Walkthrough: Designing an RDL report from multiple tables
A report object is composed of a report dataset and a visual layout. You design a report by first defining the dataset and then designing the visual layout. You define the dataset for reports directly in AL code. You can design the layout in Visual Studio Report Designer or Microsoft SQL Server Reporting Services Report Builder for an RDL layout, in Microsoft Word for a Word layout, and in Microsoft Excel for an Excel layout. After you design a report, you can make it available to applications that are running on the Business Central Web client. A report can be designed from one table or multiple tables. This walkthrough demonstrates how to design a report from multiple tables.
About this walkthrough
This walkthrough shows you how to design a report from the AL Language development environment and using Visual Studio Report Designer for designing an RDL layout.
This walkthrough illustrates the following tasks:
- Defining the dataset for multiple tables.
- Adding fields to a data item.
- Defining properties for the data items.
- Adding labels to a report.
- Making the report discoverable and understandable.
- Design a client report definition (RDL) report layout in Visual Studio.
- Setting filters to hide empty rows and fields in a report.
- Building and running a report.
Story
Viktor is a developer who is working for CRONUS International Ltd. Viktor has been asked by the manager to create a report that shows data from the Customer (ID 18), Cust. Ledger Entry (ID 21), Detailed Cust. Ledger Entry (ID 379), and the Sales Header (ID 36) tables. The report should meet the following requirements:
The report must display customer information at the top of the report.
For each customer, the report must show a list of ledger entries.
For each ledger entry, the report must show a list of detailed ledger entries under the ledger entries.
The report must display basic sales document headers information for the selected customer.
Each section of the data for each customer must begin on a new page.
The
Amountfield from theCust. Ledger Entrytable should be totaled and displayed for each customer.If there are no records to display, the report must not display that data sections. For example, if there are no sales documents for a customer, the sale header section must be skipped.
Amount fields must not display zero values.
The orientation of the report should be landscape.
The following illustration shows an example of the second page of the report.
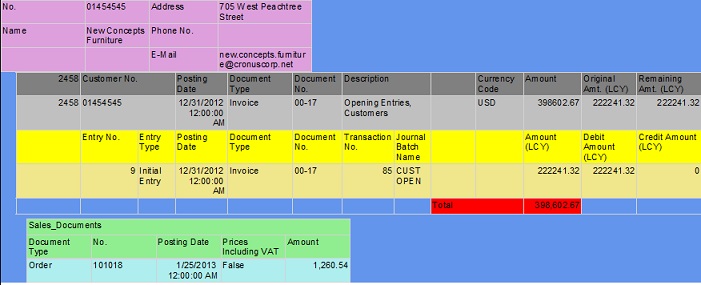
Defining the dataset
Viktor starts by creating an empty report object by using the AL Language extension in Visual Studio Code. You can use the shortcut treport to create the basic layout for a report object.
Viktor defines layout properties in the rendering section of the report, one for a printable version using an RDL layout, and one for a version for analysis using an Excel layout.
Viktor will now design the dataset to display customers and their transaction details. This is defined within the dataset part of the report object.
Adding data items and columns
The datasets for the data model come from four tables: Customer, Cust. Ledger Entry, Detailed Cust. Ledger Entry, and Sales Header. Viktor creates a data item for each table with the dataitem control. Moreover, for each table, fields that need to be added to the report are added. Each field is given by a column control, defined inside the corresponding data item.
The hierarchy of the dataitem and column controls is important because it determines the sequence in which data items are linked, which in turn control the results. Working from top-to-bottom, you start by adding the dataitem control for first table that you want in the dataset, then add column controls for each table field that you want to include in the dataset. For the next table, you add another dataitem control that is embedded within the first dataitem control, then add column controls as needed. You continue this pattern for more tables and fields.
Defining properties for the data items
Once, Viktor has specified the data item and column elements, the appropriate properties are defined. Viktor sets the DataItemTableView Property in each data item to sort the table view based on a specific field.
Viktor also sets the RequestFilterFields Property to automatically include a specific field on the filter tab of the request page. For more information about request pages, see Request Pages.
Now, Viktor uses the DataItemLink (Reports) Property to set a link between one or more fields of the data item tables. Links determine which records to include in the dataset based on the values of a common field between data items. This property must be set on the lower data item of the report object.
For each of the column controls, Viktor adds the IncludeCaption Property and sets it to True. This property specifies to include the caption of the fields in the dataset of a report.
