Copilot para Real-Time Intelligence
Copilot para Real-Time Intelligence es una herramienta de inteligencia artificial avanzada diseñada para ayudarle a explorar los datos y extraer información valiosa. Puede escribir preguntas sobre los datos, que se traducen automáticamente en consultas del lenguaje de consulta kusto (KQL). Copilot simplifica el proceso de análisis de datos para usuarios de KQL experimentados y científicos de datos ciudadanos.
Para obtener información de facturación sobre Copilot, vea Anuncio de Copilot en los precios de Fabric.
Prerrequisitos
- Un área de trabajo con una capacidad habilitada para Microsoft Fabric
- Acceso de lectura o escritura a un conjunto de consultas KQL
Nota
- El administrador debe activar el cambio de inquilino antes de empezar a usar Copilot. Consulte el artículo Copilot configuración de inquilinos para obtener más información.
- La capacidad F64 o P1 debe estar en una de las regiones enumeradas en este artículo, Disponibilidad de regiones de Fabric.
- Si el inquilino o la capacidad están fuera de EE. UU. o Francia, Copilot se deshabilita de manera predeterminada a menos que el administrador de inquilinos de Fabric habilite la configuración de inquilino Los datos enviados a Azure OpenAI se pueden procesar fuera de la región geográfica del inquilino, el límite de cumplimiento o la instancia de nube nacional en el portal de administración de Fabric.
- Copilot en Microsoft Fabric no está disponible en las SKU de prueba. Solo se admiten SKU de pago (F64 o superior, o P1 o superior).
- Copilot en Fabric se está implementando actualmente en versión preliminar pública y se espera que esté disponible para todos los clientes a finales de marzo de 2024.
- Consulte el artículo Información general sobre Copilot en Fabric y Power BI para obtener más información.
Funcionalidades de Copilot para Real-Time Intelligence
Copilot para Real-Time Intelligence le permite traducir fácilmente consultas de lenguaje natural al lenguaje de consulta kusto (KQL). El copilot actúa como un puente entre los lenguajes cotidianos y las complejidades técnicas de KQL y, al hacerlo, elimina las barreras de adopción para analistas de datos y científicos de datos ciudadanos. Al aprovechar la comprensión avanzada del lenguaje de OpenAI, esta característica le permite enviar preguntas empresariales en un formato familiar de lenguaje natural, que luego se convierten en consultas KQL. Copilot acelera la productividad al simplificar el proceso de creación de consultas con un enfoque fácil de usar y eficaz para el análisis de datos.
Copilot admite interacciones de conversación que le permiten aclarar, adaptar y ampliar las consultas dinámicamente, mientras mantiene el contexto de las entradas anteriores. Puede refinar las consultas y formular preguntas de seguimiento sin comenzar:
Refinamiento dinámico de consultas: puede refinar el KQL inicial generado por Copilot mediante la refinación de la solicitud para quitar la ambigüedad, especificar tablas o columnas o proporcionar más contexto.
Preguntas de seguimiento sin problemas: si el KQL generado es correcto, pero desea explorar los datos más profundamente, puede formular preguntas de seguimiento relacionadas con la misma tarea. Puede expandir el ámbito de la consulta, agregar filtros o explorar puntos de datos relacionados basándose en el diálogo anterior.
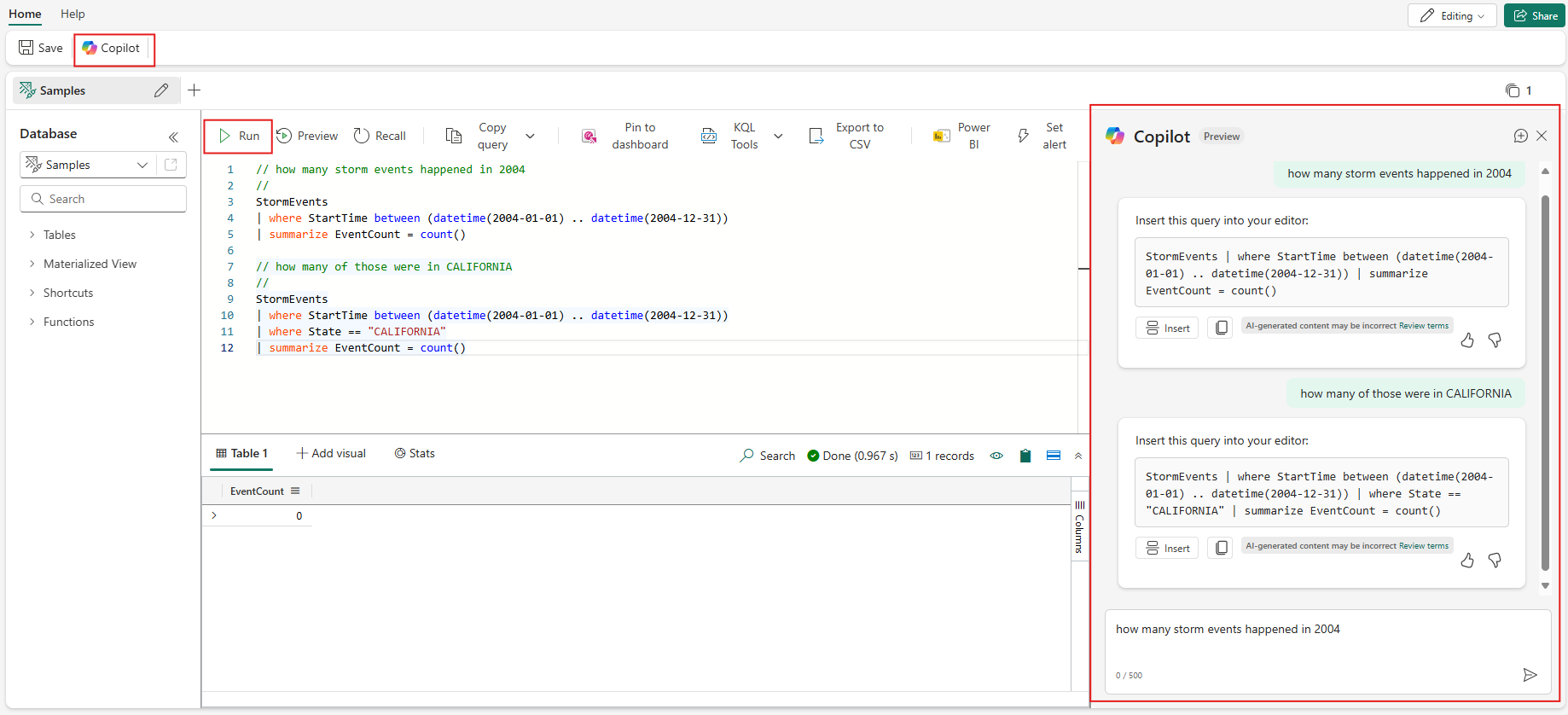
Acceso a Copilot de Real-Time Intelligence
- A fin de acceder a Copilot para Real-Time Intelligence, vaya a una consulta KQL nueva o existente.
