Use MirrorMaker to replicate Apache Kafka topics with Kafka on HDInsight
Learn how to use Apache Kafka's mirroring feature to replicate topics to a secondary cluster. You can run mirroring as a continuous process, or intermittently, to migrate data from one cluster to another.
In this article, you'll use mirroring to replicate topics between two HDInsight clusters. These clusters are in different virtual networks in different datacenters.
Warning
Don't use mirroring as a means to achieve fault-tolerance. The offset to items within a topic are different between the primary and secondary clusters, so clients can't use the two interchangeably. If you are concerned about fault tolerance, you should set replication for the topics within your cluster. For more information, see Get started with Apache Kafka on HDInsight.
How Apache Kafka mirroring works
Mirroring works by using the MirrorMaker tool, which is part of Apache Kafka. MirrorMaker consumes records from topics on the primary cluster, and then creates a local copy on the secondary cluster. MirrorMaker uses one (or more) consumers that read from the primary cluster, and a producer that writes to the local (secondary) cluster.
The most useful mirroring setup for disaster recovery uses Kafka clusters in different Azure regions. To achieve this, the virtual networks where the clusters reside are peered together.
The following diagram illustrates the mirroring process and how the communication flows between clusters:
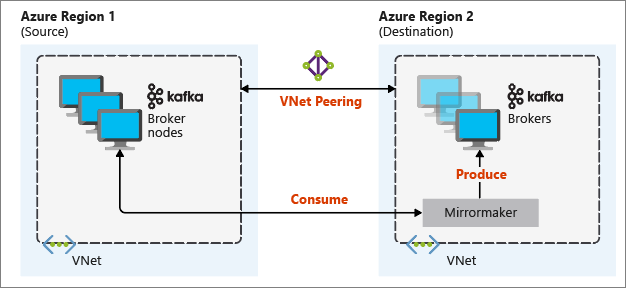
The primary and secondary clusters can be different in the number of nodes and partitions, and offsets within the topics are different also. Mirroring maintains the key value that is used for partitioning, so record order is preserved on a per-key basis.
Mirroring across network boundaries
If you need to mirror between Kafka clusters in different networks, there are the following additional considerations:
Gateways: The networks must be able to communicate at the TCP/IP level.
Server addressing: You can choose to address your cluster nodes by using their IP addresses or fully qualified domain names.
IP addresses: If you configure your Kafka clusters to use IP address advertising, you can proceed with the mirroring setup by using the IP addresses of the broker nodes and ZooKeeper nodes.
Domain names: If you don't configure your Kafka clusters for IP address advertising, the clusters must be able to connect to each other by using fully qualified domain names (FQDNs). This requires a domain name system (DNS) server in each network that is configured to forward requests to the other networks. When you're creating an Azure virtual network, instead of using the automatic DNS provided with the network, you must specify a custom DNS server and the IP address for the server. After you create the virtual network, you must then create an Azure virtual machine that uses that IP address. Then you install and configure DNS software on it.
Important
Create and configure the custom DNS server before installing HDInsight into the virtual network. There is no additional configuration required for HDInsight to use the DNS server configured for the virtual network.
For more information on connecting two Azure virtual networks, see Configure a connection.
Mirroring architecture
This architecture features two clusters in different resource groups and virtual networks: a primary and a secondary.
Creation steps
Create two new resource groups:
Resource group Location kafka-primary-rg Central US kafka-secondary-rg North Central US Create a new virtual network kafka-primary-vnet in kafka-primary-rg. Leave the default settings.
Create a new virtual network kafka-secondary-vnet in kafka-secondary-rg, also with default settings.