Finally, Viktor sets the PrintOnlyIfDetail Property to True on a data item to print data only if at least one of its child data items generates output.
Adding labels to the report
Viktor now adds labels to the report. You define the labels in the label part of the report. These labels are used later as captions.
Making the report discoverable and understandable
The Business Central client includes the Tell me feature that lets users find objects by entering search terms. Victor wants the new report to be discoverable to users in Tell me, so they set the UsageCategory property on the report.
They then add a request page section specifying the AboutTitle Property and the AboutText Property to help explain the logic behind the report for the users. This adds a teaching tip on the report.
To help users understand how to use the report, Viktor also adds a help link to the ContextSensitiveHelpPage property in case the user selects the Learn more links in the UI of Business Central. They also check if the contextSensitiveHelpUrl property is defined in the app.json (it has).
AL code for this example
The following code exemplifies the code that Viktor has written for the report.
report 50101 "Report for Multiple Tables"
{
// Make the report searchable from Tell me under the Reports and Analysis category.
UsageCategory = ReportsAndAnalysis;
ApplicationArea = All;
dataset
{
dataitem(Customer; Customer)
{
// Sort the table view based on the "No." field.
DataItemTableView = Sorting("No.");
// Include the "No." field on the filter tab of the request page.
RequestFilterFields = "No.";
// Print data only if at least one of the CustLedgerEntry and SalesHeader data items generates output.
PrintOnlyIfDetail = True;
// For each field that you want to display you add a column control.
column(No_Customer; "No.")
{
// Include the caption of the "No." field in the dataset of the report.
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(Name_Customer; Name)
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(Phone_Customer; "Phone No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(Address_Customer; Address)
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(EMail_Customer; "E-Mail")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
dataitem(CustLedger; "Cust. Ledger Entry")
{
DataItemTableView = sorting("Entry no.");
// Set a filter on the child data item, **CustLedgerEntry** to select only the records where the
// value of `Customer."No."` field and the `"Customer Ledger Entry"."Customer No."` field matches.
DataItemLink = "Customer No." = field("No.");
column(EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry; "Entry No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(CustomerNo_CustLedgerEntry; "Customer No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(PostingDate_CustLedgerEntry; "Posting Date")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(DocumentType_CustLedgerEntry; "Document Type")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(DocumentNo_CustLedgerEntry; "Document No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(Description_CustLedgerEntry; Description)
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(CurrencyCode_CustLedgerEntry; "Currency Code")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(Amount_CustLedgerEntry; Amount)
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(OriginalAmtLCY_CustLedgerEntry; "Original Amt. (LCY)")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(RemainingAmtLCY_CustLedgEntry; "Remaining Amt. (LCY)")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
dataitem(DetCustLedger; "Detailed Cust. Ledg. Entry")
{
DataItemTableView = sorting("entry no.");
DataItemLink = "Cust. Ledger Entry No." = field("Entry No."), "Customer No." = field("Customer No.");
column(EntryNo_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Entry No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(EntryType_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Entry Type")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(PostingDate_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Posting Date")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(DocumentType_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Document Type")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(DocumentNo_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Document No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(AmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Amount (LCY)")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(TransactionNo_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Transaction No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(JournalBatchName_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Journal Batch Name")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(DebitAmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Debit Amount (LCY)")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(CreditAmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntry; "Credit Amount (LCY)")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
}
}
dataitem(SalesHeader; "Sales Header")
{
DataItemTableView = sorting("Document Type", "No.");
DataItemLink = "Sell-to Customer No." = field("No.");
column(DocumentType_SalesHeader; "Document Type")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(No_SalesHeader; "No.")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(PostingDate_SalesHeader; "Posting Date")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(PricesIncludingVAT_SalesHeader; "Prices Including VAT")
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
column(Amount_SalesHeader; Amount)
{
IncludeCaption = true;
}
}
}
}
// These labels will be used later as captions in the report layout.
labels
{
Sales_Document_Caption = 'Sales Documents';
Total_Caption = 'Total';
}
requestpage
{
SaveValues = true;
AboutTitle = 'Sales by customer report';
AboutText = 'This is our new sales report. Use it to follow up with customers on their engagement with us.';
// Remember to also set contextSensitiveHelpUrl in the app.json
ContextSensitiveHelpPage = 'our-app/sales-reports';
}
rendering
{
layout(RDLCLayout)
{
Type = RDLC;
LayoutFile = './MyRDLReport.rdl';
Caption = 'Customer Sales Report (for print)';
Summary = 'Layout for the Customer Sales Report that has been optimized for print.';
}
layout(ExcelLayout)
{
Type = Excel;
LayoutFile = './MyRDLReport.xlsx';
Caption = 'Customer Sales Report (for analysis)';
Summary = 'Layout for the Customer Sales Report that has been optimized for analysis in Excel.';
}
}
}
Designing the visual RDL layout for the report
Next, Viktor designs an RDL layout for the report by using Visual Studio Report Designer. Viktor sets properties for the report and the report elements, format the report, and then add the data to the report.
