Recover from catastrophic data loss
Azure Stack Hub runs Azure services in your datacenter and can run on environments as small as four nodes installed in a single rack. In contrast, Azure runs in more than 40 regions in multiple datacenters and multiple zones in each region. User resources can span multiple servers, racks, datacenters, and regions. With Azure Stack Hub, you currently only have the choice to deploy your entire cloud to a single rack. This limitation exposes your cloud to the risk of catastrophic events at your datacenter or failures due to major product bugs. When a disaster strikes, the Azure Stack Hub instance goes offline. All of the data is potentially unrecoverable.
Depending on the root cause of the data loss, you may need to repair a single infrastructure service or restore the entire Azure Stack Hub instance. You may even need to restore to different hardware in the same location or in a different location.
This scenario addresses recovering your entire installation if there's a failure and the redeployment of the private cloud.
| Scenario | Data Loss | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Recover from catastrophic data loss due to disaster or product bug. | All infrastructure and user and app data. | Can restore to different OEM. Can restore to different generation of hardware. Can restore to different count of scale-unit nodes. User app and data are protected separately from infrastructure data. |
Workflows
The journey of protecting Azure Stack Hub starts with backing up the infrastructure and app/tenant data separately. This document covers how to protect the infrastructure.
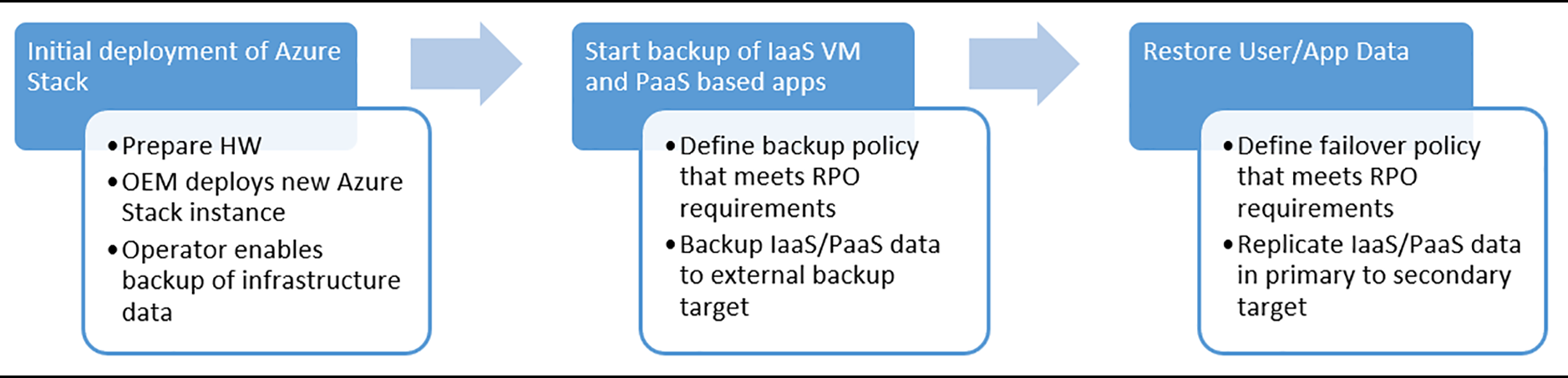
In worst case scenarios where all data is lost, recovering Azure Stack Hub is the process of restoring the infrastructure data unique to that deployment of Azure Stack Hub and all user data.