Create two new Kafka clusters:
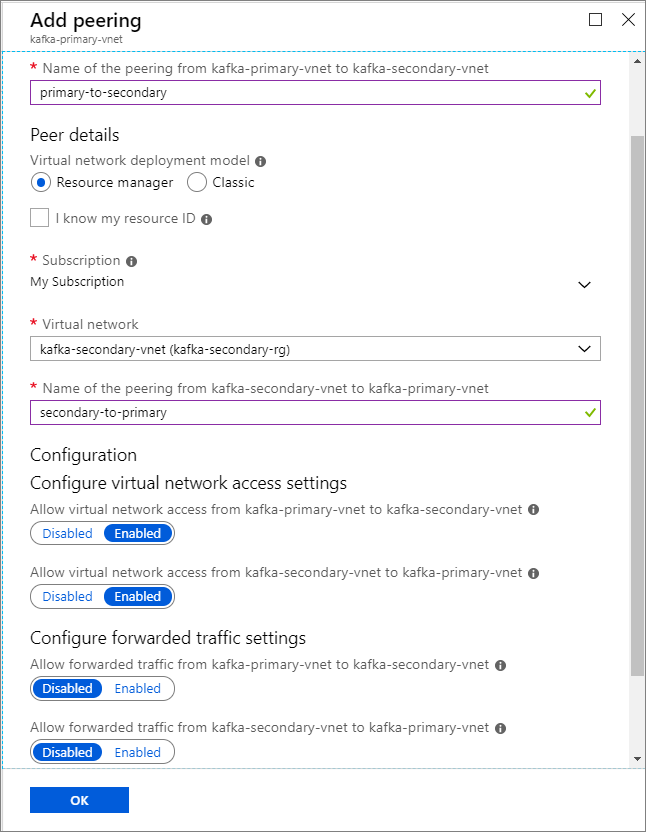
Cluster name Resource group Virtual network Storage account kafka-primary-cluster kafka-primary-rg kafka-primary-vnet kafkaprimarystorage kafka-secondary-cluster kafka-secondary-rg kafka-secondary-vnet kafkasecondarystorage Create virtual network peerings. This step will create two peerings: one from kafka-primary-vnet to kafka-secondary-vnet, and one back from kafka-secondary-vnet to kafka-primary-vnet.
Select the kafka-primary-vnet virtual network.
Under Settings, select Peerings.
Select Add.
On the Add peering screen, enter the details as shown in the following screenshot.
Configure IP advertising
Configure IP advertising to enable a client to connect by using broker IP addresses, instead of domain names.
Go to the Ambari dashboard for the primary cluster:
https://PRIMARYCLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net.Select Services > Kafka. Select the Configs tab.
Add the following config lines to the bottom kafka-env template section. Select Save.
# Configure Kafka to advertise IP addresses instead of FQDN IP_ADDRESS=$(hostname -i) echo advertised.listeners=$IP_ADDRESS sed -i.bak -e '/advertised/{/advertised@/!d;}' /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/conf/server.properties echo "advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://$IP_ADDRESS:9092" >> /usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/conf/server.propertiesEnter a note on the Save Configuration screen, and select Save.
If you get a configuration warning, select Proceed Anyway.
On Save Configuration Changes, select Ok.
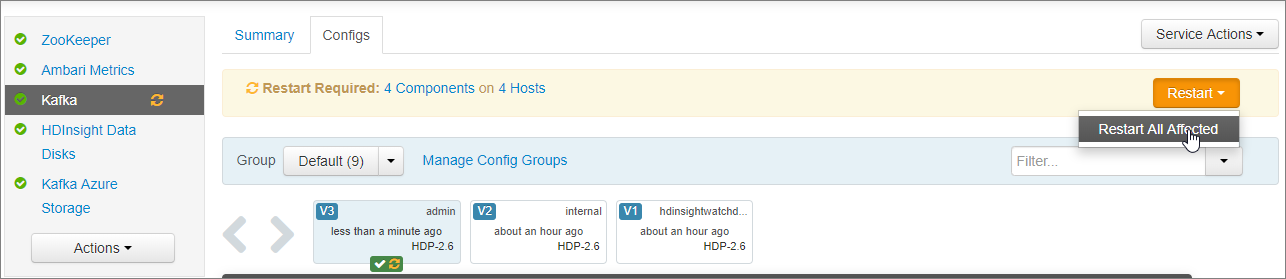
In the Restart Required notification, select Restart > Restart All Affected. Then select Confirm Restart All.
