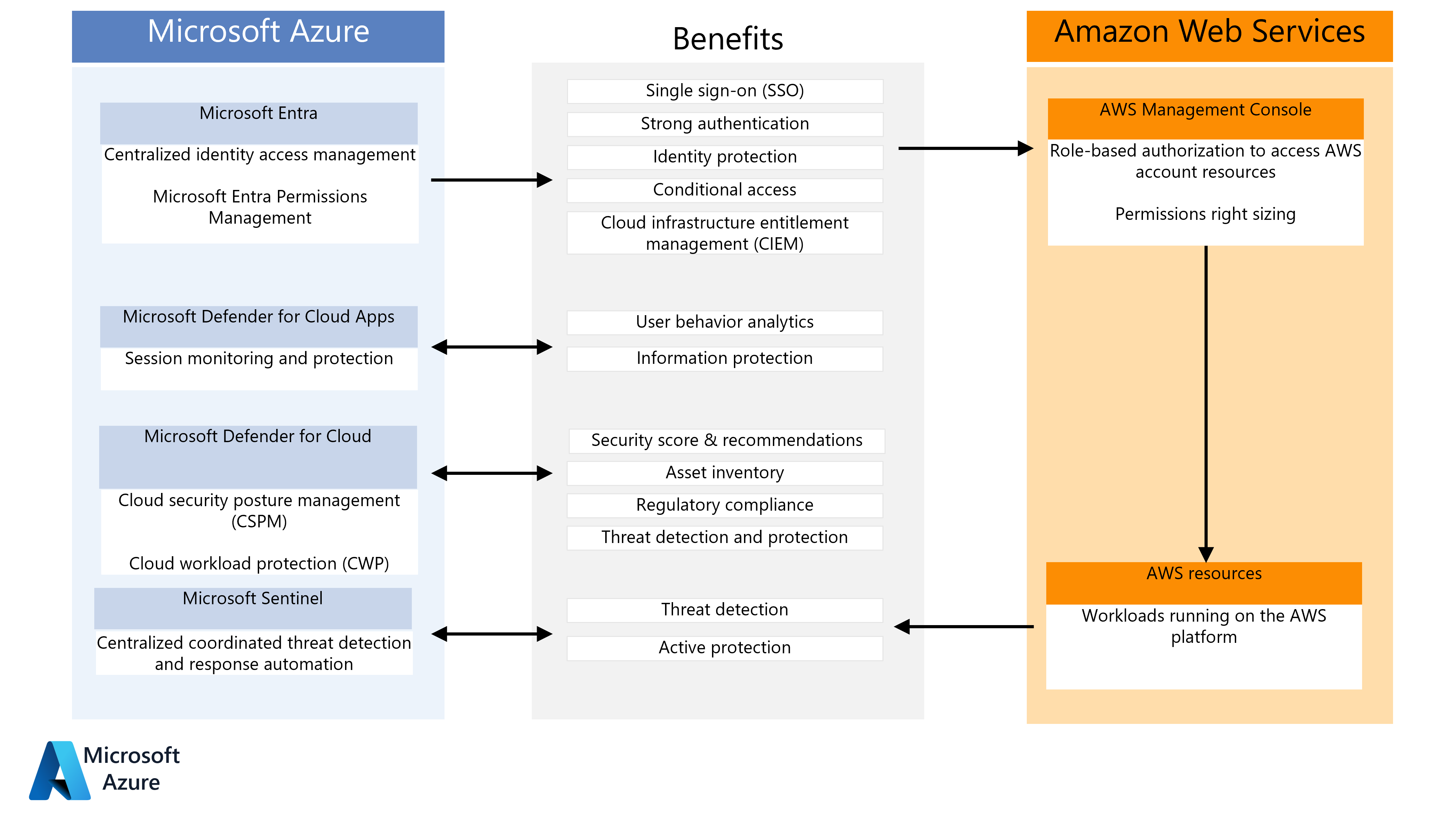
This guide describes how Microsoft security solutions can help secure and protect Amazon Web Services (AWS) account access and environments.
This diagram summarizes how AWS installations can benefit from key Microsoft security components:
Download a PowerPoint file of this diagram.
Microsoft Entra
Centralized identity and access management
Microsoft Entra ID is a comprehensive, cloud-based centralized identity and access management solution that can help secure and protect AWS accounts and environments.
