URL Path Based Routing overview
URL Path Based Routing allows you to route traffic to backend server pools based on URL Paths of the request.
One of the scenarios is to route requests for different content types to different backend server pools.
In the following example, Application Gateway is serving traffic for contoso.com from three backend server pools for example: VideoServerPool, ImageServerPool, and DefaultServerPool.
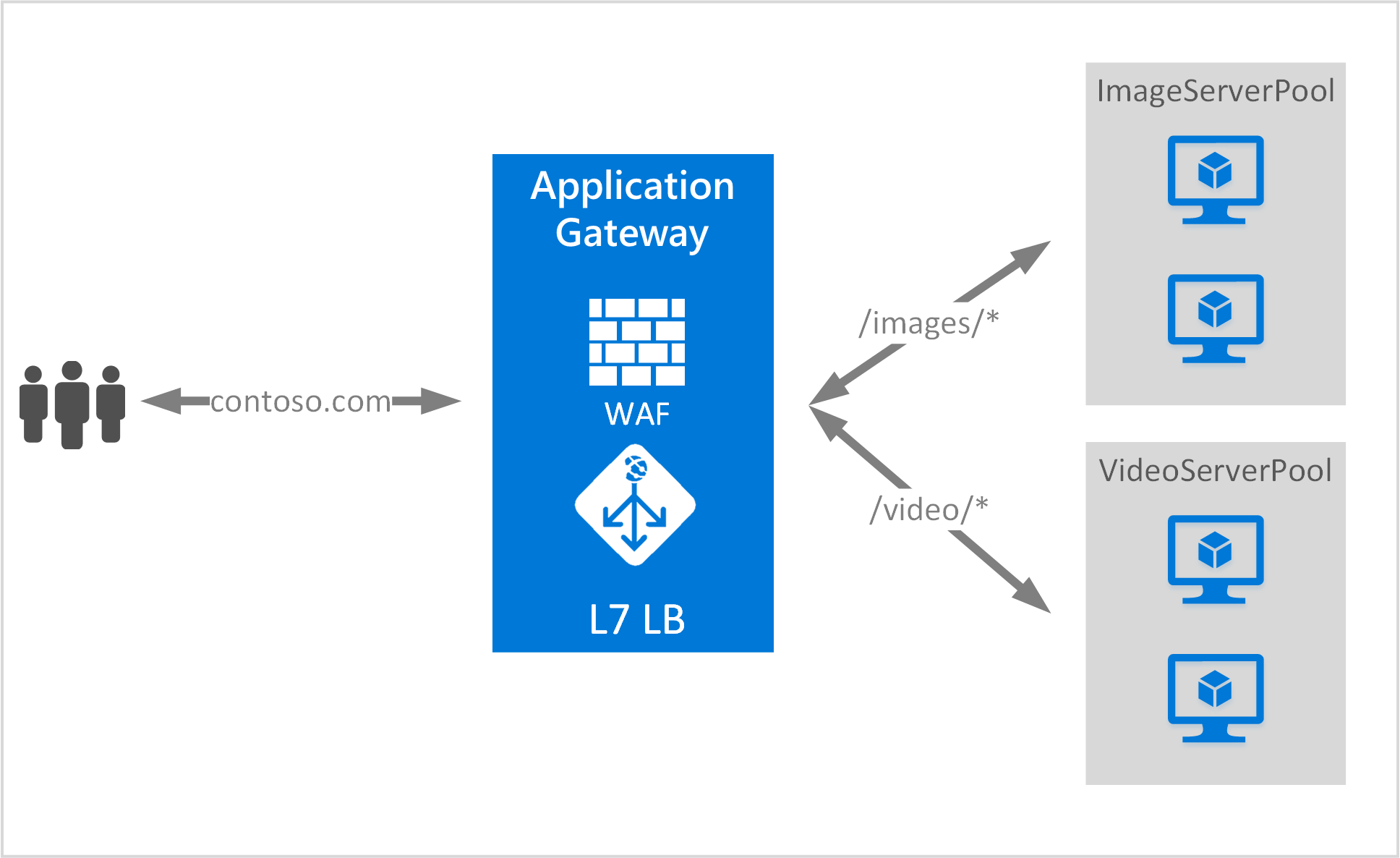
Requests for http://contoso.com/video/* are routed to VideoServerPool, and http://contoso.com/images/* are routed to ImageServerPool. DefaultServerPool is selected if none of the path patterns match.