To design the RDL layout for the report
Build the extension (Ctrl+Shift+B) to generate the
MyRDLReport.rdlfile, and then open the file with Visual Studio 2019.Right-click anywhere outside the report (in the shaded area) and then choose Add Page Header.
Right-click anywhere outside the report (in the shaded area), and then choose Report Properties.
In the Report Properties window, choose the Page Setup tab. In the Paper size section, under Orientation, choose Landscape, and then choose the OK button.
On the View menu, choose Toolbox. Select the List control, and then choose the body of the report to add the List control to the report. This control contains and groups all the data.
Move the List control to the top of the report body and resize it to cover the whole report body.
Right-click the middle of the List controls, and then select on the box to open the Rectangle Properties.
In the Rectangle Properties window, choose the Fill tab, in the Fill Color list color pallet, select Cornflower Blue from the color pallet, and then choose the OK button. You can choose any color.
Note
Changing the color of report elements helps you identify elements on the report preview. You can set different color properties for table header, detail rows, text boxes, and so on.
Viktor sets the properties of the List control to hold the dataset, group the data by Customer No. and set up how the groups should be displayed.
To set the list control properties
Select the List control, right-click the shaded border to the left of the List control, and then choose Tablix Properties.
In the Tablix Properties window, on the General tab, under Dataset name, select DataSet_Result from the drop-down list, and then choose the OK button.
Select the List control, right-click the shaded border to the left of the list control, choose Row Group, and then Group Properties.
In the Group Properties window, on the General tab, under Group expressions:, choose the Add button, and then select [No_Customer] from the Group on: drop-down list. This groups all the data in the List control by customer number.
On the Page Breaks tab, select Between each instance of a group, and then choose the OK button.
Viktor is now ready to add the customer data. The table displays one customer at a time, therefore Viktor must put all the fields into table header rows. The table data and footer rows are disabled.
To add customer data
From the Toolbox pane, drag a Table control into the List control and resize the table to about the half the width of the list control. This table contains the customer data.
The following illustration shows the list control and the table.
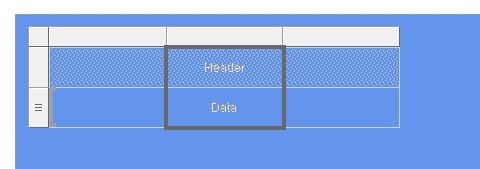
The table contains two table rows, a header row (first row), and a data row (second row). The three parallel lines in the left border of the second row identify the data row.
Select any table row, right-click the shaded border, and then choose Tablix Properties to open the Tablix Properties window.
On the General tab, verify that the Dataset name field is set to DataSet_Result, and then choose the OK button.
The table has three columns. Viktor adds a fourth column to the table to hold all the customer data.
Right-click the middle column header, choose Insert Column, and then select Right to insert the fourth column into the table.
Select the second table row (the data row), right-click the row, choose Delete Rows to delete the data row, and then choose the OK button in the Delete Rows window to delete the row and its associated groups.
Select the remaining table row, right-click the shaded border on the left, choose Insert Row, and then choose Below to insert another table header row.
Repeat step 6 to insert a third table header row. There should now be three header rows in the table.
Right-click the first cell (row 1, column 1) in the table, and then choose Expression to open the Expression window.
In the Category column, select Parameters, in the Item column, verify that All is selected, and then in the Values column, double-click No_CustomerCaption. Verify that the Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
=Parameters!No_CustomerCaption.Value. This cell displays the customer No. caption in the report.Modify the expression to
=First(Parameters!No_CustomerCaption.Value). Choose the OK button.Note
All caption fields must begin with
=Firstso that the first value for the caption fields in the data set is retrieved and used as caption. If the First function is not used, the report will return the current value for a field. The current value however may be incorrect. For example, the current value could be empty.Right-click the second cell (row 1, column 2) in the table, and then choose Expression to open the Expression window.