- Conéctese a una base de datos. Para obtener más información, consulte Seleccionar una base de datos
- Seleccione el botón Copilot.
- En el panel Copilot, escriba la pregunta empresarial en lenguaje natural.
- Presione Entrar. Después de unos segundos, Copilot generará una consulta KQL basada en la entrada. Puede copiar la consulta en el Portapapeles, o bien insertarla directamente en el editor de consultas KQL. Para ejecutar la consulta en el editor de consultas, debe tener acceso de escritura al conjunto de consultas KQL.
- Seleccione el botón Ejecutar para ejecutar la consulta.
Nota
- Copilot no genera comandos de control.
- Copilot no ejecuta automáticamente la consulta KQL generada. Se recomienda a los usuarios ejecutar las consultas como consideren oportuno.
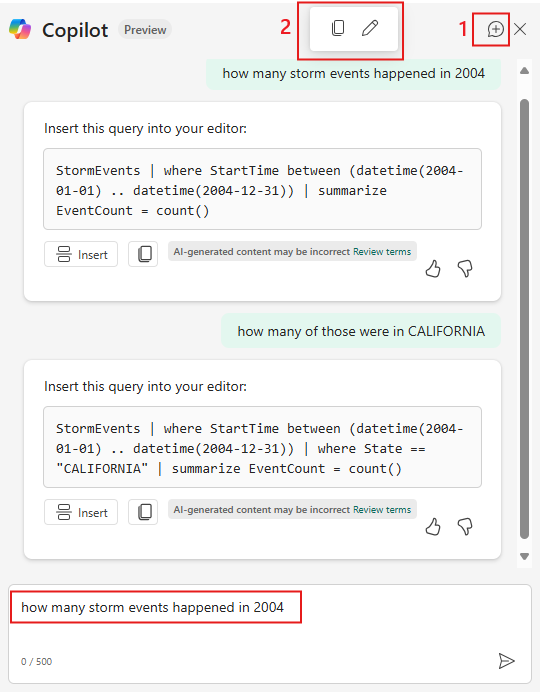
Puede seguir realizando preguntas de seguimiento o refinar aún más la consulta. Para iniciar un nuevo chat, seleccione la burbuja de voz en la parte superior derecha del panel Copilot (1).
Pase el puntero sobre una pregunta anterior (2) y seleccione el icono de lápiz para copiarla en el cuadro de preguntas y editarla, o copiarla en el portapapeles.
Mejora de la precisión de Copilot para Real-Time Intelligence
Estas son algunas sugerencias que pueden ayudar a mejorar la precisión de las consultas KQL generadas por Copilot:
- Comience con indicaciones de lenguaje natural simples para aprender las funcionalidades y limitaciones actuales. A continuación, continúe gradualmente hacia indicaciones más complejas.
- Indique la tarea con precisión y evite la ambigüedad. Imagina que compartiste la instrucción en lenguaje natural con algunos expertos de KQL de tu equipo sin añadir instrucciones verbales, ¿podrían generar la consulta correcta?
- Para generar la consulta más precisa, proporcione cualquier información relevante que pueda ayudar al modelo. Si puede, especifique tablas, operadores o funciones que son fundamentales para la consulta.
- Preparar la base de datos: agregue propiedades docstring para describir tablas y columnas comunes. Esto puede ser redundante para nombres descriptivos (por ejemplo, marca de tiempo), pero es fundamental para describir tablas o columnas con nombres sin significado. No es necesario agregar docstring a tablas o columnas que rara vez se usan. Para más información, vea Comando .alter table column-docstrings.
- Para mejorar los resultados Copilot, seleccione el icono de gusto o el icono de disgusto para enviar sus comentarios en el formulario 'Enviar comentarios' .
Nota
El formulario de Enviar comentarios envía el nombre de la base de datos, su URL, la consulta KQL generada por copilot y cualquier respuesta de texto libre que incluya en la presentación de comentarios. Los resultados de la consulta KQL ejecutada no se envían.
Limitaciones
- Copilot podría sugerir consultas KQL sugeridas potencialmente inexactas o engañosas debido a:
- Entrada de usuario compleja y larga.
- Entrada de usuario que dirige a entidades de base de datos que no son tablas de base de datos KQL o vistas materializadas (por ejemplo, función KQL).
- Más de 10 000 usuarios simultáneos dentro de una organización pueden producir errores o un impacto importante en el rendimiento.