Agile process work item types for workflow management in Azure Boards
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019 | TFS 2018 - TFS 2013
Teams use the work item types (WITs) provided with the Agile process. Work item types help your team to plan and track progress of software projects. You define user stories to manage the backlog of work. Then, using the Kanban board, you track progress by updating the status of those stories.
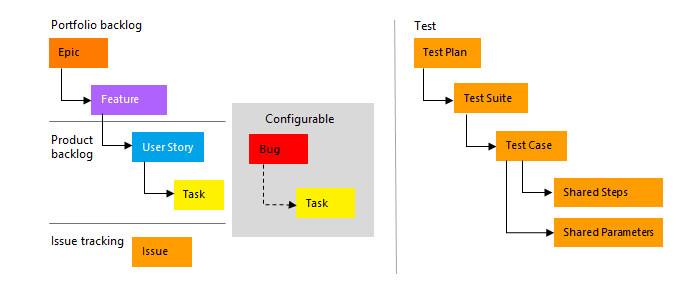
To gain insight into a portfolio of features, scenarios, or user experiences, product owners and program managers map user stories to features. When a team works in sprints, they define tasks that automatically link to user stories. If you are new to the Agile process, review the section Plan and track work with Agile to get started.
Using the web portal or Microsoft Test Manager, testers can create and run test cases. Bugs and issues are used to track code defects and blocking issues.
Note
Work item tracking forms and features available to you differ depending on whether you open the form from the web portal or Visual Studio Team Explorer. Forms and guidance provided in this article reflect those available with the new form experience (Azure DevOps Services and TFS 2017 and later versions).
For guidance on the work item form for TFS 2015 or earlier versions or Visual Studio Team Explorer, see Add work items and select the earlier TFS version from the content version selector (above the table of contents).
Define user stories
User stories define the applications, requirements, and elements that teams need to create. Product owners typically define and stack rank user stories. The team then estimates the effort and work to deliver the highest priority items.
Create user stories from the quick add panel on the product backlog page. From that page, you can also drag-and-drop items to reorder them or map them to features.
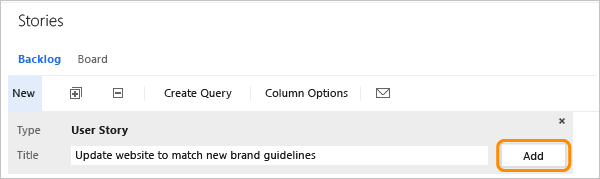
Later, you can open each user story to provide more details and estimate the story points.

By defining the Story Points, your team can use the forecast feature and velocity charts to estimate future sprints or work efforts. By prioritizing the user stories on the backlog page (that's captured in the Stack Rank field), product owners can indicate which items should be given higher priority.
Use the following guidance and that provided for fields used in common across work item types when filling out the form.
Field/tab
Usage
For user stories, provide enough detail for estimating how much work will be required to implement the story. Focus on who the feature is for, what users want to accomplish, and why. Don't describe how the feature should be developed. Do provide sufficient details so that your team can write tasks and test cases to implement the item.
Provide the criteria to be met before the bug or user story can be closed. Before work begins, describe the customer acceptance criteria as clearly as possible. Conversations between the team and customers to define the acceptance criteria will help ensure that your team understands your customers' expectations. You can use the acceptance criteria as the basis for acceptance tests to more effectively evaluate whether an item is satisfactorily completed.
The area of customer value addressed by the epic, feature, requirement, or backlog item. Values include:
Architectural: Technical services to implement business features that deliver solution
Business: Services that fulfill customers or stakeholder needs that directly deliver customer value to support the business (Default)
Estimate the amount of work required to complete a user story using any numeric unit of measurement your team prefers.
Agile velocity charts and forecast tools reference the values in this field. For more information, see the Estimating white paper.
A subjective rating of the user story, feature, or requirement as it relates to the business. Allowed values are:
- 1: Product can't ship without the feature.
- 2: Product can't ship without the feature, but it doesn't have to be addressed immediately.
- 3: Implementation of the feature is optional based on resources, time, and risk.
A subjective rating of the relative uncertainty around the successful completion of a user story. Allowed values are:
- 1 - High
- 2 - Medium
- 3 - Low
Capture comments in the Discussion section
Use the Discussion section to add and review comments made about the work being performed.
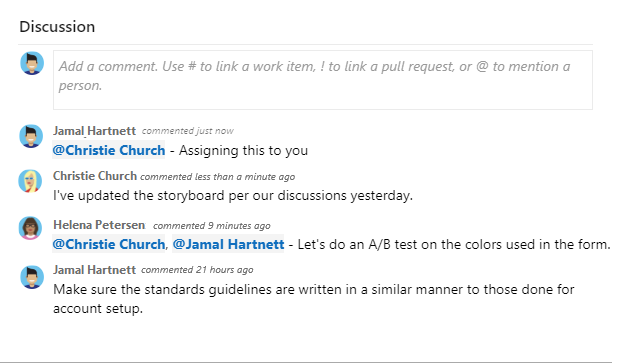
Use the @mention control to notify another team member about the discussion. Simply type @ and their name. To reference a work item, use the #ID control. Type # and a list of work items that you've recently referenced will appear from which you can select.
To reference a work item, use the #ID control. Type # and a list of work items that you've recently referenced will appear from which you can select.
You can't edit or delete comments once you've entered them.
Important
For on-premises Azure DevOps Server, you must configure an SMTP server in order for team members to receive notifications.
Track progress
As work progresses, you change the State field to update the status. Optionally, you can specify a reason. The state and reason fields appear on the work item form in the header area.