In the Category column, select Field(DataSet_Result), in the Item column verify that All is selected, and then in the Values column double-click No_Customer. Verify that the Set expression for: Value box contains the following value
=Fields!No_Customer.Value. Choose the OK button. This cell displays the Customer No..Repeat steps 8 through 12 to enter captions and values in the following cells.
Note
Columns 1 and 3 will contain the captions and columns 2 and 4 will contain the values.
Row Column Caption Value 2 1 Name_CustomerCaption None 2 2 None Name_Customer 1 3 Address_CustomerCaption None 1 4 None Address_Customer 2 3 PhoneNo_CustomerCaption None 2 4 None PhoneNo_Customer 3 3 Email_CustomerCaption None 3 4 None Email_Customer Select all table rows (not the whole table), and then on the View menu, choose Properties Window to open the Properties window in Visual Studio.
In the Properties window, under Fill, set the BackgroundColor property to Plum. You can choose any color.
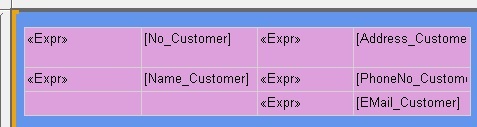
The layout that Viktor has designed to this point resembles the following illustration.
On the Build menu, choose Build Web site to build the project. Inspect the Output pane and make sure that there are no build errors. Close Visual Studio.
Note
It's a good practice to build the project periodically during the report design to make sure that there are no build errors.
Viktor runs the report and previews everything that's done to this point.
Go back to your project in Visual Studio Code and Reload the Window.
In the
launch.jsonfile set the"startupObjectId"to the Id of the report object and the"startupObjectType"toReport.Select the F5 key to run the report.
In the request page that's displayed, choose the Preview button to view the report. The first customer is displayed on the first page. If you page through the report, each customer is displayed on a separate page.
Viktor now adds the data for the customer ledger entries and detailed ledger entries. The entries are put in a different table.
To add the data for ledger entry and detailed ledger entry
Open the
MyRDLReport.rdlreport in Microsoft Visual Studio.From the Toolbox, drag a table control into the list control. Put the table under the table that contains the customer data.
Note
You may have to resize the report body and the list controls to make them larger.
Select the table, right-click the shaded border, choose Tablix Properties. On the General tab, verify that the Dataset name field is set to DataSet_Result, and then choose the OK button.
Select the table data row, choose Insert Row and then choose Outside Group – Below. This adds another data row to the table. You now have one header row and two data rows.
Delete the first row (header row) in the table and then insert columns in the table so that the total number of columns is 11.
Choose the first data row, right-click the shaded border to the left, choose Add Group, and then choose Parent Group.
In the Tablix group window, select Group by, select EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry from the drop-down list. Select Add group header, and then choose the OK button.
Right-click the first row, choose Insert Row, and then choose Inside Group – Above. This header holds the captions for the Customer Ledger entries.
Right-click the cell in the row1, column 2, and then choose Expression to open the Expression window.
In the Category column, select Parameters and then in the Values column double-click EntryNo_CustLedgerEntryCaption. The Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
=Parameters!EntryNo_CustLedgerEntryCaption.ValueModify the expression to the following value:
=First(Parameters!EntryNo_CustLedgerEntryCaption.Value).Repeat steps 9 through 11 to add captions for the table cells in the rest of the first row as shown in the following table.
Column Caption expression 3 CustomerNo_CustLedgerEntryCaption 4 PostingDate_CustLedgerEntryCaption 5 DocumentType_CustLedgerEntryCaption 6 DocumentNo_CustLedgerEntryCaption 7 Description_CustLedgerEntryCaption 8 Skip this cell. You'll use this cell later. 9 CurrencyCode_CustLedgerEntryCaption 10 Amount_CustLedgerEntryCaption 11 OriginalAmtLCY_CustLedgerEntryCaption 12 RemainingAmtLCY_CustLedgerEntryCaption Right-click the left-most grouping cell (the cell that contains the EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry field) in the table, select Text Box Properties, in the Text Box Properties window, select the Visibility tab, under the Change display options, select the Hide option.
Select the first row in the table, in the Properties pane, under Fill, set the BackgroundColor property to Dim Grey.
Right-click the cell in the row2, column 2, and then choose Expression to open the Expression window.
