Grounding with Bing Search
Grounding with Bing Search allows your Azure AI Agents to incorporate real-time public web data when generating responses. You need to create a Grounding with Bing Search resource, and then connect this resource to your Azure AI Agents. When a user sends a query, Azure AI Agents decide if Grounding with Bing Search should be leveraged or not. If so, it will leverage Bing to search over public web data and return relevant chunks. Lastly, Azure AI Agents will use returned chunks to generate a response.
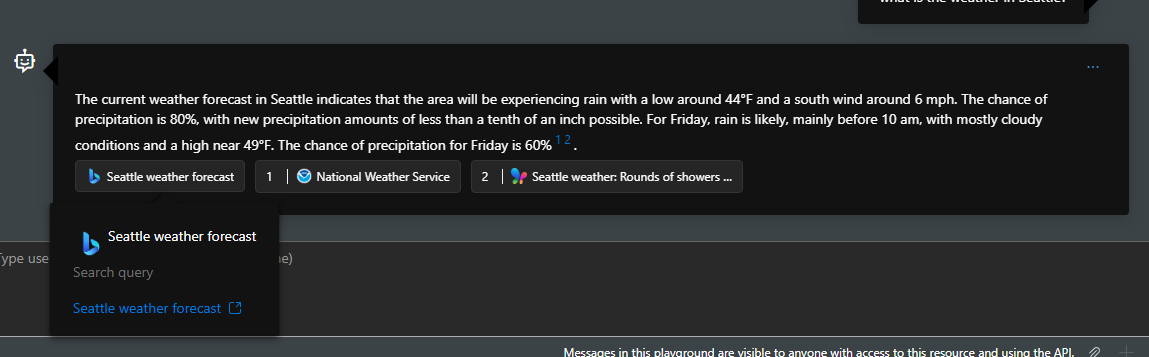
You can ask questions such as "what is the top news today" or "what is the recent update in the retail industry in the US?", which require real-time public data.
Developers and end users don't have access to raw content returned from Grounding with Bing Search. The response, however, includes citations with links to the websites used to generate the response, and a link to the Bing query used for the search. These two References must be retained and displayed in the exact form provided by Microsoft, as per Grounding with Bing Search's Use and Display Requirements. See the how to display Grounding with Bing Search results section for details.
Important
- Your usage of Grounding with Bing Search can incur costs. See the pricing page for details.
- By creating and using a Grounding with Bing Search resource through code-first experience, such as Azure CLI, or deploying through deployment template, you agree to be bound by and comply with the terms available at https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/bing/apis/grounding-legal, which may be updated from time to time.
- When you use Grounding with Bing Search, your customer data is transferred outside of the Azure compliance boundary to the Grounding with Bing Search service. Grounding with Bing Search is not subject to the same data processing terms (including location of processing) and does not have the same compliance standards and certifications as the Azure AI Agent Service, as described in the Grounding with Bing Search Terms of Use. It is your responsibility to assess whether use of Grounding with Bing Search in your agent meets your needs and requirements.
Usage support
| Azure AI foundry support | Python SDK | C# SDK | JavaScript SDK | Basic agent setup | Standard agent setup |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ | ✔️ |
Setup
Note
- Grounding with Bing Search only works with the following Azure OpenAI models:
gpt-3.5-turbo-0125,gpt-4-0125-preview,gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09,gpt-4o-0513
Create an Azure AI Agent by following the steps in the quickstart.