Agile workflow states
By updating the workflow, teams know which items are new, in progress, or completed. Most WITs support transition both forward and backward from each workflow state. These diagrams show the main progression and regression states of the user story, bug, and task WITs.
| User Story | Bug | Task |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
A typical workflow progression for a user story follows:
- The product owner creates a user story in the New state with the default reason, New user story
- The team updates the status to Active when they decide to complete the work during the sprint
- A user story is moved to Resolved when the team has completed all its associated tasks and unit tests for the story pass
- A user story is moved to the Closed state when the product owner agrees that the story has been implemented according to the Acceptance Criteria and acceptance tests pass.
Update status with Kanban or taskboards
Teams can use the Kanban board to update the status of requirements, and the sprint taskboard to update the status of tasks. Dragging items to a new state column updates both the State and Reason fields.

You can customize the Kanban board to support more swim lanes or columns. For more customization options, see Customize your work tracking experience.
Map user stories to features
When you manage a suite of products or user experiences, you might want to view the scope and progress of work across the product portfolio. You can view the scope and progress of work by defining features and mapping user stories to features.
Using portfolio backlogs, you can drill down from one backlog to another to view the level of detail you want. Also, use portfolio backlogs to view a rollup of work in progress across several teams when you setup a hierarchy of teams.
Define tasks
When your team manages their work in sprints, they can use the sprint backlog page to break down the work to be accomplished into distinct tasks.
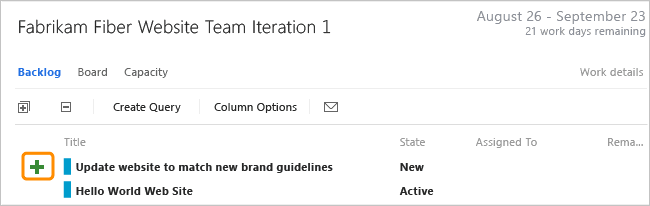
Name the task and estimate the work it will take.