In the Category column, select Fields (DataSet_Result), in the Values column, double-click EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry, and then choose the OK button. The Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
=Fields!EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry.ValueRepeat steps 15 and 16 for row 3 to add fields from the ledger entry dataset. Put the fields under the corresponding captions.
Select the row that you filled in and set the BackgroundColor property to Silver.
Build the project, inspect the Output pane, and make sure that there are no build errors.
Select the second table row, right-click the shaded border to the left, choose Insert Row, and then choose Below. The table should now have three group rows, one group data row, and one table footer row. This row stores the captions of Detailed Cust. Ledg. Entry data item.
Add the captions and fields for the Detailed Cust. Ledger Entry table as shown in the following table.
Third row (Caption) Forth row (Fields) EntryNo_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption EntryNo_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value EntryType_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption EntryType_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value PostingDate_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption. PostingDate_DetailedCustLedgEntr.Value DocumentType_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption DocumentType_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value DocumentNo_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption DocumentNo_DetailedCustLedgEnt.Value TransactionNo_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption TransactionNo_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value JournalBatchName_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption JournalBatchName_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value AmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption AmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntr.Value DebitAmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption DebitAmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value CreditAmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntryCaption CreditAmountLCY_DetailedCustLedgEntry.Value Shrink the column that contains the Customer No. field of the Cust. Ledger Entry to about half of its size.
Right-click the column header that contains the Customer No. field, choose Insert Column, and then choose Right.
Select the cell that contains the Customer No. caption and the empty cell that you created, and then choose Merge Cells to merge the two cells.
Repeat step 24 to merge the cell that contains the value of the Customer No. field and the empty cell that you created.
Assign the expression from the EntryType caption and field cells of the Detailed Cust. Ledg. Entry to the empty cell that you created to the right. You might have to cut the expressions and paste them into the empty cells.
Repeat 26 to move the EntryNo caption and field 1 cell to the right. This makes sure that the EntryNo and the EntryType data are located directly under the CustomerNo cell.
The following illustration shows EntryNo and the EntryType cells directly under the CustomerNo cell
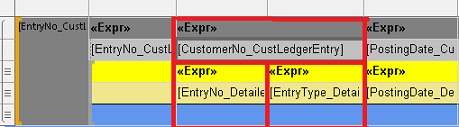
Repeat steps through 27 to put the Transaction No. and Journal Batch Name captions and fields under the Description data. This creates a blank cell under the CurrencyCode field.
Select the third row and set the BackgroundColor property to Yellow and then set the BackgroundColor property of the fourth row to Khaki.
Viktor will now hide all empty cells and add the totals to the footer row. To hide empty cells Viktor adds a filter that selects rows that have [EntryNo] value that is greater than zero.
To hide empty cells and add totals
Select the first row, right-click the shaded border to the left of the row, choose Row Group, and then choose Group Properties.
In the Group Properties window, select the Filters tab, and then choose the Add button.
Set Expression to [EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry], change Text to Integer, set Operator to >, set Value to 0, and then choose the OK button.
The filter set, applies to the other rows in the table.
In the Group Properties window, under the Filters tab, verify that the Expression box contains [EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry].
Viktor will now add the total of the amount field to the footer row of the table, format the cells and hide the total cell if customer ledger entry isn't available.
In the last row of the table, right-click the empty cell under the Amount (LCY) field, and then choose Expression.
In the Category column, select Fields (DataSet_Result), in the Values column double-click Amount_CustLedgerEntry, and then change the expression in the Set expression for: Value box to the following value:
=Sum(Fields!Amount_CustLedgerEntry.Value). Choose the OK button.In the Properties window, locate the Format property, choose the drop-down arrow and select Expression.
In the Expression window, enter the following formatting expression in Set expression for: Value box:
=Fields!Amount_CustLedgerEntryFormat.Value. Choose the OK button.Note
Alternatively, you set this value by double-clicking Amount_CustLedgerEntryFormat in the Values field of Fields(DataSet) category.
Select the two empty cells to the left of the total cell, right-click the cells, and then choose Merge Cells.
Right-click the merged cell, choose Expression, choose the Parameters category, and then set the caption to Total_Caption
Set the BackgroundColor property of the cells that contain the total and total caption to Red.
If you run the report now, the total amount cell is displayed even if there are no ledger entries. Viktor adds an expression to hide the footer row when there are no ledger entries.