Note
When the request is routed the full URL path is sent to the backend pool. If the resources requested are on a different path (for example if a request to http://contoso.com/video/* requires videos to be served from the root of the site behind the VideoServerPool) then you will also need to configure either a URL Rewrite Rule, or override the backend path in your backend settings.
Important
For both the v1 and v2 SKUs, rules are processed in the order they are listed in the portal. The best practice when you create path rules is to have the least specific path (the ones with wildcards) at the end. If wildcards are on the top, then they take priority even if there's a more specific match in subsequent path rules.
If a basic listener is listed first and matches an incoming request, it gets processed by that listener. However, it's highly recommended to configure multi-site listeners first prior to configuring a basic listener. This ensures that traffic gets routed to the right back end.
UrlPathMap configuration element
The urlPathMap element is used to specify Path patterns to backend server pool mappings. The following code example is the snippet of urlPathMap element from template file.
"urlPathMaps": [{
"name": "{urlpathMapName}",
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/urlPathMaps/{urlpathMapName}",
"properties": {
"defaultBackendAddressPool": {
"id": "/subscriptions/ {subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/backendAddressPools/{poolName1}"
},
"defaultBackendHttpSettings": {
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/backendHttpSettingsCollection/{settingname1}"
},
"pathRules": [{
"name": "{pathRuleName}",
"properties": {
"paths": [
"{pathPattern}"
],
"backendAddressPool": {
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/backendAddressPools/{poolName2}"
},
"backendHttpsettings": {
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/backendHttpSettingsCollection/{settingName2}"
}
}
}]
}
}]
PathPattern
PathPattern is a list of path patterns to match. Each path must start with / and may use * as a wildcard character. The string fed to the path matcher doesn't include any text after the first ? or #, and those chars aren't allowed here. Otherwise, any characters allowed in a URL are allowed in PathPattern.
Path rules are case insensitive.
| Path pattern | Is supported? |
|---|---|
/images/* |
yes |
/images* |
yes |
/images/*.jpg |
no |
/*.jpg |
no |
/Repos/*/Comments/* |
no |
/CurrentUser/Comments/* |
yes |
Path rules are processed in order, based on how they're listed in the portal. The least specific path (with wildcards) should be at the end of the list, so that it will be processed last. If wildcard rules are present at the top of the list, they take priority and will be processed first. See the following example scenarios.
Examples
Path-based rule processing when wildcard (*) is used:
Example 1:
/master-dev* to contoso.com
/master-dev/api-core/ to fabrikam.com
/master-dev/* to microsoft.com
Because the wildcard path /master-dev* is present above more granular paths, all client requests containing /master-dev are routed to contoso.com, including the specific /master-dev/api-core/. To ensure that the client requests are routed to the appropriate paths, it's critical to have the granular paths above wildcard paths.
Example 2:
/ (default) to contoso.com
/master-dev/api-core/ to fabrikam.com
/master-dev/api to bing.com
/master-dev/* to microsoft.com
All client requests with the path pattern /master-dev/* are processed in the order as listed. If there's no match within the path rules, the request is routed to the default target.
For more information, see Resource Manager template using URL-based routing.
PathBasedRouting rule
RequestRoutingRule of type PathBasedRouting is used to bind a listener to a urlPathMap. All requests that are received for this listener are routed based on policy specified in urlPathMap. Snippet of PathBasedRouting rule:
"requestRoutingRules": [
{
"name": "{ruleName}",
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/requestRoutingRules/{ruleName}",
"properties": {
"ruleType": "PathBasedRouting",
"httpListener": {
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/httpListeners/<listenerName>"
},
"urlPathMap": {
"id": "/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/../microsoft.network/applicationGateways/{gatewayName}/urlPathMaps/{urlpathMapName}"
}
}
}
]
Next steps
After learning about URL-based content routing, go to create an application gateway using URL-based routing to create an application gateway with URL routing rules.