Configure Kafka to listen on all network interfaces
- Stay on the Configs tab under Services > Kafka. In the Kafka Broker section, set the listeners property to
PLAINTEXT://0.0.0.0:9092. - Select Save.
- Select Restart > Confirm Restart All.
Record broker IP addresses and ZooKeeper addresses for the primary cluster
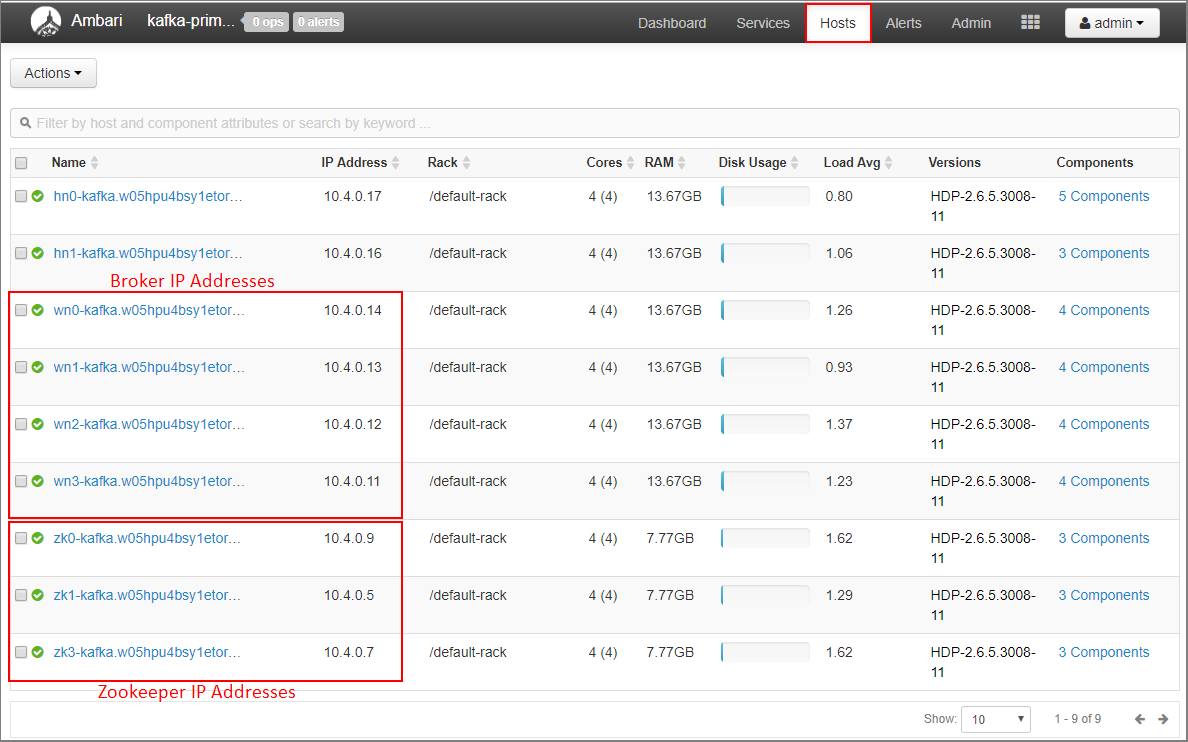
Select Hosts on the Ambari dashboard.
Make a note of the IP addresses for the brokers and ZooKeepers. The broker nodes have wn as the first two letters of the host name, and the ZooKeeper nodes have zk as the first two letters of the host name.
Repeat the previous three steps for the second cluster, kafka-secondary-cluster: configure IP advertising, set listeners, and make a note of the broker and ZooKeeper IP addresses.
Create topics
Connect to the primary cluster by using SSH:
ssh sshuser@PRIMARYCLUSTER-ssh.azurehdinsight.netReplace
sshuserwith the SSH user name that you used when creating the cluster. ReplacePRIMARYCLUSTERwith the base name that you used when creating the cluster.For more information, see Use SSH with HDInsight.