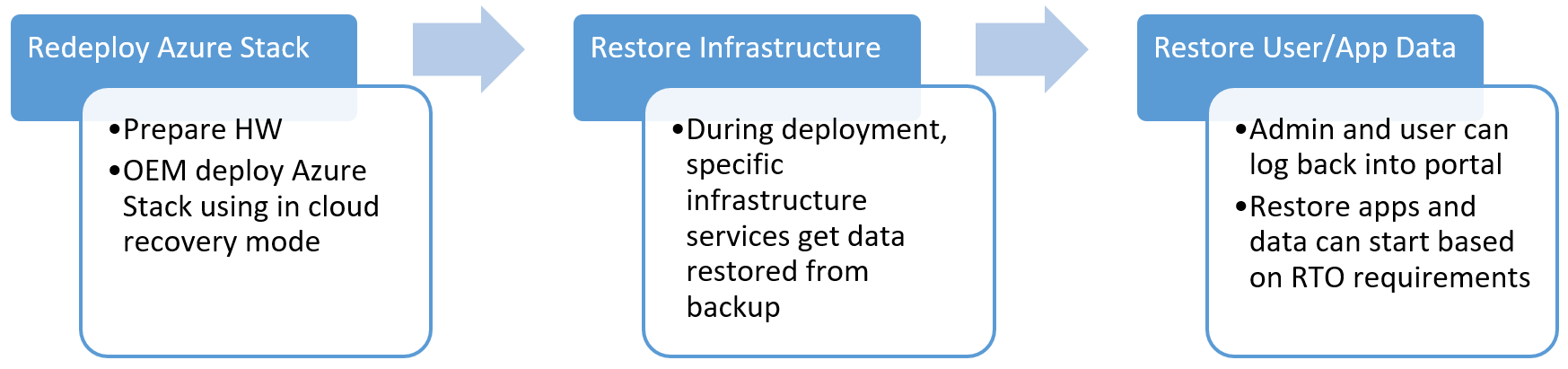
Restore
If there's catastrophic data loss but the hardware is still usable, redeployment of Azure Stack Hub is required. During redeployment, you can specify the storage location and credentials required to access backups. In this mode, there's no need to specify the services that need to be restored. Infrastructure Backup Controller injects control plane state as part of the deployment workflow.
If there's a disaster that renders the hardware unusable, redeployment is only possible on new hardware. Redeployment can take several weeks while replacement hardware is ordered and arrives in the datacenter. Restore of control plane data is possible at any time. However, restore isn't supported if the version of the redeployed instance is more than one version greater than the version used in the last backup.
| Deployment mode | Starting point | End point |
|---|---|---|
| Clean install | Baseline build | OEM deploys Azure Stack Hub and updates to the latest supported version. |
| Recovery mode | Baseline build | OEM deploys Azure Stack Hub in recovery mode and handles the version matching requirements based on the latest backup available. The OEM completes the deployment by updating to latest supported version. |
Data in backups
Azure Stack Hub supports a type of deployment called cloud recovery mode. This mode is used only if you choose to recover Azure Stack Hub after a disaster or product bug rendered the solution unrecoverable. This deployment mode doesn't recover any of the user data stored in the solution. The scope of this deployment mode is limited to restoring the following data:
- Deployment inputs
- Internal identity service data
- Federated identify configuration (ADFS deployments).
- Root certificates used by internal certificate authority.
- Azure Resource Manager configuration user data, such as subscriptions, plans, offers, resource groups, tags, storage quotas, network quotas, and compute resources.
- Key Vault secrets and vaults.
- RBAC policy assignments and role assignments.
None of the user Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or Platform as a Service (PaaS) resources are recovered during deployment. These losses include IaaS VMs, storage accounts, blobs, tables, network configuration, and so on. The purpose of cloud recovery is to ensure your operators and users can sign back in to the portal after deployment is complete. Users signing back in won't see any of their resources. Users have their subscriptions restored and along with that the original plans, offers, and policies defined by the admin. Users signing back in to the system operate under the same constraints imposed by the original solution before the disaster. After cloud recovery completes, the operator can manually restore value-add and third-party RPs and associated data.
Validate backups
You can use ASDK to test a backup to confirm that the data is valid and usable. For more information, see Use the ASDK to validate an Azure Stack backup.
Next steps
Learn about the best practices for using the Infrastructure Backup Service.