Microsoft Entra ID provides strong SSO authentication to almost any app or platform that follows common web authentication standards, including AWS. AWS accounts that support critical workloads and highly sensitive information need strong identity protection and access control. AWS identity management is enhanced when you combine it with Microsoft Entra ID.
AWS organizations that use Microsoft Entra ID for Microsoft 365 or hybrid cloud identity and access protection can quickly and easily deploy Microsoft Entra ID for AWS accounts, often without incurring additional costs. Microsoft Entra ID provides several capabilities for direct integration with AWS:
Integration with AWS IAM Identity Center for enhanced security, improved user experience, centralized access control, and SSO across legacy, traditional, and modern authentication solutions.
Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication, including integration with several third-party solutions from Microsoft Intelligent Security Association partners.
Powerful Conditional Access features for strong authentication and strict governance. Microsoft Entra ID uses Conditional Access policies and risk-based assessments to authenticate and authorize user access to the AWS Management Console and AWS resources.
Improved protection against identity-based attacks via real-time detection and remediation of risky sign-ins and unusual user behavior.
Privileged Identity Management (PIM) to enable just-in-time provisioning of specific resources. You can expand PIM to any delegated permission by controlling access to custom groups, like groups that you create for access to AWS roles.
For more information and detailed instructions, see Microsoft Entra identity and access management for AWS.
Microsoft Entra Permissions Management
Permissions Management is a cloud infrastructure entitlement management solution that provides comprehensive visibility into and control over permissions on identities, actions, and resources across multicloud infrastructure on Azure, AWS, and Google Cloud Platform. You can use Permissions Management to:
Discover the number of unused or excessive permissions across all AWS accounts to identify risks via a multidimensional view of identities, permissions, and resources.
Remediate and right-size permissions via enforcement of the principle of least privilege across all AWS accounts.
Monitor and alert anomalous activities to help prevent data breaches caused by misuse and malicious exploitation of permissions.
For more information and detailed onboarding instructions, see Onboard an Amazon Web Services (AWS) account.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps
When several users or roles make administrative changes, configuration drift away from intended security architecture and standards can occur. Security standards can also change over time. Security personnel must constantly and consistently detect new risks, evaluate mitigation options, and update security architecture to help prevent potential breaches. Security management across multiple public cloud and private infrastructure environments can become burdensome.
Defender for Cloud Apps provides enhanced protection for software as a service (SaaS) applications. It provides the following features to help you monitor and protect your cloud app data:
Fundamental Cloud Access Security Broker functionality, including shadow IT discovery, visibility into cloud app usage, enhanced protection against app-based threats from anywhere in the cloud, and information protection and compliance assessments.
SaaS Security Posture Management features that enable security teams to improve the organization's security posture.
Advanced threat protection, as part of the Microsoft extended detection and response solution, which enables powerful correlation of signal and visibility across the full cyberattack chain of advanced attacks.
App-to-app protection, which extends the core threat scenarios to OAuth-enabled apps that have permissions and privileges to critical data and resources.
Connecting AWS to Defender for Cloud Apps helps you secure your assets and detect potential threats by monitoring administrative and sign-in activities. You get notifications of possible brute force attacks, malicious use of privileged user accounts, unusual deletions of VMs, and publicly exposed storage buckets. Defender for Cloud Apps helps protect AWS environments from abuse of cloud resources, compromised accounts and insider threats, data leakage, and resource misconfiguration and insufficient access control. The following Defender for Cloud Apps capabilities are especially useful when you work with AWS environments.
Detect cloud threats, compromised accounts, malicious insiders, and ransomware. Defender for Cloud Apps anomaly detection policies are triggered when there are unusual activities performed by users in AWS. Defender for Cloud Apps continually monitors your users' activities and uses UEBA and machine learning to learn and understand the typical behavior of your users and trigger alerts on any deviations.
Limit exposure of shared data and enforce collaboration policies. Automate governance controls via actions like notifying users about alerts, requiring re-authentication or suspending users, making an S3 bucket private, or removing collaborators from an S3 bucket.
Audit activities. Connect AWS auditing to Defender for Cloud apps to get visibility into user, admin, and sign-in activities.
Get enhanced real-time protection for AWS. Use Defender for Cloud Apps Conditional Access app control to block and help protect downloads of sensitive AWS data by risky users.
For more information on how to connect AWS environments to Defender for Cloud Apps, see Protect your Amazon Web Services environment.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Defender for Cloud is a Cloud-Native Application Protection Platform that's made up of security measures and practices that are designed to protect cloud-based applications from various cyberthreats and vulnerabilities. Defender for Cloud provides the following capabilities:
A development security operations solution that unifies security management at the code level across multicloud and multiple-pipeline environments
A cloud security posture management (CSPM) solution that surfaces actions that you can take to help prevent breaches
A cloud workload protection platform (CWPP) that provides protection for servers, containers, storage, databases, and other workloads
Defender for Cloud native AWS support provides several benefits:
Foundational CSPM for AWS resources
Defender CSPM for AWS resources
CWPP support for Amazon EKS clusters
CWPP support for AWS EC2 instances
CWPP support for SQL servers running on AWS EC2 and RDS Custom for SQL Server
The foundational CPSM and Defender CSPM are both completely agentless. Foundational CSPM provides recommendations on how to best harden your AWS resources and remediate misconfigurations. Defender for Cloud offers foundational multicloud CSPM capabilities for free.
Defender CSPM provides advanced posture management capabilities like attack path analysis, cloud security explorer, advanced threat hunting, and security governance capabilities. It also provides tools to assess your security compliance with a wide range of benchmarks, regulatory standards, and any custom security policies required in your organization, industry, or region.
The CWPP support for AWS EC2 instances provides capabilities like automatic provisioning of prerequisites on existing and new machines, vulnerability assessment, an integrated license for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, file integrity monitoring, and more.
The CWPP support for Amazon EKS clusters provides capabilities like discovery of unprotected clusters, advanced threat detection for the control plane and workload level, Kubernetes data plane recommendations (via the Azure Policy extension), and more.
The CWPP support for SQL servers running on AWS EC2 and AWS RDS Custom for SQL Server provides capabilities like advanced threat protection, vulnerability assessment scanning, and more.
Security standards provide support for assessing resources and workloads in AWS against regulatory compliance standards like Center for Internet Security (CIS) and Payment Card Industry (PCI) standards, and for the AWS Foundational Security Best Practices standard.
For more information about protecting workloads in AWS, see Connect your AWS account and Assign regulatory compliance standards in Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
Microsoft Sentinel
Microsoft Sentinel is a scalable cloud-native security information and event management (SIEM) system that provides an intelligent and comprehensive solution for SIEM and security orchestration, automation, and response. Microsoft Sentinel provides cyberthreat detection, investigation, response, and proactive hunting. It gives you a bird's-eye view across your enterprise.
You can use the AWS connectors to pull AWS service logs into Microsoft Sentinel. These connectors work by granting Microsoft Sentinel access to your AWS resource logs. Setting up the connector establishes a trust relationship between AWS and Microsoft Sentinel. You create this relationship on AWS by creating a role that gives permission to Microsoft Sentinel to access your AWS logs.
The connector can ingest logs from the following AWS services by pulling them from an S3 bucket:
| Service | Data source |
|---|---|
| Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | VPC Flow Logs |
| Amazon GuardDuty | GuardDuty findings |
| AWS CloudTrail | Management and data events |
| AWS CloudWatch | CloudWatch Logs |
For more information on how to install and configure the AWS connector in Microsoft Sentinel, see Connect Microsoft Sentinel to Amazon Web Services to ingest AWS service log data.
Recommendations
Use the Microsoft security solutions and basic AWS security recommendations to protect AWS accounts.
Basic AWS account security
For information about basic security hygiene for AWS accounts and resources, review the AWS security guidance at Best practices for securing AWS accounts and resources.
Reduce the risk of uploading and downloading malware and other malicious content by actively inspecting all data transfers via the AWS Management Console. Content that you upload or download directly to resources within the AWS platform, such as web servers or databases, might need additional protection.
Provide security for access keys by rotating the keys periodically. Avoid embedding them in code. Use IAM roles instead of long-term access keys wherever possible.
Use security groups and network ACLs to control inbound and outbound traffic to your resources. Implement VPC to isolate resources.
Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit by using AWS Key Management Services.
Protect devices that administrators and developers use to access the AWS Management Console.
Contributors
This article is maintained by Microsoft. It was originally written by the following contributor.
Principal author:
- Lavanya Murthy | Principal Cloud Solution Architect
To see non-public LinkedIn profiles, sign in to LinkedIn.
Next steps
- Monitor and protect AWS administrative and sign-in activities
- Protect workloads in AWS
- Connect Microsoft Sentinel to Amazon Web Services to ingest AWS service log data