Use the following command to create two environment variables with the Apache ZooKeeper hosts and broker hosts for the primary cluster. Replace strings like
ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS1with the actual IP addresses recorded earlier, such as10.23.0.11and10.23.0.7. The same goes forBROKER_IP_ADDRESS1. If you're using FQDN resolution with a custom DNS server, follow these steps to get broker and ZooKeeper names.# get the ZooKeeper hosts for the primary cluster export PRIMARY_ZKHOSTS='ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS1:2181, ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS2:2181, ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS3:2181' # get the broker hosts for the primary cluster export PRIMARY_BROKERHOSTS='BROKER_IP_ADDRESS1:9092,BROKER_IP_ADDRESS2:9092,BROKER_IP_ADDRESS2:9092'To create a topic named
testtopic, use the following command:/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --replication-factor 2 --partitions 8 --topic testtopic --zookeeper $PRIMARY_ZKHOSTSUse the following command to verify that the topic was created:
/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper $PRIMARY_ZKHOSTSThe response contains
testtopic.Use the following to view the broker host information for this (the primary) cluster:
echo $PRIMARY_BROKERHOSTSThis returns information similar to the following text:
10.23.0.11:9092,10.23.0.7:9092,10.23.0.9:9092Save this information. It's used in the next section.
Configure mirroring
Connect to the secondary cluster by using a different SSH session:
ssh sshuser@SECONDARYCLUSTER-ssh.azurehdinsight.netReplace
sshuserwith the SSH user name that you used when creating the cluster. ReplaceSECONDARYCLUSTERwith the name that you used when creating the cluster.For more information, see Use SSH with HDInsight.
Use a
consumer.propertiesfile to configure communication with the primary cluster. To create the file, use the following command:nano consumer.propertiesUse the following text as the contents of the
consumer.propertiesfile:bootstrap.servers=PRIMARY_BROKERHOSTS group.id=mirrorgroupReplace
PRIMARY_BROKERHOSTSwith the broker host IP addresses from the primary cluster.This file describes the consumer information to use when reading from the primary Kafka cluster. For more information, see Consumer Configs at
kafka.apache.org.To save the file, press Ctrl+X, press Y, and then press Enter.
Before configuring the producer that communicates with the secondary cluster, set up a variable for the broker IP addresses of the secondary cluster. Use the following commands to create this variable:
export SECONDARY_BROKERHOSTS='BROKER_IP_ADDRESS1:9092,BROKER_IP_ADDRESS2:9092,BROKER_IP_ADDRESS2:9092'The command
echo $SECONDARY_BROKERHOSTSshould return information similar to the following text:10.23.0.14:9092,10.23.0.4:9092,10.23.0.12:9092Use a
producer.propertiesfile to communicate the secondary cluster. To create the file, use the following command:nano producer.propertiesUse the following text as the contents of the
producer.propertiesfile:bootstrap.servers=SECONDARY_BROKERHOSTS compression.type=noneReplace
SECONDARY_BROKERHOSTSwith the broker IP addresses used in the previous step.For more information, see Producer Configs at
kafka.apache.org.Use the following commands to create an environment variable with the IP addresses of the ZooKeeper hosts for the secondary cluster:
# get the ZooKeeper hosts for the secondary cluster export SECONDARY_ZKHOSTS='ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS1:2181,ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS2:2181,ZOOKEEPER_IP_ADDRESS3:2181'The default configuration for Kafka on HDInsight doesn't allow the automatic creation of topics. You must use one of the following options before starting the mirroring process:
Create the topics on the secondary cluster: This option also allows you to set the number of partitions and the replication factor.
You can create topics ahead of time by using the following command:
/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --replication-factor 2 --partitions 8 --topic testtopic --zookeeper $SECONDARY_ZKHOSTSReplace
testtopicwith the name of the topic to create.Configure the cluster for automatic topic creation: This option allows MirrorMaker to automatically create topics. Note that it might create them with a different number of partitions or a different replication factor than the primary topic.
To configure the secondary cluster to automatically create topics, perform these steps:
- Go to the Ambari dashboard for the secondary cluster:
https://SECONDARYCLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net. - Select Services > Kafka. Then select the Configs tab.