Using Agile processes, teams forecast work and define tasks at the start of each sprint. Each team member then performs a subset of those tasks. Tasks can include development, testing, and other kinds of work. For example, a developer defines tasks to implement user stories, and a tester defines tasks to write and run test cases.
When teams estimate work using hours or days, they define tasks and the Remaining Work and Activity (optional) fields.
Field/tab
Usage
The amount of estimated work required to complete a task. Typically, this field doesn't change after it's assigned.
You can specify work in hours or in days. There are no inherent time units associated with this field.
The amount of work remaining to complete a task. As work progresses, update this field. It's used to calculate capacity charts, the sprint burndown chart, and the following (TFS only) reports: Burndown and Burn Rate, Remaining Work, and Status on All Iterations.
If you divide a task into subtasks, specify hours for the subtasks only. You can specify work in any unit of measurement your team chooses.
The amount of work spent implementing a task.
Select the type of activity this task represents when your team estimates sprint capacity by activity.
Product build number that incorporates the code or fixes a bug.
If you use Microsoft Project to assign resources and track a schedule.
Track test progress
Test user stories
From the web portal or Test Manager, you can create test cases that automatically link to a user story or bug. Or, you can link a user story to a test case from the ![]() (links tab).
(links tab).
The test case contains multiple fields, many of which are automated and integrated with Test Manager and the build process. For a description of each field, see Query based on build and test integration fields.

The ![]() (links tab) captures the links to user stories and bugs in a test case. By linking user stories and bugs to test cases, the team can track the progress made in testing each item. By defining these links, you support information that appears in the Stories Overview Report report.
(links tab) captures the links to user stories and bugs in a test case. By linking user stories and bugs to test cases, the team can track the progress made in testing each item. By defining these links, you support information that appears in the Stories Overview Report report.
Track code defects
You can create bugs from the web portal, Visual Studio, or when testing with Test Manager.
Definitions for common work tracking fields
The following fields and tabs appear in most work items. Each tab is used to track specific information, such as ![]() history,
history, ![]() links, or
links, or ![]() attachments. These three tabs provide a history of changes, view of linked work items, and ability to view and attach files.
attachments. These three tabs provide a history of changes, view of linked work items, and ability to view and attach files.
The only required field for all work item types is Title. When the work item is saved, the system assigns it a unique ID. The form highlights required field in yellow. For information about other fields, see Work item field index.
Field/tab
Usage
Enter a description of 255 characters or less. You can always modify the title later.
Assign the work item to the team member responsible for performing the work. Depending on the context you are working in, the drop-down menu will list only team members or contributors to the project.
When the work item is created, the State defaults to the first state in the workflow. As work progresses, update it to reflect the current state.
Use the default first. Update it when you change state. Each State is associated with a default reason.
Choose the area path associated with the product or team, or leave blank until assigned during a planning meeting.
To change the dropdown list of areas, see Add and modify area and iteration paths.
Choose the sprint or iteration in which the work is to be completed, or leave it blank and assign it later, during a planning meeting.
To change the drop-down list of iterations, see Add and modify area and iteration paths.
Review the audit trail that the system captures and capture additional information.
Every time that the work item is updated, information is appended to the history. History includes the date of the change, who made the change, and which fields were changed. You can also add formatted text to the history field.
Add all types of links, such as hyperlinks, changesets, source files, and so on.
This tab also lists all links defined for the work item.
Share more detailed information by adding files to the work item, such as email threads, documents, images, log files, or other file types.
Customize work item types
You can add fields, change the workflow, add custom rules, and add custom pages to the work item form of most work item types. You can also add custom work item types. For details, see Customize the On-premises XML process model.
Related articles
Before you start tracking work, you must have a project. To create one, see Create a project.
If you have a project, start tracking work:
- Add work items to manage a project - to gain more familiarity with the work item form features
- Create a backlog - to develop your product backlog
- Kanban - to start working in Kanban
- Plan a sprint - to start working in Scrum
- Excel.
For more information on Agile tools:
Track issues
Issues are used to track events that may block progress or shipping a user story. Bugs, on the other hand, are used to track code defects. You can add an issue from the New work item widget added to a team dashboard, or from the New menu on the Queries page.
Work items you add from the widget are automatically scoped to your team's default area and iteration paths. To change the team context, see Switch team context.
Track business value
You can use the Priority field to differentiate the value of various stories. Or, you can add a custom field to the User Story WIT that tracks the relative value of stories. To learn how, see Customize a field for a process.
Backlog list order
The Stack Rank field is used to track the relative ranking of user stories, however by default it doesn't appear on the work item form. The sequence of items on the backlog page is determined according to where you've added the items or moved the items on the page. As you drag items, a background process updates this field.