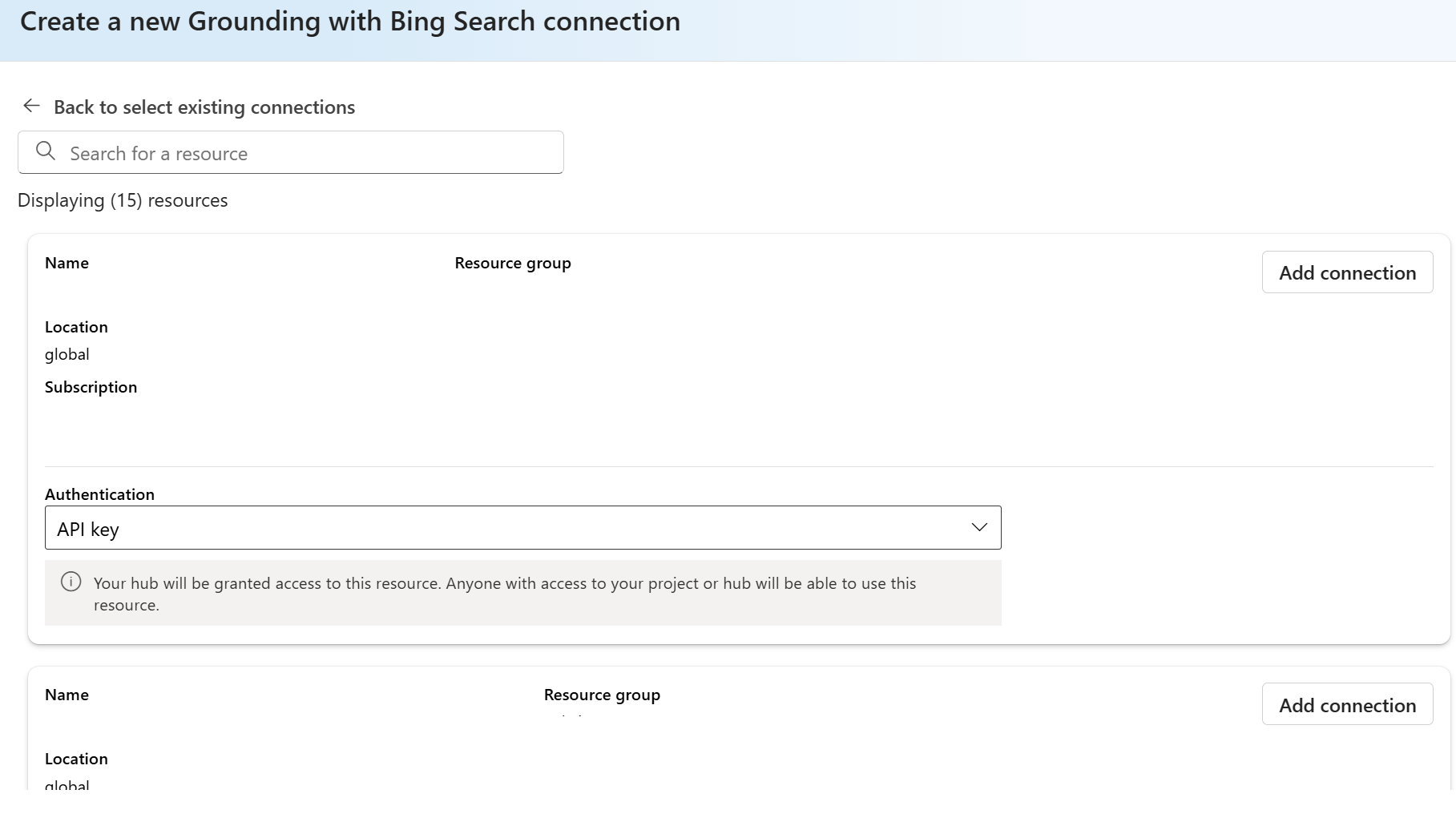
Create a Grounding with Bing Search resource. You need to have
ownerorcontributorrole in your subscription or resource group to create it.You can create one in the Azure portal, and select the different fields in the creation form. Make sure you create this Grounding with Bing Search resource in the same resource group as your Azure AI Agent, AI Project, and other resources.
You can also create one through code-first experience. If so, you need to manually register Bing Search as an Azure resource provider. You must have permission to perform the
/register/actionoperation for the resource provider. The permission is included in the Contributor and Owner roles.