- In the Filter field, enter a value of
auto.create. This filters the list of properties and displays theauto.create.topics.enablesetting. - Change the value of
auto.create.topics.enabletotrue, and then select Save. Add a note, and then select Save again. - Select the Kafka service, select Restart, and then select Restart all affected. When prompted, select Confirm restart all.
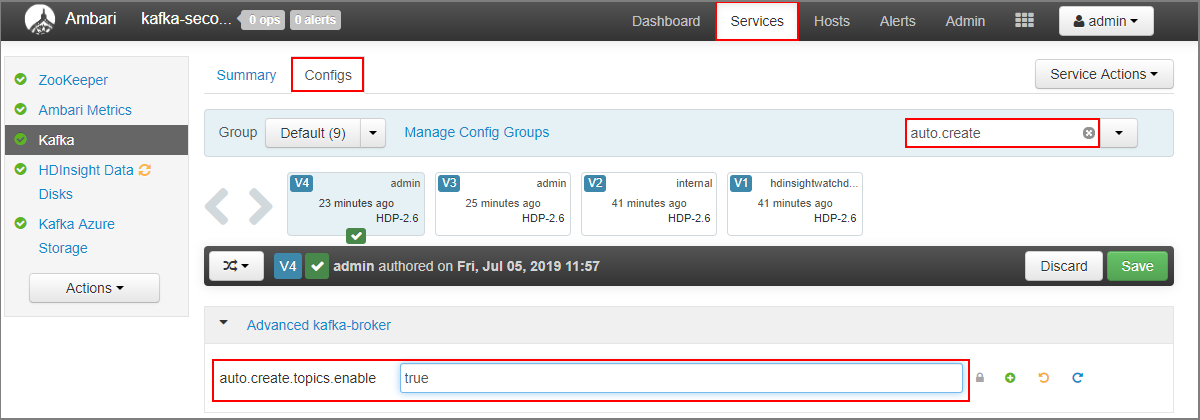
- Go to the Ambari dashboard for the secondary cluster:
Start MirrorMaker
Note
This article contains references to a term that Microsoft no longer uses. When the term is removed from the software, we'll remove it from this article.
From the SSH connection to the secondary cluster, use the following command to start the MirrorMaker process:
/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.MirrorMaker --consumer.config consumer.properties --producer.config producer.properties --whitelist testtopic --num.streams 4The parameters used in this example are:
Parameter Description --consumer.configSpecifies the file that contains consumer properties. You use these properties to create a consumer that reads from the primary Kafka cluster. --producer.configSpecifies the file that contains producer properties. You use these properties to create a producer that writes to the secondary Kafka cluster. --whitelistA list of topics that MirrorMaker replicates from the primary cluster to the secondary. --num.streamsThe number of consumer threads to create. The consumer on the secondary node is now waiting to receive messages.
From the SSH connection to the primary cluster, use the following command to start a producer and send messages to the topic:
/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list $PRIMARY_BROKERHOSTS --topic testtopicWhen you arrive at a blank line with a cursor, type in a few text messages. The messages are sent to the topic on the primary cluster. When done, press Ctrl+C to end the producer process.
From the SSH connection to the secondary cluster, press Ctrl+C to end the MirrorMaker process. It might take several seconds to end the process. To verify that the messages were replicated to the secondary, use the following command:
/usr/hdp/current/kafka-broker/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server $SECONDARY_BROKERHOSTS --topic testtopic --from-beginningThe list of topics now includes
testtopic, which is created when MirrorMaster mirrors the topic from the primary cluster to the secondary. The messages retrieved from the topic are the same as the ones you entered on the primary cluster.
Delete the cluster
Warning
Billing for HDInsight clusters is prorated per minute, whether you use them or not. Be sure to delete your cluster after you finish using it. See how to delete an HDInsight cluster.
The steps in this article created clusters in different Azure resource groups. To delete all of the resources created, you can delete the two resource groups created: kafka-primary-rg and kafka-secondary-rg. Deleting the resource groups removes all of the resources created by following this article, including clusters, virtual networks, and storage accounts.
Next steps
In this article, you learned how to use MirrorMaker to create a replica of an Apache Kafka cluster. Use the following links to discover other ways to work with Kafka: