TLS termination with Key Vault certificates
Azure Key Vault is a platform-managed secret store that you can use to safeguard secrets, keys, and TLS/SSL certificates. Azure Application Gateway supports integration with Key Vault for server certificates that are attached to HTTPS-enabled listeners. This support is limited to the v2 SKU of Application Gateway.
Application Gateway offers two models for TLS termination:
- Provide TLS/SSL certificates attached to the listener. This model is the traditional way to pass TLS/SSL certificates to Application Gateway for TLS termination.
- Provide a reference to an existing Key Vault certificate or secret when you create a HTTPS-enabled listener.
Application Gateway integration with Key Vault offers many benefits, including:
- Stronger security, because TLS/SSL certificates aren't directly handled by the application development team. Integration allows a separate security team to:
- Set up application gateways.
- Control application gateway lifecycles.
- Grant permissions to selected application gateways to access certificates that are stored in your Key Vault.
- Support for importing existing certificates into your Key Vault. Or use Key Vault APIs to create and manage new certificates with any of the trusted Key Vault partners.
- Support for automatic renewal of certificates that are stored in your Key Vault.
Supported certificates
Application Gateway currently supports software-validated certificates only. Hardware security module (HSM)-validated certificates aren’t supported.
After Application Gateway is configured to use Key Vault certificates, its instances retrieve the certificate from Key Vault and install them locally for TLS termination. The instances poll Key Vault at four-hour intervals to retrieve a renewed version of the certificate, if it exists. If an updated certificate is found, the TLS/SSL certificate that's associated with the HTTPS listener is automatically rotated.
Tip
Any change to Application Gateway forces a check against Key Vault to see if any new versions of certificates are available. This includes, but not limited to, changes to Frontend IP Configurations, Listeners, Rules, Backend Pools, Resource Tags, and more. If an updated certificate is found, the new certificate is immediately presented.
Application Gateway uses a secret identifier in Key Vault to reference the certificates. For Azure PowerShell, the Azure CLI, or Azure Resource Manager, we strongly recommend that you use a secret identifier that doesn't specify a version. This way, Application Gateway automatically rotates the certificate if a newer version is available in your Key Vault. An example of a secret URI without a version is https://myvault.vault.azure.net/secrets/mysecret/. You may refer to the PowerShell steps provided in the following section.
The Azure portal supports only Key Vault certificates, not secrets. Application Gateway still supports referencing secrets from Key Vault, but only through non-portal resources like PowerShell, the Azure CLI, APIs, and Azure Resource Manager templates (ARM templates). Key Vault certificates must have an exportable private key in order for the Application Gateway to be able to use them.
References to Key Vaults in other Azure subscriptions are supported, but must be configured via ARM Template, Azure PowerShell, CLI, Bicep, etc. Cross-subscription key vault configuration is not supported by Application Gateway via Azure portal today.
Certificate settings in Key Vault
For TLS termination, Application Gateway only supports certificates in Personal Information Exchange (PFX) format. You can either import an existing certificate or create a new one in your Key Vault. To avoid any failures, ensure that the certificate's status is set to Enabled in Key Vault.
How integration works
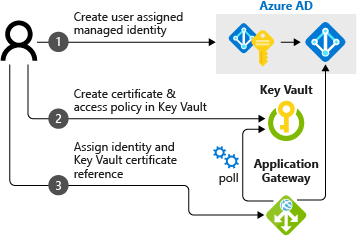
Application Gateway integration with Key Vault is a three-step configuration process:
Note
Azure Application Gateway integration with Key Vault supports both Vault access policy and Azure role-based access control permission models.
Obtain a user-assigned managed identity
Application Gateway uses a managed identity to retrieve certificates from Key Vault on your behalf.
You can either create a new user-assigned managed identity or reuse an existing with the integration. To create a new user-assigned managed identity, see Create a user-assigned managed identity using the Azure portal.
Delegate user-assigned managed identity to Key Vault
Define access policies to use the user-assigned managed identity with your Key Vault:
In the Azure portal, go to Key Vault.
Select the Key Vault that contains your certificate.
If you're using the permission model Vault access policy: Select Access Policies, select + Add Access Policy, select Get for Secret permissions, and choose your user-assigned managed identity for Select principal. Then select Save.
If you're using Azure role-based access control follow the article Assign a managed identity access to a resource and assign the user-assigned managed identity the Key Vault Secrets User role to the Azure Key Vault.
Verify Firewall Permissions to Key Vault
As of March 15, 2021, Key Vault recognizes Application Gateway as a trusted service by leveraging User Managed Identities for authentication to Azure Key Vault. With the use of service endpoints and enabling the trusted services option for Key Vault's firewall, you can build a secure network boundary in Azure. You can deny access to traffic from all networks (including internet traffic) to Key Vault but still make Key Vault accessible for an Application Gateway resource under your subscription.
When you're using a restricted Key Vault, use the following steps to configure Application Gateway to use firewalls and virtual networks:
Tip
Steps 1-3 are not required if your Key Vault has a Private Endpoint enabled. The application gateway can access the Key Vault using the private IP address.
Important
If using Private Endpoints to access Key Vault, you must link the privatelink.vaultcore.azure.net private DNS zone, containing the corresponding record to the referenced Key Vault, to the virtual network containing Application Gateway. Custom DNS servers may continue to be used on the virtual network instead of the Azure DNS provided resolvers, however the private DNS zone needs to remain linked to the virtual network as well.
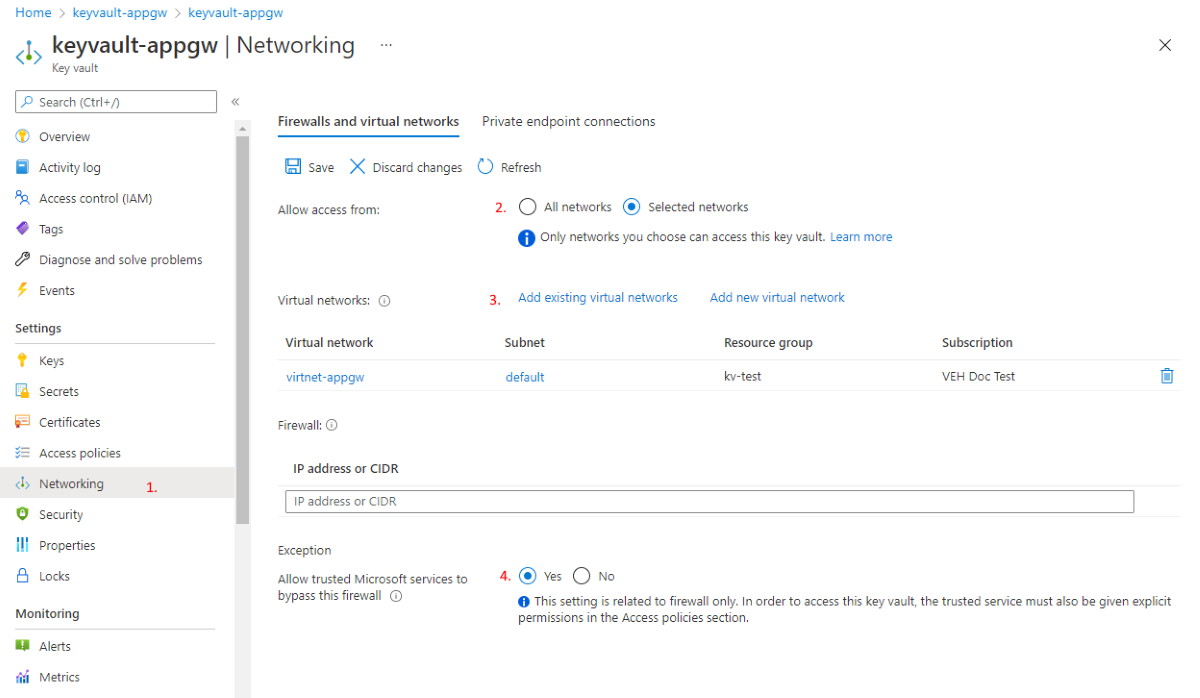
In the Azure portal, in your Key Vault, select Networking.
On the Firewalls and virtual networks tab, select Selected networks.
For Virtual networks, select + Add existing virtual networks, and then add the virtual network and subnet for your Application Gateway instance. If prompted, ensure the Do not configure 'Microsoft.KeyVault' service endpoint(s) at this time checkbox is unchecked to ensure the
Microsoft.KeyVaultservice endpoint is enabled on the subnet.Select Yes to allow trusted services to bypass the Key Vault's firewall.
Note
If you deploy the Application Gateway instance via an ARM template by using either the Azure CLI or PowerShell, or via an Azure application deployed from the Azure portal, the SSL certificate is stored in the Key Vault as a Base64-encoded PFX file. You must complete the steps in Use Azure Key Vault to pass secure parameter value during deployment.
It's particularly important to set enabledForTemplateDeployment to true. The certificate might or might not have a password. For a certificate with a password, the following example shows a possible configuration for the sslCertificates entry in properties for the ARM template configuration for Application Gateway.
"sslCertificates": [
{
"name": "appGwSslCertificate",
"properties": {
"data": "[parameters('appGatewaySSLCertificateData')]",
"password": "[parameters('appGatewaySSLCertificatePassword')]"
}
}
]
The values of appGatewaySSLCertificateData and appGatewaySSLCertificatePassword are looked up from the Key Vault, as described in Reference secrets with dynamic ID. Follow the references backward from parameters('secretName') to see how the lookup happens. If the certificate is passwordless, omit the password entry.
Configure Application Gateway Listener
Key Vault permission Vault access policy model
Navigate to your Application Gateway in the Azure portal and select the Listeners tab. Select Add Listener (or select an existing listener) and specify HTTPS for the protocol.
Under Choose a certificate, select Create new and then select Choose a certificate from Key Vault under Https settings.
For Cert name, type a friendly name for the certificate to be referenced in Key Vault. Choose your Managed identity, Key Vault, and Certificate.
Once selected, select Add (if creating) or Save (if editing) to apply the referenced Key Vault certificate to the listener.
Key Vault Azure role-based access control permission model
Application Gateway supports certificates referenced in Key Vault via the Role-based access control permission model. The first few steps to reference the Key Vault must be completed via ARM template, Bicep, CLI, or PowerShell.
Note
Specifying Azure Key Vault certificates that are subject to the role-based access control permission model is not supported via the portal.
In this example, we’ll use PowerShell to reference a new Key Vault secret.
# Get the Application Gateway we want to modify
$appgw = Get-AzApplicationGateway -Name MyApplicationGateway -ResourceGroupName MyResourceGroup
# Specify the resource id to the user assigned managed identity - This can be found by going to the properties of the managed identity
Set-AzApplicationGatewayIdentity -ApplicationGateway $appgw -UserAssignedIdentityId "/subscriptions/xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx/resourceGroups/MyResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/MyManagedIdentity"
# Get the secret ID from Key Vault
$secret = Get-AzKeyVaultSecret -VaultName "MyKeyVault" -Name "CertificateName"
$secretId = $secret.Id.Replace($secret.Version, "") # Remove the secret version so Application Gateway uses the latest version in future syncs
# Specify the secret ID from Key Vault
Add-AzApplicationGatewaySslCertificate -KeyVaultSecretId $secretId -ApplicationGateway $appgw -Name $secret.Name
# Commit the changes to the Application Gateway
Set-AzApplicationGateway -ApplicationGateway $appgw
Once the commands have been executed, you can navigate to your Application Gateway in the Azure portal and select the Listeners tab. Click Add Listener (or select an existing) and specify the Protocol to HTTPS.
Under Choose a certificate select the certificate named in the previous steps. Once selected, select Add (if creating) or Save (if editing) to apply the referenced Key Vault certificate to the listener.
Investigating and resolving Key Vault errors
Note
It is important to consider any impact on your application gateway resource when making changes or revoking access to your Key Vault resource. If your application gateway is unable to access the associated key vault or locate the certificate object in it, the application gateway automatically sets the listener to a disabled state.
You can identify this user-driven event by viewing the Resource Health for your application gateway. Learn more.
Azure Application Gateway doesn't just poll for the renewed certificate version on Key Vault at every four-hour interval. It also logs any error and is integrated with Azure Advisor to surface any misconfiguration with a recommendation for its fix.
- Sign-in to your Azure portal
- Select Advisor
- Select Operational Excellence category from the left menu.
- You find a recommendation titled Resolve Azure Key Vault issue for your Application Gateway, if your gateway is experiencing this issue. Ensure the correct subscription is selected from the drop-down options above.
- Select it to view the error details, the associated key vault resource and the troubleshooting guide to fix your exact issue.
By identifying such an event through Azure Advisor or Resource Health, you can quickly resolve any configuration problems with your Key Vault. We strongly recommend you take advantage of Azure Advisor and Resource Health alerts to stay informed when a problem is detected.
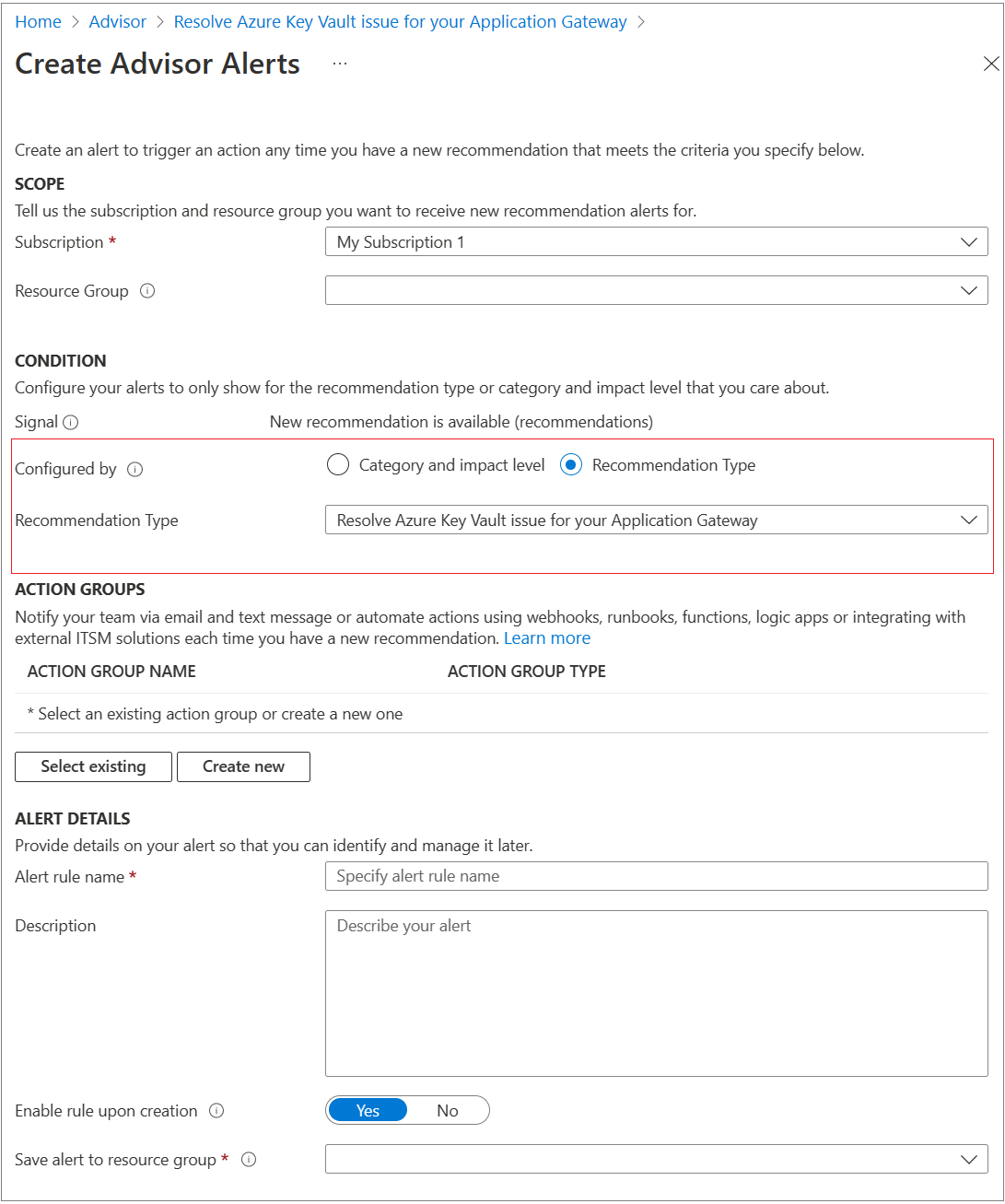
For Advisor alert, use "Resolve Azure Key Vault issue for your Application Gateway" in the recommendation type shown:
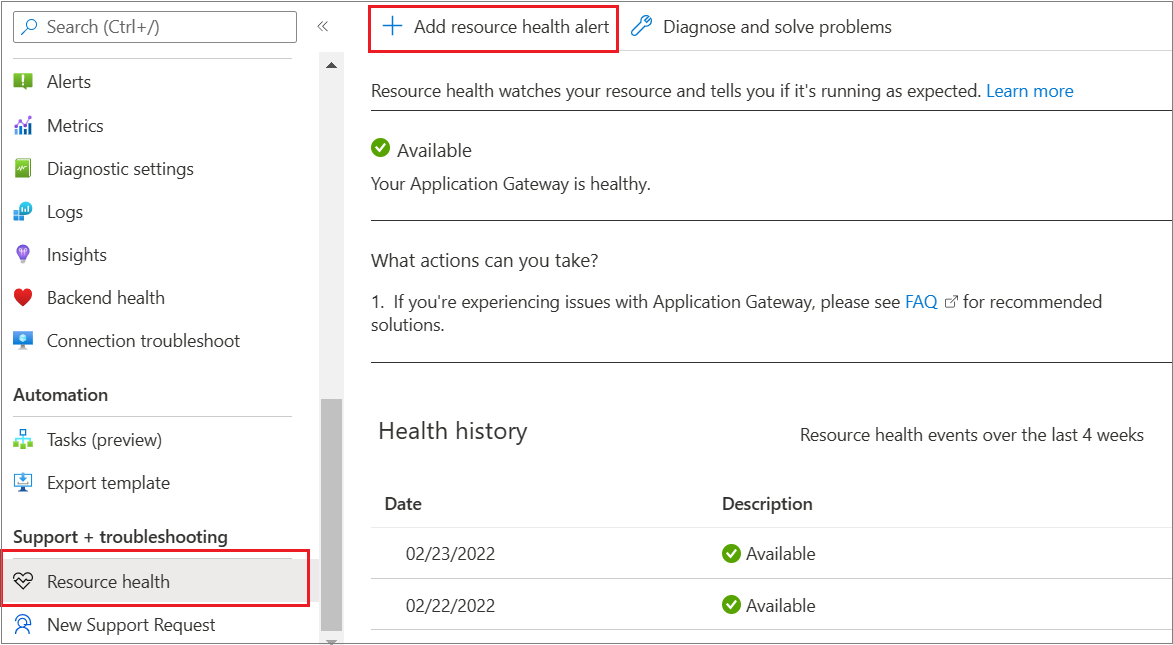
You can configure the Resource health alert as illustrated:
Next steps
Configure TLS termination with Key Vault certificates by using Azure PowerShell