Select the last row, in the Properties window, locate the Hidden property, choose the drop-down arrow, and then choose Expression.
In the Expression window, in the Set expression for: Hidden box, enter the following expression to hide the row:
=Fields!EntryNo_CustLedgerEntry.Value = 0. Choose the OK button. This hides the row if there are no entry values.Right-click the left-most cell in the last table row, select Text Box Properties, select the Visibility tab, under Change display options, select the Hide option, and then choose the OK button.
The next step is to add the data from the Sales Header table.
To add the sales header data
From the Toolbox, drag a Table control to the List control, and then put the table control under the table that contains the Cust. Ledger Entry table
Right-click a column and add columns to create five columns for the table.
Delete the first header row from the table.
Right-click the data row, choose Tablix Properties, verify that the DataSet name is set to DataSet_Result, and then choose the OK button.
Right-click the data row, choose Add Group, and then choose Parent Group to open the Tablix group window.
Select the Group by: option and then choose the fx button to open the Expression window.
In the Category column, select Parameters, and then in the Values, column double-click Sales_Document_Caption. Verify that the Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
=Parameters!Sales_Document_Caption.Value. Choose the OK button.In the Tablix group window, select Add group header, and then choose the OK button.
Right-click the first row in the table, choose Insert Row, and then choose Inside Group – Above.
Reduce the size of the first column, and then in the Properties window, under Visibility, set the Hidden property to True. This hides the first column.
In the first table row, merge all the cells except the first grouping cell.
Right-click the merged cell, and then choose Expression.
In the Category column, select Parameters, and then in the Values column double-click Sales_Document_Caption. Verify that the Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
=Parameters!Sales_Document_Caption.Value. Choose the OK button.Modify the expression to
=First(Parameters!Sales_Document_Caption.Value).Right-click the cell in row2, column 2, and then choose Expression to open the Expression window.
In the Category column, select Parameters, and then in the Values column double-click DocumentType_SalesHeader. Verify that the Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
Parameters!DocumentType_SalesHeaderCaption.Value.Modify the expression to the following value:
=First(Parameters!DocumentType_SalesHeaderCaption.Value)and then choose the OK button.Right-click the cell that is under the caption that you created, choose Expression. In the Category column, select Fields (DataSet_Result), and then in the Values column double-click DocumentType_SalesHeader. Choose the OK button. Verify that the Set expression for: Value box contains the following value:
=Fields!DocumentType_SalesHeader.ValueRepeat steps 15 through 18 and add the following captions and the corresponding fields.
Caption Corresponding field No_SalesHeaderCaption No_SalesHeader PostingDate_SalesHeaderCaption PostingDate_SalesHeader PricesIncludingVAT_SalesHeaderCaption PricesIncludingVAT_SalesHeader Amount_SalesHeaderCaption Amount_SalesHeader Select the first two rows and in the Properties window, set the BackgroundColor property to Lime.
Select the data row (last row), in the Properties window, set the BackgroundColor property to Turquoise.
Viktor now sets a filter that hides empty rows.
To set a filter, hide empty row
Select any row from this table, right-click the shaded border to the left of the table, and then choose Tablix Properties.
Choose the Filters tab and then choose the Add button.
In the Expression list box, select No_SalesHeader, set Operator to >, set Value to 0, and then choose the OK button.
Save the report.
Building and running the report
Viktor runs the report to view how it looks like. For this, do the following steps:
Make sure that the
"startupObjectId"is set to the Id of the report object and the"startupObjectType"toReportin thelaunch.jsonfile.Select the F5 key to compile and run the report in Dynamics 365 Business Central.
If you haven't switched off the UseRequestPage Property you'll be shown a request page in the Web Client.
The following illustration shows an example of the request page that is displayed when the report is run.
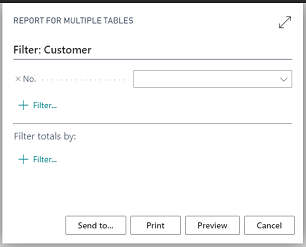
If you choose the Preview button on the request page, the report is displayed with the RLD layout created.
Other tasks to consider
Viktor can now add advanced features to the report such as displaying the company name and logo on every page on the report. Viktor might also want to add features that enable users to apply filters on the request page.
To make the report fully discoverable for users, Victor might also add actions that run the report to pages such as the customer list and also add links to the report to appropriate role centers.
Related information
Report Overview
Defining a Report Dataset
Using request pages with reports
Creating an RDL Layout Report