az provider register --namespace 'Microsoft.Bing'After you have created a Grounding with Bing Search resource, you can find it in Azure portal. Navigate to the resource group you've created the resource in, search for the Grounding with Bing Search resource you have created.
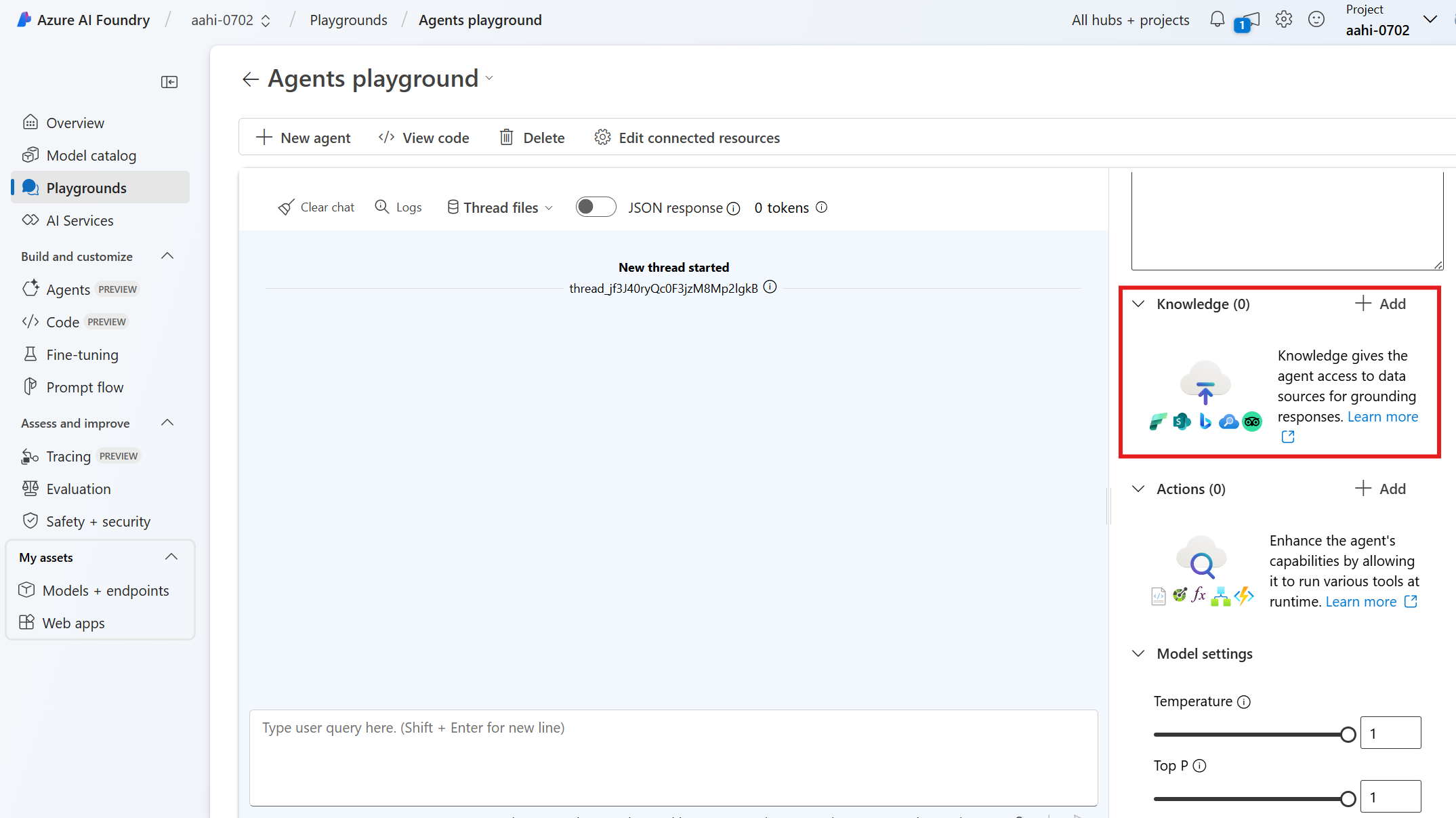
You can add the Grounding with Bing Search tool to an agent programatically using the code examples listed at the top of this article, or the Azure AI Foundry portal. If you want to use the portal, in the Create and debug screen for your agent, scroll down the Setup pane on the right to knowledge. Then select Add.
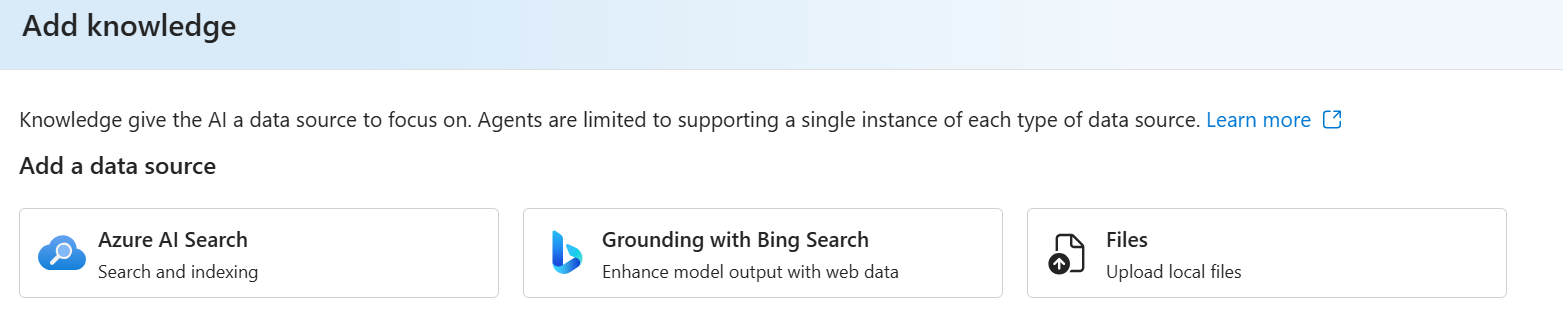
Select Grounding with Bing Search and follow the prompts to add the tool. Note you can add only one per agent.
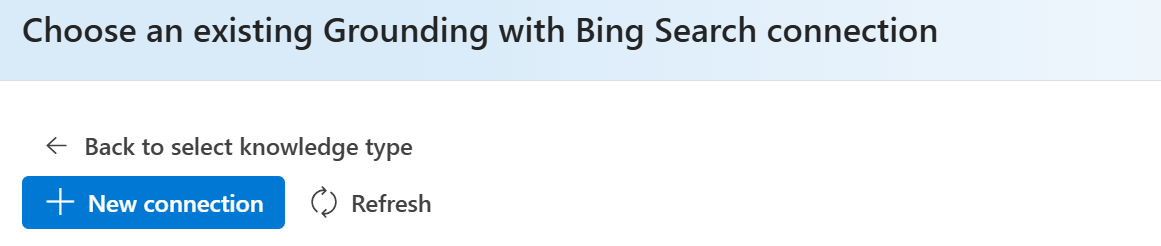
Click to add new connections. Once you have added a connection, you can directly select from existing list.
Select the Grounding with Bing Search resource you want to use and click to add connection.
How to display Grounding with Bing Search results
According to Grounding with Bing's terms of use and use and display requirements, you need to display both website URLs and Bing search query URLs in your custom interface. You can find website URLs through annotations parameter in API response and Bing search query URLs through runstep details. To render the webpage, we recommend you replace the endpoint of Bing search query URLs with www.bing.com and your Bing search query URL would look like "https://www.bing.com/search?q={search query}"
run_steps = project_client.agents.list_run_steps(run_id=run.id, thread_id=thread.id)
run_steps_data = run_steps['data']
print(f"Last run step detail: {run_steps_data}")
Other legal considerations
Microsoft will use data you send to Grounding with Bing to improve Microsoft products and services. Where you send personal data to this service, you are responsible for obtaining sufficient consent from the data subjects. The Data Protection Terms in the Online Services Terms do not apply to Grounding with Bing.
Your use of Grounding with Bing Search will be governed by the Terms of Use. By using Grounding with Bing Search, you agree to be bound by and comply with these Terms of Use.
Step 1: Create an agent with Grounding with Bing Search
Create a client object, which will contain the connection string for connecting to your AI project and other resources.
import os
from azure.ai.projects import AIProjectClient
from azure.identity import DefaultAzureCredential
from azure.ai.projects.models import BingGroundingTool
# Create an Azure AI Client from a connection string, copied from your Azure AI Foundry project.
# At the moment, it should be in the format "<HostName>;<AzureSubscriptionId>;<ResourceGroup>;<HubName>"
# Customer needs to login to Azure subscription via Azure CLI and set the environment variables
project_client = AIProjectClient.from_connection_string(
credential=DefaultAzureCredential(),
conn_str=os.environ["PROJECT_CONNECTION_STRING"],
)
Step 2: Enable the Grounding with Bing search tool
To make the Grounding with Bing search tool available to your agent, use a connection to initialize the tool and attach it to the agent. You can find your connection in the connected resources section of your project in the Azure AI Foundry portal.
bing_connection = project_client.connections.get(
connection_name=os.environ["BING_CONNECTION_NAME"]
)
conn_id = bing_connection.id
print(conn_id)
# Initialize agent bing tool and add the connection id
bing = BingGroundingTool(connection_id=conn_id)
# Create agent with the bing tool and process assistant run
with project_client:
agent = project_client.agents.create_agent(
model="gpt-4o",
name="my-assistant",
instructions="You are a helpful assistant",
tools=bing.definitions,
headers={"x-ms-enable-preview": "true"}
)
print(f"Created agent, ID: {agent.id}")
Step 3: Create a thread
# Create thread for communication
thread = project_client.agents.create_thread()
print(f"Created thread, ID: {thread.id}")
# Create message to thread
message = project_client.agents.create_message(
thread_id=thread.id,
role="user",
content="What is the top news today",
)
print(f"Created message, ID: {message.id}")
Step 4: Create a run and check the output
Create a run and observe that the model uses the Grounding with Bing Search tool to provide a response to the user's question.
# Create and process agent run in thread with tools
run = project_client.agents.create_and_process_run(thread_id=thread.id, assistant_id=agent.id)
print(f"Run finished with status: {run.status}")
# Retrieve run step details to get Bing Search query link
# To render the webpage, we recommend you replace the endpoint of Bing search query URLs with `www.bing.com` and your Bing search query URL would look like "https://www.bing.com/search?q={search query}"
run_steps = project_client.agents.list_run_steps(run_id=run.id, thread_id=thread.id)
run_steps_data = run_steps['data']
print(f"Last run step detail: {run_steps_data}")
if run.status == "failed":
print(f"Run failed: {run.last_error}")
# Delete the assistant when done
project_client.agents.delete_agent(agent.id)
print("Deleted agent")
# Fetch and log all messages
messages = project_client.agents.list_messages(thread_id=thread.id)
print(f"Messages: {messages}")